Laura Davies
Expanding on the BRIAR Dataset: A Comprehensive Whole Body Biometric Recognition Resource at Extreme Distances and Real-World Scenarios (Collections 1-4)
Jan 23, 2025
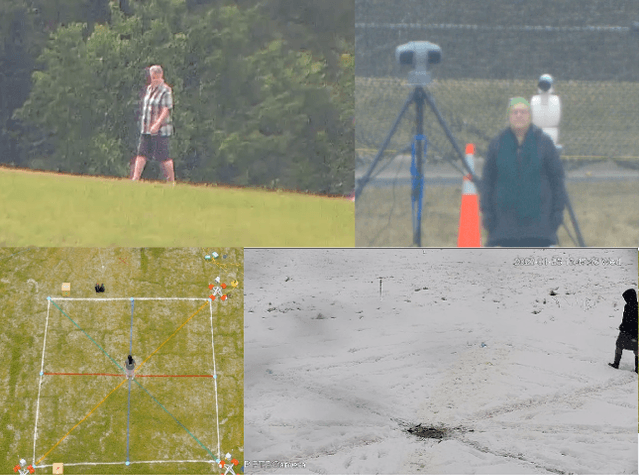
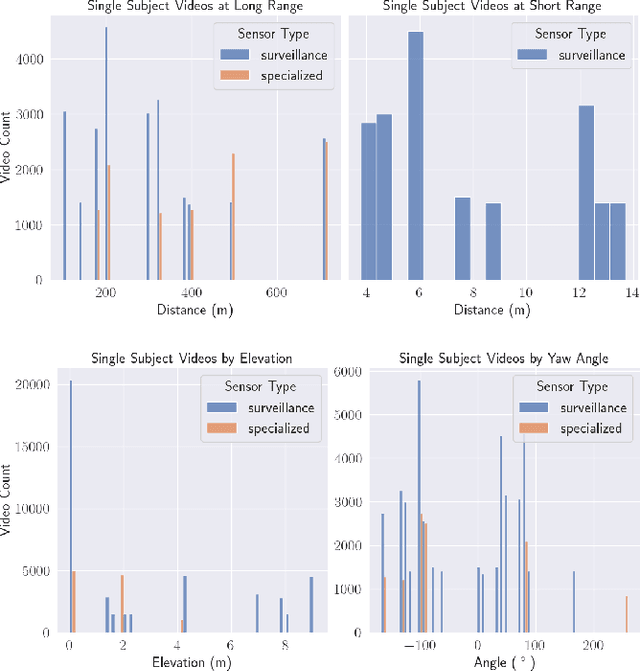
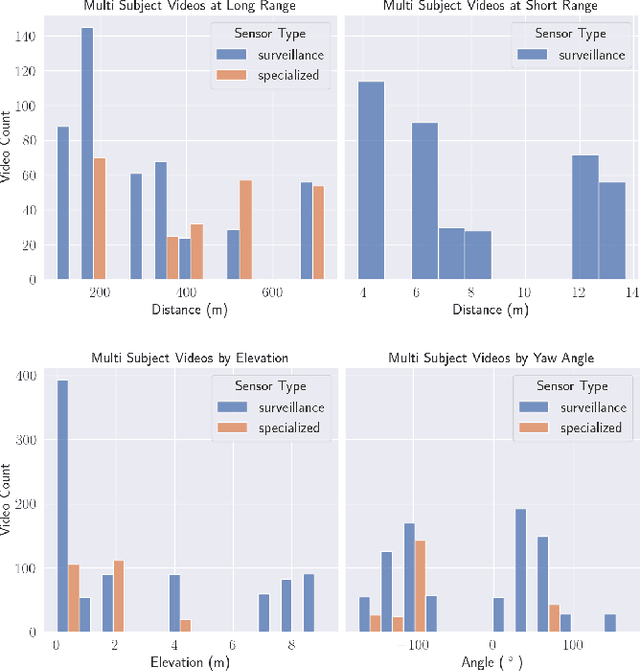

Abstract:The state-of-the-art in biometric recognition algorithms and operational systems has advanced quickly in recent years providing high accuracy and robustness in more challenging collection environments and consumer applications. However, the technology still suffers greatly when applied to non-conventional settings such as those seen when performing identification at extreme distances or from elevated cameras on buildings or mounted to UAVs. This paper summarizes an extension to the largest dataset currently focused on addressing these operational challenges, and describes its composition as well as methodologies of collection, curation, and annotation.
From Data to Insights: A Covariate Analysis of the IARPA BRIAR Dataset for Multimodal Biometric Recognition Algorithms at Altitude and Range
Sep 03, 2024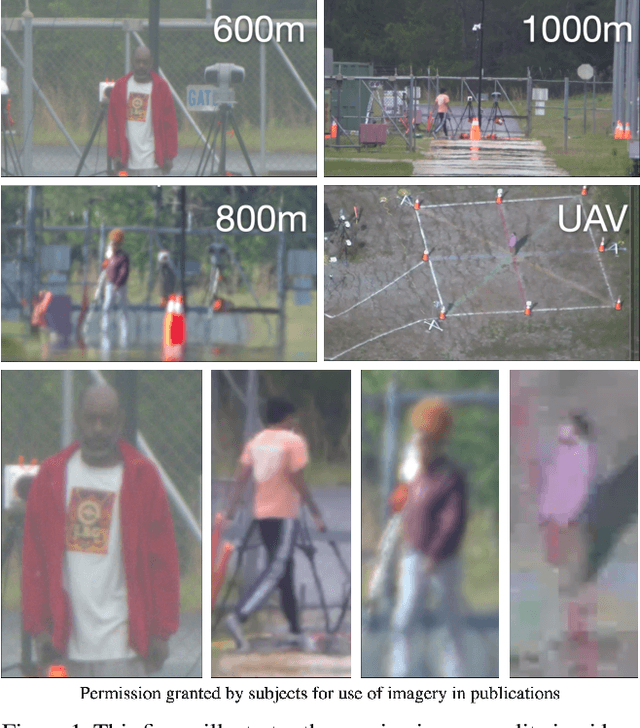


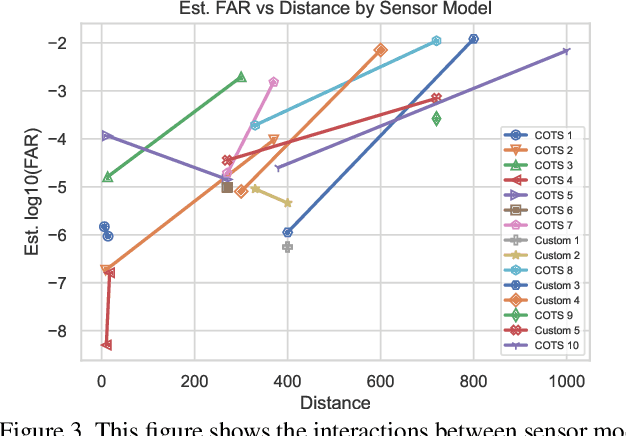
Abstract:This paper examines covariate effects on fused whole body biometrics performance in the IARPA BRIAR dataset, specifically focusing on UAV platforms, elevated positions, and distances up to 1000 meters. The dataset includes outdoor videos compared with indoor images and controlled gait recordings. Normalized raw fusion scores relate directly to predicted false accept rates (FAR), offering an intuitive means for interpreting model results. A linear model is developed to predict biometric algorithm scores, analyzing their performance to identify the most influential covariates on accuracy at altitude and range. Weather factors like temperature, wind speed, solar loading, and turbulence are also investigated in this analysis. The study found that resolution and camera distance best predicted accuracy and findings can guide future research and development efforts in long-range/elevated/UAV biometrics and support the creation of more reliable and robust systems for national security and other critical domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge