Lennart Ries
CLIPping the Limits: Finding the Sweet Spot for Relevant Images in Automated Driving Systems Perception Testing
Apr 08, 2024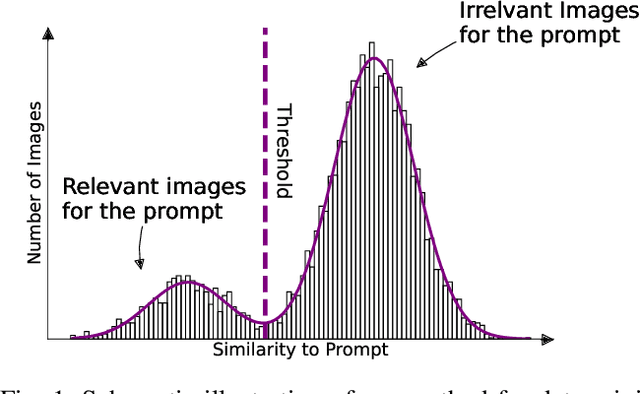
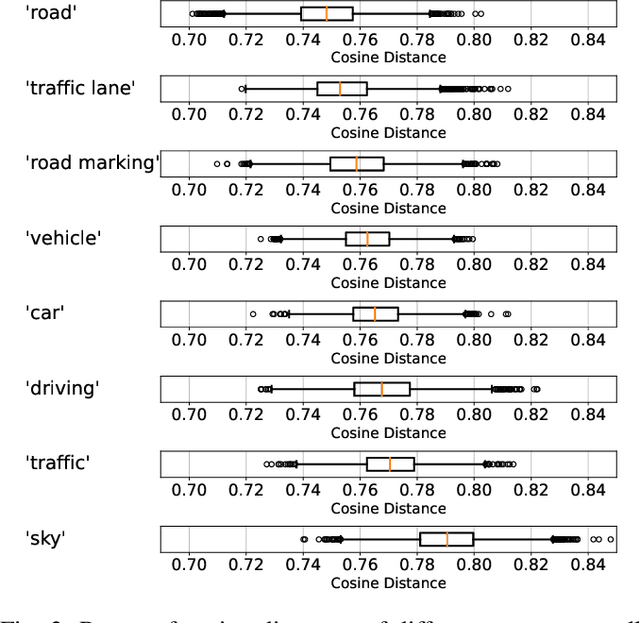
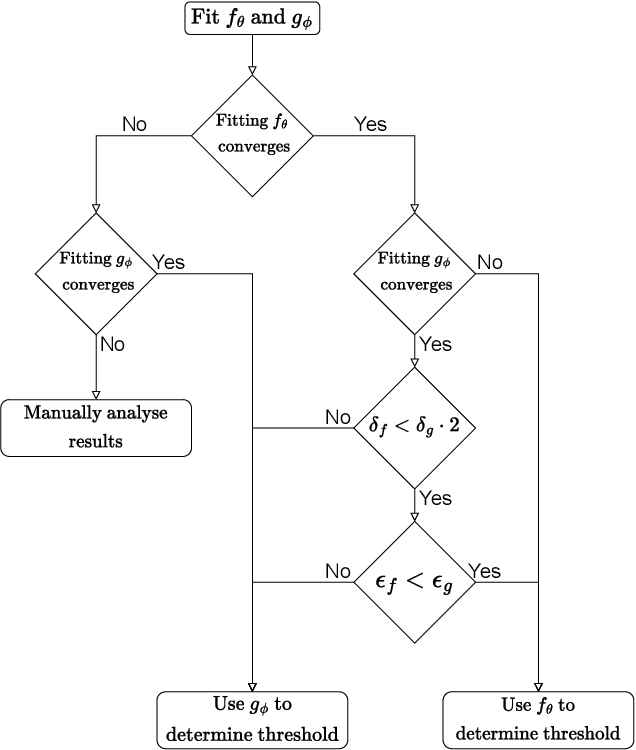
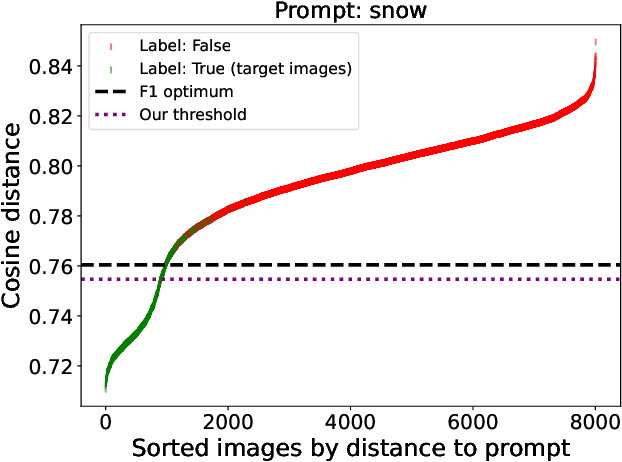
Abstract:Perception systems, especially cameras, are the eyes of automated driving systems. Ensuring that they function reliably and robustly is therefore an important building block in the automation of vehicles. There are various approaches to test the perception of automated driving systems. Ultimately, however, it always comes down to the investigation of the behavior of perception systems under specific input data. Camera images are a crucial part of the input data. Image data sets are therefore collected for the testing of automated driving systems, but it is non-trivial to find specific images in these data sets. Thanks to recent developments in neural networks, there are now methods for sorting the images in a data set according to their similarity to a prompt in natural language. In order to further automate the provision of search results, we make a contribution by automating the threshold definition in these sorted results and returning only the images relevant to the prompt as a result. Our focus is on preventing false positives and false negatives equally. It is also important that our method is robust and in the case that our assumptions are not fulfilled, we provide a fallback solution.
The Machine Vision Iceberg Explained: Advancing Dynamic Testing by Considering Holistic Environmental Circumstances
Feb 05, 2024Abstract:Are we heading for an iceberg with the current testing of machine vision? This work delves into the landscape of Machine Vision (MV) testing, which is heavily required in Highly Automated Driving (HAD) systems. Utilizing the metaphorical notion of navigating towards an iceberg, we discuss the potential shortcomings concealed within current testing strategies. We emphasize the urgent need for a deeper understanding of how to deal with the opaque functions of MV in development processes. As overlooked considerations can cost lives. Our main contribution is the hierarchical level model, which we call Granularity Grades. The model encourages a refined exploration of the multi-scaled depths of understanding about the circumstances of environments in which MV is intended to operate. This model aims to provide a holistic overview of all entities that may impact MV functions, ranging from relations of individual entities like object attributes to entire environmental scenes. The application of our model delivers a structured exploration of entities in a specific domain, their relationships and assigning results of a MV-under-test to construct an entity-relationship graph. Through clustering patterns of relations in the graph general MV deficits are arguable. In Summary, our work contributes to a more nuanced and systematized identification of deficits of a MV test object in correlation to holistic circumstances in HAD operating domains.
Focus on the Challenges: Analysis of a User-friendly Data Search Approach with CLIP in the Automotive Domain
Apr 21, 2023Abstract:Handling large amounts of data has become a key for developing automated driving systems. Especially for developing highly automated driving functions, working with images has become increasingly challenging due to the sheer size of the required data. Such data has to satisfy different requirements to be usable in machine learning-based approaches. Thus, engineers need to fully understand their large image data sets for the development and test of machine learning algorithms. However, current approaches lack automatability, are not generic and are limited in their expressiveness. Hence, this paper aims to analyze a state-of-the-art text and image embedding neural network and guides through the application in the automotive domain. This approach enables the search for similar images and the search based on a human understandable text-based description. Our experiments show the automatability and generalizability of our proposed method for handling large data sets in the automotive domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge