Laura Deming
Peptide-Spectra Matching from Weak Supervision
Aug 22, 2018



Abstract:As in many other scientific domains, we face a fundamental problem when using machine learning to identify proteins from mass spectrometry data: large ground truth datasets mapping inputs to correct outputs are extremely difficult to obtain. Instead, we have access to imperfect hand-coded models crafted by domain experts. In this paper, we apply deep neural networks to an important step of the protein identification problem, the pairing of mass spectra with short sequences of amino acids called peptides. We train our model to differentiate between top scoring results from a state-of-the art classical system and hard-negative second and third place results. Our resulting model is much better at identifying peptides with spectra than the model used to generate its training data. In particular, we achieve a 43% improvement over standard matching methods and a 10% improvement over a combination of the matching method and an industry standard cross-spectra reranking tool. Importantly, in a more difficult experimental regime that reflects current challenges facing biologists, our advantage over the previous state-of-the-art grows to 15% even after reranking. We believe this approach will generalize to other challenging scientific problems.
Genetic Architect: Discovering Genomic Structure with Learned Neural Architectures
May 23, 2016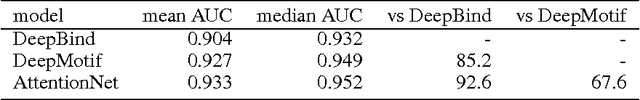
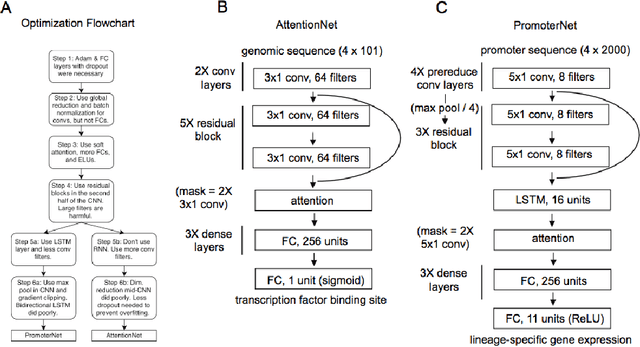
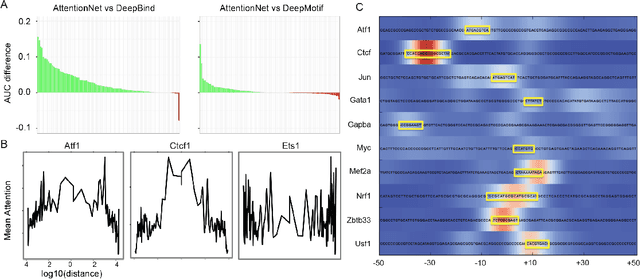

Abstract:Each human genome is a 3 billion base pair set of encoding instructions. Decoding the genome using deep learning fundamentally differs from most tasks, as we do not know the full structure of the data and therefore cannot design architectures to suit it. As such, architectures that fit the structure of genomics should be learned not prescribed. Here, we develop a novel search algorithm, applicable across domains, that discovers an optimal architecture which simultaneously learns general genomic patterns and identifies the most important sequence motifs in predicting functional genomic outcomes. The architectures we find using this algorithm succeed at using only RNA expression data to predict gene regulatory structure, learn human-interpretable visualizations of key sequence motifs, and surpass state-of-the-art results on benchmark genomics challenges.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge