Leandro Di Bella
ReferGPT: Towards Zero-Shot Referring Multi-Object Tracking
Apr 12, 2025Abstract:Tracking multiple objects based on textual queries is a challenging task that requires linking language understanding with object association across frames. Previous works typically train the whole process end-to-end or integrate an additional referring text module into a multi-object tracker, but they both require supervised training and potentially struggle with generalization to open-set queries. In this work, we introduce ReferGPT, a novel zero-shot referring multi-object tracking framework. We provide a multi-modal large language model (MLLM) with spatial knowledge enabling it to generate 3D-aware captions. This enhances its descriptive capabilities and supports a more flexible referring vocabulary without training. We also propose a robust query-matching strategy, leveraging CLIP-based semantic encoding and fuzzy matching to associate MLLM generated captions with user queries. Extensive experiments on Refer-KITTI, Refer-KITTIv2 and Refer-KITTI+ demonstrate that ReferGPT achieves competitive performance against trained methods, showcasing its robustness and zero-shot capabilities in autonomous driving. The codes are available on https://github.com/Tzoulio/ReferGPT
HybridTrack: A Hybrid Approach for Robust Multi-Object Tracking
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:The evolution of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) has increased the need for robust and generalizable algorithms for multi-object tracking. Traditional statistical model-based tracking methods rely on predefined motion models and assumptions about system noise distributions. Although computationally efficient, they often lack adaptability to varying traffic scenarios and require extensive manual design and parameter tuning. To address these issues, we propose a novel 3D multi-object tracking approach for vehicles, HybridTrack, which integrates a data-driven Kalman Filter (KF) within a tracking-by-detection paradigm. In particular, it learns the transition residual and Kalman gain directly from data, which eliminates the need for manual motion and stochastic parameter modeling. Validated on the real-world KITTI dataset, HybridTrack achieves 82.08% HOTA accuracy, significantly outperforming state-of-the-art methods. We also evaluate our method under different configurations, achieving the fastest processing speed of 112 FPS. Consequently, HybridTrack eliminates the dependency on scene-specific designs while improving performance and maintaining real-time efficiency. The code will be publicly available at the time of publishing: https://github.com/leandro-svg/HybridTrack.git.
LAM3D: Leveraging Attention for Monocular 3D Object Detection
Aug 03, 2024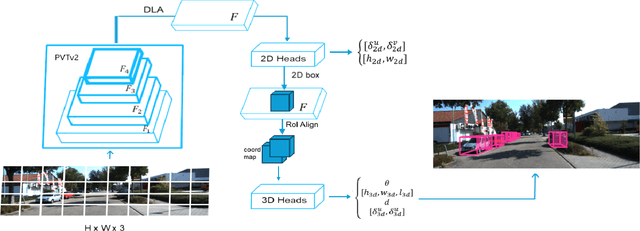



Abstract:Since the introduction of the self-attention mechanism and the adoption of the Transformer architecture for Computer Vision tasks, the Vision Transformer-based architectures gained a lot of popularity in the field, being used for tasks such as image classification, object detection and image segmentation. However, efficiently leveraging the attention mechanism in vision transformers for the Monocular 3D Object Detection task remains an open question. In this paper, we present LAM3D, a framework that Leverages self-Attention mechanism for Monocular 3D object Detection. To do so, the proposed method is built upon a Pyramid Vision Transformer v2 (PVTv2) as feature extraction backbone and 2D/3D detection machinery. We evaluate the proposed method on the KITTI 3D Object Detection Benchmark, proving the applicability of the proposed solution in the autonomous driving domain and outperforming reference methods. Moreover, due to the usage of self-attention, LAM3D is able to systematically outperform the equivalent architecture that does not employ self-attention.
DeepKalPose: An Enhanced Deep-Learning Kalman Filter for Temporally Consistent Monocular Vehicle Pose Estimation
Apr 25, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents DeepKalPose, a novel approach for enhancing temporal consistency in monocular vehicle pose estimation applied on video through a deep-learning-based Kalman Filter. By integrating a Bi-directional Kalman filter strategy utilizing forward and backward time-series processing, combined with a learnable motion model to represent complex motion patterns, our method significantly improves pose accuracy and robustness across various conditions, particularly for occluded or distant vehicles. Experimental validation on the KITTI dataset confirms that DeepKalPose outperforms existing methods in both pose accuracy and temporal consistency.
* 4 pages, 3 Figures, published to IET Electronic Letters
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge