Leonardo Mariani
GreenServ: Energy-Efficient Context-Aware Dynamic Routing for Multi-Model LLM Inference
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable capabilities, but their broad deployment is limited by significant computational resource demands, particularly energy consumption during inference. Static, one-model-fits-all inference strategies are often inefficient, as they do not exploit the diverse range of available models or adapt to varying query requirements. This paper presents GreenServ, a dynamic, context-aware routing framework that optimizes the trade-off between inference accuracy and energy efficiency. GreenServ extracts lightweight contextual features from each query, including task type, semantic cluster, and text complexity, and routes queries to the most suitable model from a heterogeneous pool, based on observed accuracy and energy usage. We employ a multi-armed bandit approach to learn adaptive routing policies online. This approach operates under partial feedback, eliminates the need for extensive offline calibration, and streamlines the integration of new models into the inference pipeline. We evaluated GreenServ across five benchmark tasks and a pool of 16 contemporary open-access LLMs. Experimental results show that GreenServ consistently outperforms static (single-model) and random baselines. In particular, compared to random routing, GreenServ achieved a 22% increase in accuracy while reducing cumulative energy consumption by 31%. Finally, we evaluated GreenServ with RouterBench, achieving an average accuracy of 71.7% with a peak accuracy of 75.7%. All artifacts are open-source and available as an anonymous repository for review purposes here: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/llm-inference-router-EBEA/README.md
Analyzing Prompt Influence on Automated Method Generation: An Empirical Study with Copilot
Feb 13, 2024Abstract:Generative AI is changing the way developers interact with software systems, providing services that can produce and deliver new content, crafted to satisfy the actual needs of developers. For instance, developers can ask for new code directly from within their IDEs by writing natural language prompts, and integrated services based on generative AI, such as Copilot, immediately respond to prompts by providing ready-to-use code snippets. Formulating the prompt appropriately, and incorporating the useful information while avoiding any information overload, can be an important factor in obtaining the right piece of code. The task of designing good prompts is known as prompt engineering. In this paper, we systematically investigate the influence of eight prompt features on the style and the content of prompts, on the level of correctness, complexity, size, and similarity to the developers' code of the generated code. We specifically consider the task of using Copilot with 124,800 prompts obtained by systematically combining the eight considered prompt features to generate the implementation of 200 Java methods. Results show how some prompt features, such as the presence of examples and the summary of the purpose of the method, can significantly influence the quality of the result.
MutaBot: A Mutation Testing Approach for Chatbots
Jan 18, 2024Abstract:Mutation testing is a technique aimed at assessing the effectiveness of test suites by seeding artificial faults into programs. Although available for many platforms and languages, no mutation testing tool is currently available for conversational chatbots, which represent an increasingly popular solution to design systems that can interact with users through a natural language interface. Note that since conversations must be explicitly engineered by the developers of conversational chatbots, these systems are exposed to specific types of faults not supported by existing mutation testing tools. In this paper, we present MutaBot, a mutation testing tool for conversational chatbots. MutaBot addresses mutations at multiple levels, including conversational flows, intents, and contexts. We designed the tool to potentially target multiple platforms, while we implemented initial support for Google Dialogflow chatbots. We assessed the tool with three Dialogflow chatbots and test cases generated with Botium, revealing weaknesses in the test suites.
An Energy-Aware Approach to Design Self-Adaptive AI-based Applications on the Edge
Aug 31, 2023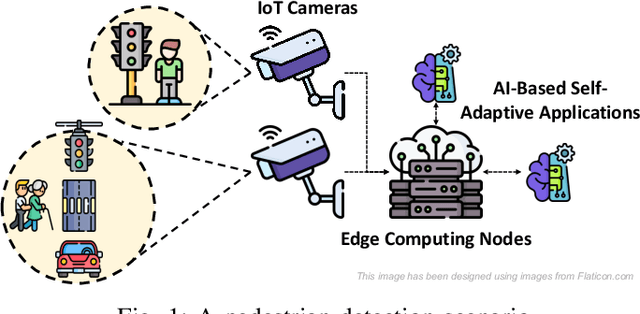
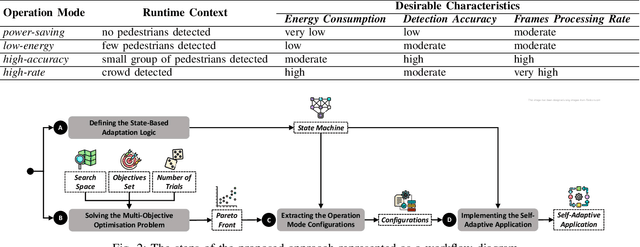
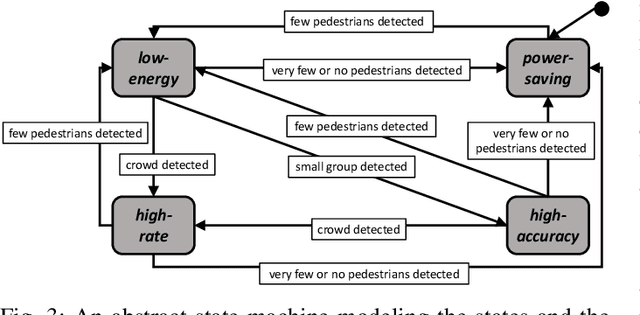
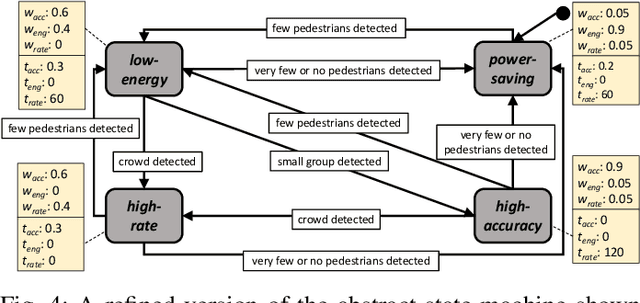
Abstract:The advent of edge devices dedicated to machine learning tasks enabled the execution of AI-based applications that efficiently process and classify the data acquired by the resource-constrained devices populating the Internet of Things. The proliferation of such applications (e.g., critical monitoring in smart cities) demands new strategies to make these systems also sustainable from an energetic point of view. In this paper, we present an energy-aware approach for the design and deployment of self-adaptive AI-based applications that can balance application objectives (e.g., accuracy in object detection and frames processing rate) with energy consumption. We address the problem of determining the set of configurations that can be used to self-adapt the system with a meta-heuristic search procedure that only needs a small number of empirical samples. The final set of configurations are selected using weighted gray relational analysis, and mapped to the operation modes of the self-adaptive application. We validate our approach on an AI-based application for pedestrian detection. Results show that our self-adaptive application can outperform non-adaptive baseline configurations by saving up to 81\% of energy while loosing only between 2% and 6% in accuracy.
Cloud Failure Prediction with Hierarchical Temporary Memory: An Empirical Assessment
Oct 06, 2021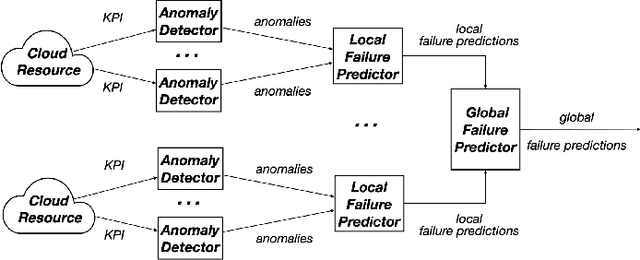
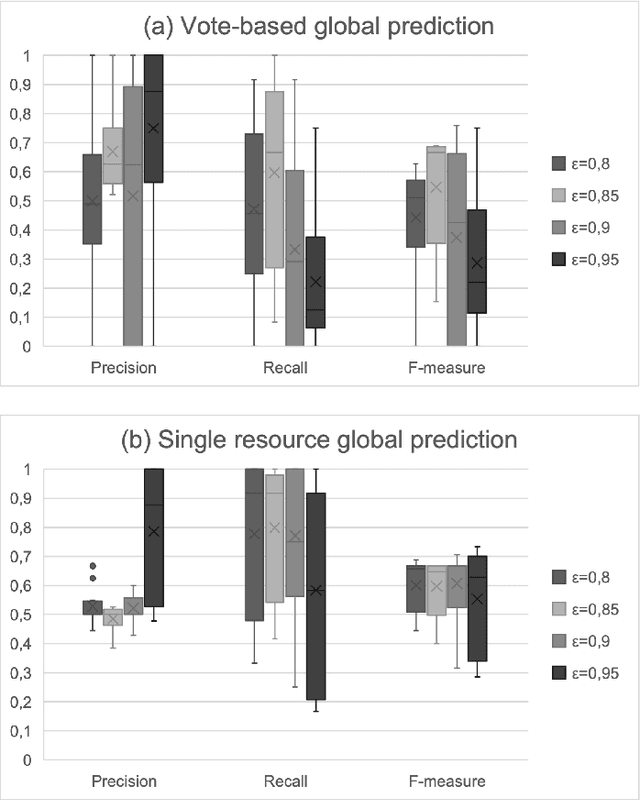
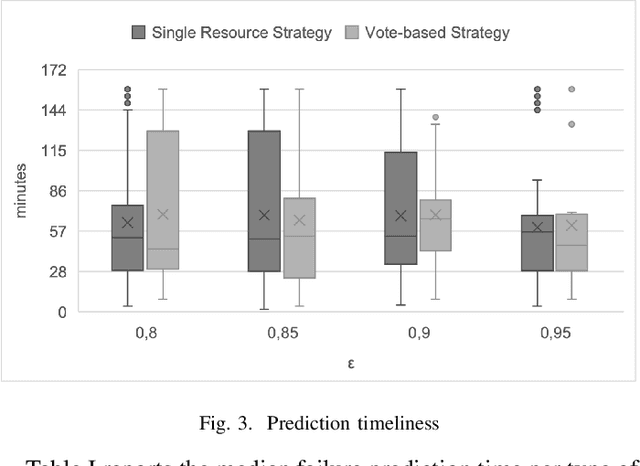
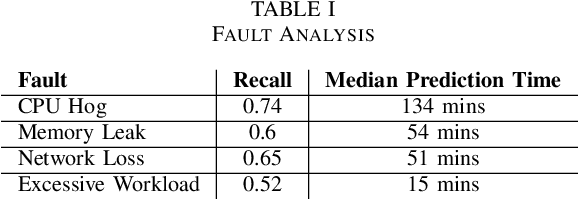
Abstract:Hierarchical Temporary Memory (HTM) is an unsupervised learning algorithm inspired by the features of the neocortex that can be used to continuously process stream data and detect anomalies, without requiring a large amount of data for training nor requiring labeled data. HTM is also able to continuously learn from samples, providing a model that is always up-to-date with respect to observations. These characteristics make HTM particularly suitable for supporting online failure prediction in cloud systems, which are systems with a dynamically changing behavior that must be monitored to anticipate problems. This paper presents the first systematic study that assesses HTM in the context of failure prediction. The results that we obtained considering 72 configurations of HTM applied to 12 different types of faults introduced in the Clearwater cloud system show that HTM can help to predict failures with sufficient effectiveness (F-measure = 0.76), representing an interesting practical alternative to (semi-)supervised algorithms.
On Introducing Automatic Test Case Generation in Practice: A Success Story and Lessons Learned
Feb 28, 2021



Abstract:The level and quality of automation dramatically affects software testing activities, determines costs and effectiveness of the testing process, and largely impacts on the quality of the final product. While costs and benefits of automating many testing activities in industrial practice (including managing the quality process, executing large test suites, and managing regression test suites) are well understood and documented, the benefits and obstacles of automatically generating system test suites in industrial practice are not well reported yet, despite the recent progresses of automated test case generation tools. Proprietary tools for automatically generating test cases are becoming common practice in large software organisations, and commercial tools are becoming available for some application domains and testing levels. However, generating system test cases in small and medium-size software companies is still largely a manual, inefficient and ad-hoc activity. This paper reports our experience in introducing techniques for automatically generating system test suites in a medium-size company. We describe the technical and organisational obstacles that we faced when introducing automatic test case generation in the development process of the company, and present the solutions that we successfully experienced in that context. In particular, the paper discusses the problems of automating the generation of test cases by referring to a customised ERP application that the medium-size company developed for a third party multinational company, and presents ABT2.0, the test case generator that we developed by tailoring ABT, a research state-of-the-art GUI test generator, to their industrial environment. This paper presents the new features of ABT2.0, and discusses how these new features address the issues that we faced.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge