Leo Long
Learnings from Federated Learning in the Real world
Feb 08, 2022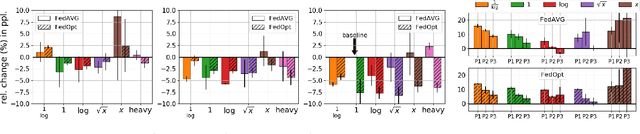
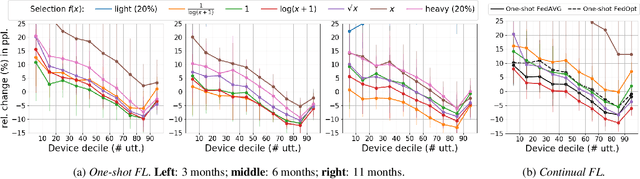
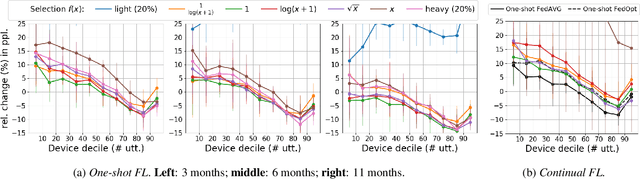
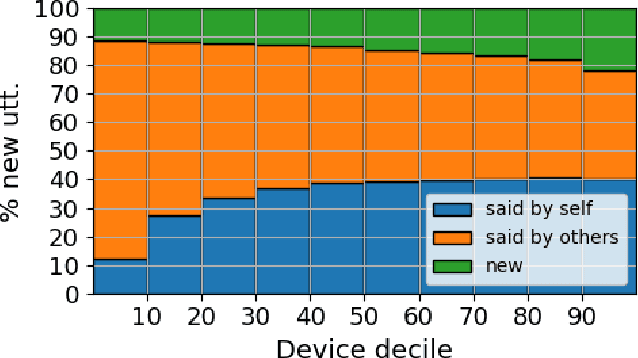
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) applied to real world data may suffer from several idiosyncrasies. One such idiosyncrasy is the data distribution across devices. Data across devices could be distributed such that there are some "heavy devices" with large amounts of data while there are many "light users" with only a handful of data points. There also exists heterogeneity of data across devices. In this study, we evaluate the impact of such idiosyncrasies on Natural Language Understanding (NLU) models trained using FL. We conduct experiments on data obtained from a large scale NLU system serving thousands of devices and show that simple non-uniform device selection based on the number of interactions at each round of FL training boosts the performance of the model. This benefit is further amplified in continual FL on consecutive time periods, where non-uniform sampling manages to swiftly catch up with FL methods using all data at once.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge