Laura M. Ferrari
From Multimodal to Unimodal Attention in Transformers using Knowledge Distillation
Oct 19, 2021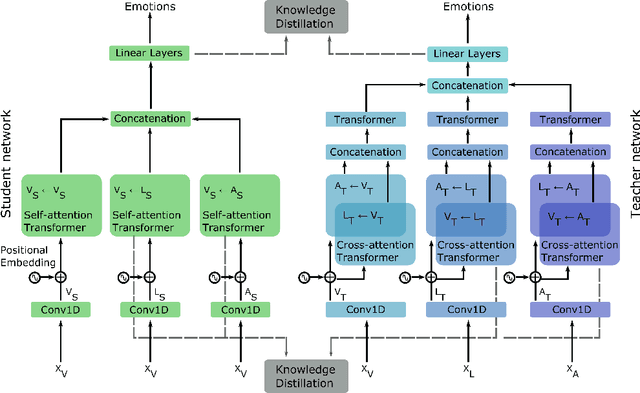
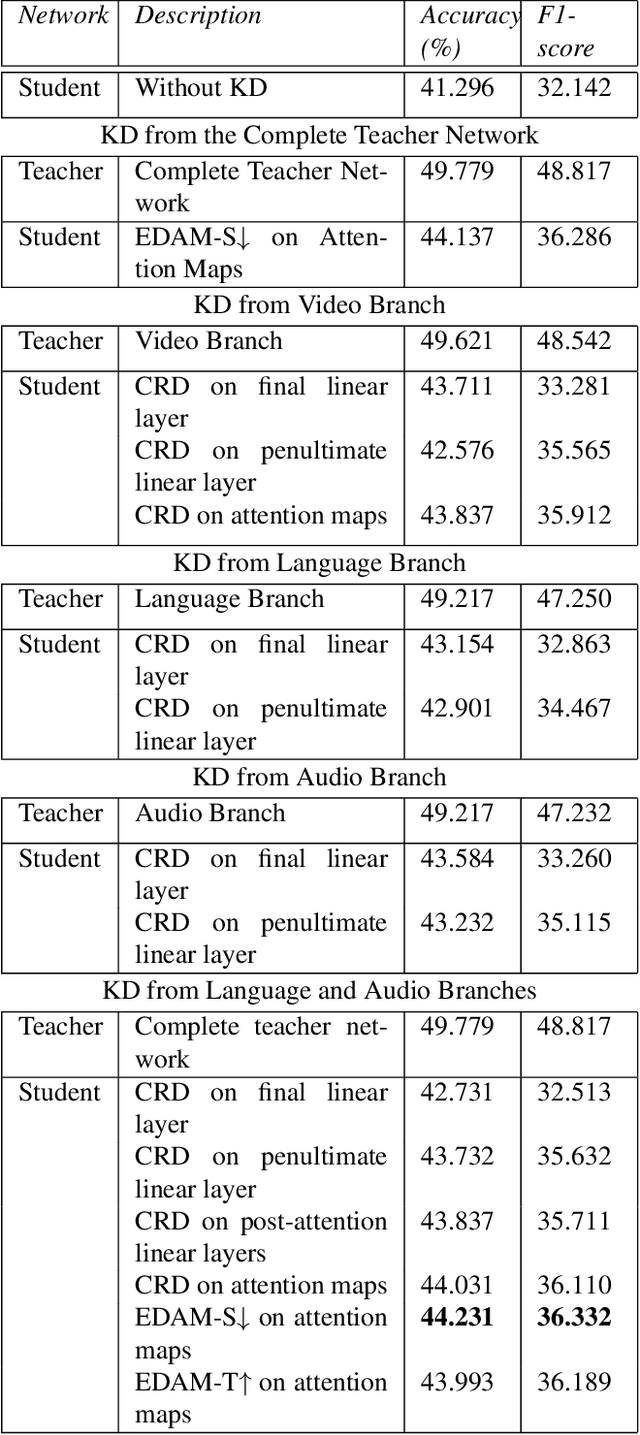
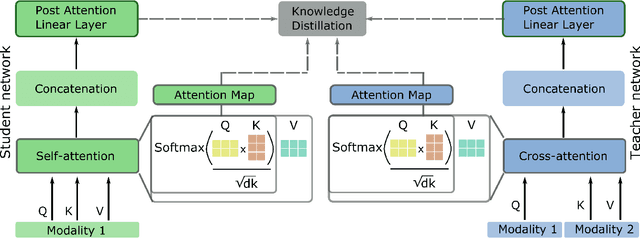

Abstract:Multimodal Deep Learning has garnered much interest, and transformers have triggered novel approaches, thanks to the cross-attention mechanism. Here we propose an approach to deal with two key existing challenges: the high computational resource demanded and the issue of missing modalities. We introduce for the first time the concept of knowledge distillation in transformers to use only one modality at inference time. We report a full study analyzing multiple student-teacher configurations, levels at which distillation is applied, and different methodologies. With the best configuration, we improved the state-of-the-art accuracy by 3%, we reduced the number of parameters by 2.5 times and the inference time by 22%. Such performance-computation tradeoff can be exploited in many applications and we aim at opening a new research area where the deployment of complex models with limited resources is demanded.
One-class Autoencoder Approach for Optimal Electrode Set-up Identification in Wearable EEG Event Monitoring
Apr 13, 2021


Abstract:A limiting factor towards the wide routine use of wearables devices for continuous healthcare monitoring is their cumbersome and obtrusive nature. This is particularly true for electroencephalography (EEG) recordings, which require the placement of multiple electrodes in contact with the scalp. In this work, we propose to identify the optimal wearable EEG electrode set-up, in terms of minimal number of electrodes, comfortable location and performance, for EEG-based event detection and monitoring. By relying on the demonstrated power of autoencoder (AE) networks to learn latent representations from high-dimensional data, our proposed strategy trains an AE architecture in a one-class classification setup with different electrode set-ups as input data. The resulting models are assessed using the F-score and the best set-up is chosen according to the established optimal criteria. Using alpha wave detection as use case, we demonstrate that the proposed method allows to detect an alpha state from an optimal set-up consisting of electrodes in the forehead and behind the ear, with an average F-score of 0.78. Our results suggest that a learning-based approach can be used to enable the design and implementation of optimized wearable devices for real-life healthcare monitoring.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge