Lanyu Xu
Neighbor-Aware Token Reduction via Hilbert Curve for Vision Transformers
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) have achieved remarkable success in visual recognition tasks, but redundant token representations limit their computational efficiency. Existing token merging and pruning strategies often overlook spatial continuity and neighbor relationships, resulting in the loss of local context. This paper proposes novel neighbor-aware token reduction methods based on Hilbert curve reordering, which explicitly preserves the neighbor structure in a 2D space using 1D sequential representations. Our method introduces two key strategies: Neighbor-Aware Pruning (NAP) for selective token retention and Merging by Adjacent Token similarity (MAT) for local token aggregation. Experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art accuracy-efficiency trade-offs compared to existing methods. This work highlights the importance of spatial continuity and neighbor structure, offering new insights for the architectural optimization of ViTs.
MTMed3D: A Multi-Task Transformer-Based Model for 3D Medical Imaging
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:In the field of medical imaging, AI-assisted techniques such as object detection, segmentation, and classification are widely employed to alleviate the workload of physicians and doctors. However, single-task models are predominantly used, overlooking the shared information across tasks. This oversight leads to inefficiencies in real-life applications. In this work, we propose MTMed3D, a novel end-to-end Multi-task Transformer-based model to address the limitations of single-task models by jointly performing 3D detection, segmentation, and classification in medical imaging. Our model uses a Transformer as the shared encoder to generate multi-scale features, followed by CNN-based task-specific decoders. The proposed framework was evaluated on the BraTS 2018 and 2019 datasets, achieving promising results across all three tasks, especially in detection, where our method achieves better results than prior works. Additionally, we compare our multi-task model with equivalent single-task variants trained separately. Our multi-task model significantly reduces computational costs and achieves faster inference speed while maintaining comparable performance to the single-task models, highlighting its efficiency advantage. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to leverage Transformers for multi-task learning that simultaneously covers detection, segmentation, and classification tasks in 3D medical imaging, presenting its potential to enhance diagnostic processes. The code is available at https://github.com/fanlimua/MTMed3D.git.
Hilbert-Guided Block-Sparse Local Attention
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:The quadratic compute and memory costs of global self-attention severely limit its use in high-resolution images. Local attention reduces complexity by restricting attention to neighborhoods. Block-sparse kernels can further improve the efficiency of local attention, but conventional local attention patterns often fail to deliver significant speedups because tokens within a window are not contiguous in the 1D sequence. This work proposes a novel method for constructing windows and neighborhoods based on the Hilbert curve. Image tokens are first reordered along a Hilbert curve, and windows and neighborhoods are then formed on the reordered 1D sequence. From a block-sparse perspective, this strategy significantly increases block sparsity and can be combined with existing block-sparse kernels to improve the efficiency of 2D local attention. Experiments show that the proposed Hilbert Window Attention and Hilbert Slide Attention can accelerate window attention and slide attention by about $4\times$ and $18\times$, respectively. To assess practicality, the strategy is instantiated as the Hilbert Window Transformer and the Hilbert Neighborhood Transformer, both of which achieve end-to-end speedups with minimal accuracy loss. Overall, combining Hilbert-guided local attention with block-sparse kernels offers a general and practical approach to enhancing the efficiency of 2D local attention for images. The code is available at https://github.com/Yunge6666/Hilbert-Local-Attention.
Panoptic Perception for Autonomous Driving: A Survey
Aug 27, 2024Abstract:Panoptic perception represents a forefront advancement in autonomous driving technology, unifying multiple perception tasks into a singular, cohesive framework to facilitate a thorough understanding of the vehicle's surroundings. This survey reviews typical panoptic perception models for their unique inputs and architectures and compares them to performance, responsiveness, and resource utilization. It also delves into the prevailing challenges faced in panoptic perception and explores potential trajectories for future research. Our goal is to furnish researchers in autonomous driving with a detailed synopsis of panoptic perception, positioning this survey as a pivotal reference in the ever-evolving landscape of autonomous driving technologies.
OpenEI: An Open Framework for Edge Intelligence
Jun 05, 2019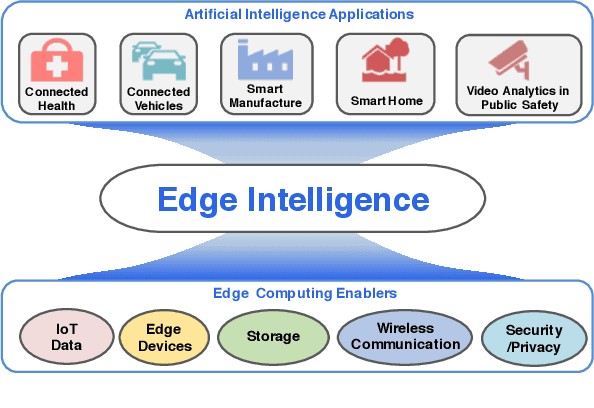
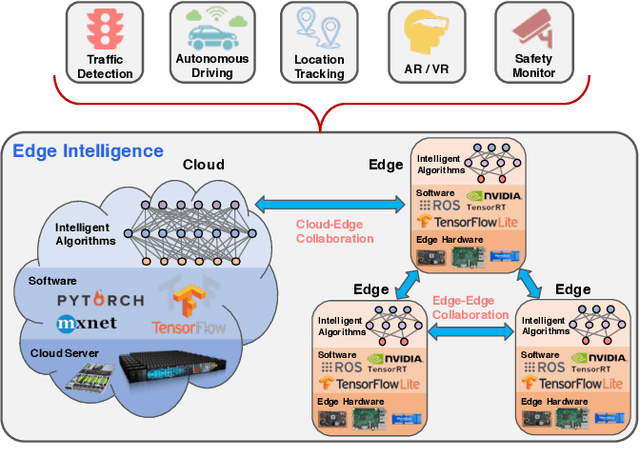
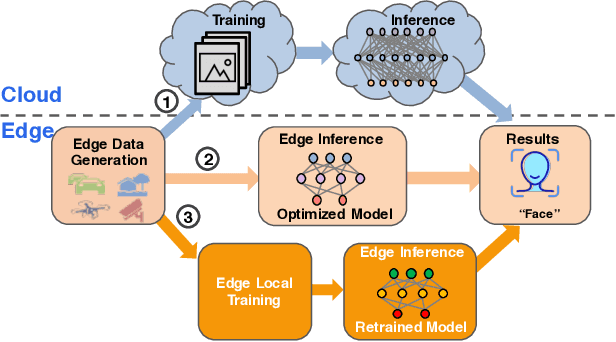
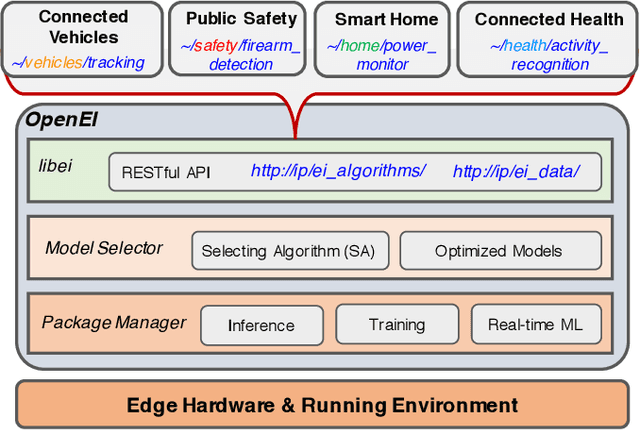
Abstract:In the last five years, edge computing has attracted tremendous attention from industry and academia due to its promise to reduce latency, save bandwidth, improve availability, and protect data privacy to keep data secure. At the same time, we have witnessed the proliferation of AI algorithms and models which accelerate the successful deployment of intelligence mainly in cloud services. These two trends, combined together, have created a new horizon: Edge Intelligence (EI). The development of EI requires much attention from both the computer systems research community and the AI community to meet these demands. However, existing computing techniques used in the cloud are not applicable to edge computing directly due to the diversity of computing sources and the distribution of data sources. We envision that there missing a framework that can be rapidly deployed on edge and enable edge AI capabilities. To address this challenge, in this paper we first present the definition and a systematic review of EI. Then, we introduce an Open Framework for Edge Intelligence (OpenEI), which is a lightweight software platform to equip edges with intelligent processing and data sharing capability. We analyze four fundamental EI techniques which are used to build OpenEI and identify several open problems based on potential research directions. Finally, four typical application scenarios enabled by OpenEI are presented.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge