Laura E. Boucheron
Estimation of non-uniform blur using a patch-based regression convolutional neural network
Feb 12, 2024



Abstract:The non-uniform blur of atmospheric turbulence can be modeled as a superposition of linear motion blur kernels at a patch level. We propose a regression convolutional neural network (CNN) to predict angle and length of a linear motion blur kernel for varying sized patches. We analyze the robustness of the network for different patch sizes and the performance of the network in regions where the characteristics of the blur are transitioning. Alternating patch sizes per epoch in training, we find coefficient of determination scores across a range of patch sizes of $R^2>0.78$ for length and $R^2>0.94$ for angle prediction. We find that blur predictions in regions overlapping two blur characteristics transition between the two characteristics as overlap changes. These results validate the use of such a network for prediction of non-uniform blur characteristics at a patch level.
Neural-based Compression Scheme for Solar Image Data
Nov 06, 2023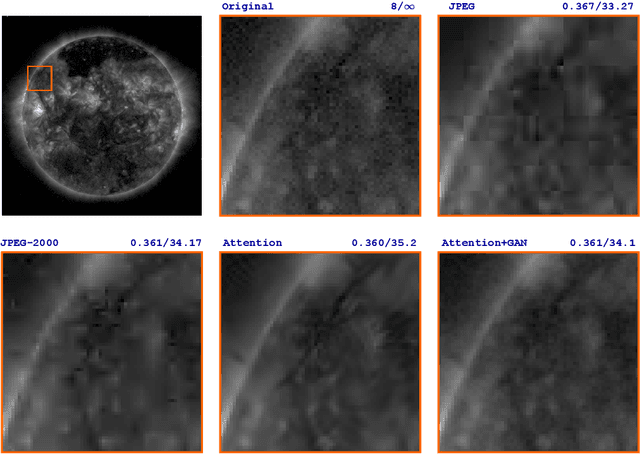
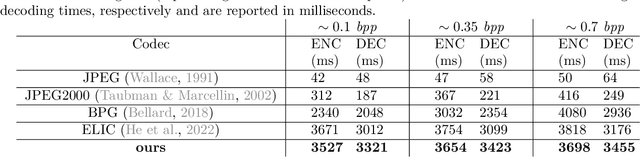
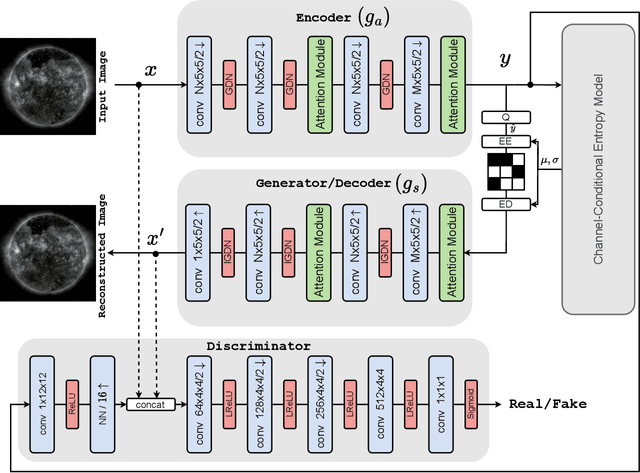
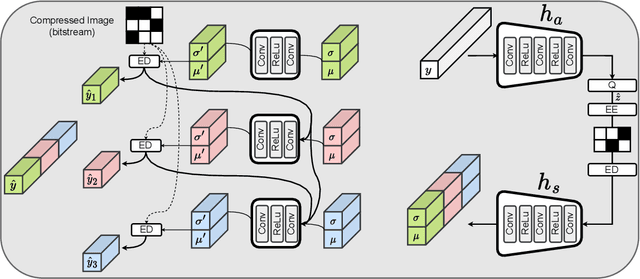
Abstract:Studying the solar system and especially the Sun relies on the data gathered daily from space missions. These missions are data-intensive and compressing this data to make them efficiently transferable to the ground station is a twofold decision to make. Stronger compression methods, by distorting the data, can increase data throughput at the cost of accuracy which could affect scientific analysis of the data. On the other hand, preserving subtle details in the compressed data requires a high amount of data to be transferred, reducing the desired gains from compression. In this work, we propose a neural network-based lossy compression method to be used in NASA's data-intensive imagery missions. We chose NASA's SDO mission which transmits 1.4 terabytes of data each day as a proof of concept for the proposed algorithm. In this work, we propose an adversarially trained neural network, equipped with local and non-local attention modules to capture both the local and global structure of the image resulting in a better trade-off in rate-distortion (RD) compared to conventional hand-engineered codecs. The RD variational autoencoder used in this work is jointly trained with a channel-dependent entropy model as a shared prior between the analysis and synthesis transforms to make the entropy coding of the latent code more effective. Our neural image compression algorithm outperforms currently-in-use and state-of-the-art codecs such as JPEG and JPEG-2000 in terms of the RD performance when compressing extreme-ultraviolet (EUV) data. As a proof of concept for use of this algorithm in SDO data analysis, we have performed coronal hole (CH) detection using our compressed images, and generated consistent segmentations, even at a compression rate of $\sim0.1$ bits per pixel (compared to 8 bits per pixel on the original data) using EUV data from SDO.
Estimation of motion blur kernel parameters using regression convolutional neural networks
Aug 02, 2023Abstract:Many deblurring and blur kernel estimation methods use MAP or classification deep learning techniques to sharpen an image and predict the blur kernel. We propose a regression approach using neural networks to predict the parameters of linear motion blur kernels. These kernels can be parameterized by its length of blur and the orientation of the blur.This paper will analyze the relationship between length and angle of linear motion blur. This analysis will help establish a foundation to using regression prediction in uniformed motion blur images.
Solar Active Region Magnetogram Image Dataset for Studies of Space Weather
May 18, 2023Abstract:In this dataset we provide a comprehensive collection of magnetograms (images quantifying the strength of the magnetic field) from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA's) Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). The dataset incorporates data from three sources and provides SDO Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) magnetograms of solar active regions (regions of large magnetic flux, generally the source of eruptive events) as well as labels of corresponding flaring activity. This dataset will be useful for image analysis or solar physics research related to magnetic structure, its evolution over time, and its relation to solar flares. The dataset will be of interest to those researchers investigating automated solar flare prediction methods, including supervised and unsupervised machine learning (classical and deep), binary and multi-class classification, and regression. This dataset is a minimally processed, user configurable dataset of consistently sized images of solar active regions that can serve as a benchmark dataset for solar flare prediction research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge