Liane Vogel
Towards Foundation Models for Relational Databases [Vision Paper]
May 24, 2023Abstract:Tabular representation learning has recently gained a lot of attention. However, existing approaches only learn a representation from a single table, and thus ignore the potential to learn from the full structure of relational databases, including neighboring tables that can contain important information for a contextualized representation. Moreover, current models are significantly limited in scale, which prevents that they learn from large databases. In this paper, we thus introduce our vision of relational representation learning, that can not only learn from the full relational structure, but also can scale to larger database sizes that are commonly found in real-world. Moreover, we also discuss opportunities and challenges we see along the way to enable this vision and present initial very promising results. Overall, we argue that this direction can lead to foundation models for relational databases that are today only available for text and images.
Investigating User Radicalization: A Novel Dataset for Identifying Fine-Grained Temporal Shifts in Opinion
Apr 29, 2022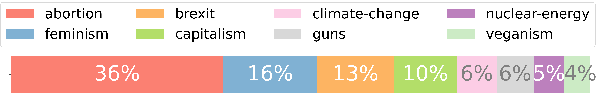

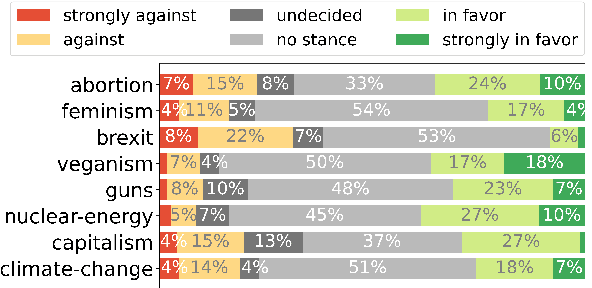

Abstract:There is an increasing need for the ability to model fine-grained opinion shifts of social media users, as concerns about the potential polarizing social effects increase. However, the lack of publicly available datasets that are suitable for the task presents a major challenge. In this paper, we introduce an innovative annotated dataset for modeling subtle opinion fluctuations and detecting fine-grained stances. The dataset includes a sufficient amount of stance polarity and intensity labels per user over time and within entire conversational threads, thus making subtle opinion fluctuations detectable both in long term and in short term. All posts are annotated by non-experts and a significant portion of the data is also annotated by experts. We provide a strategy for recruiting suitable non-experts. Our analysis of the inter-annotator agreements shows that the resulting annotations obtained from the majority vote of the non-experts are of comparable quality to the annotations of the experts. We provide analyses of the stance evolution in short term and long term levels, a comparison of language usage between users with vacillating and resolute attitudes, and fine-grained stance detection baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge