Lahoucine Ballihi
FacEnhance: Facial Expression Enhancing with Recurrent DDPMs
Jun 13, 2024Abstract:Facial expressions, vital in non-verbal human communication, have found applications in various computer vision fields like virtual reality, gaming, and emotional AI assistants. Despite advancements, many facial expression generation models encounter challenges such as low resolution (e.g., 32x32 or 64x64 pixels), poor quality, and the absence of background details. In this paper, we introduce FacEnhance, a novel diffusion-based approach addressing constraints in existing low-resolution facial expression generation models. FacEnhance enhances low-resolution facial expression videos (64x64 pixels) to higher resolutions (192x192 pixels), incorporating background details and improving overall quality. Leveraging conditional denoising within a diffusion framework, guided by a background-free low-resolution video and a single neutral expression high-resolution image, FacEnhance generates a video incorporating the facial expression from the low-resolution video performed by the individual with background from the neutral image. By complementing lightweight low-resolution models, FacEnhance strikes a balance between computational efficiency and desirable image resolution and quality. Extensive experiments on the MUG facial expression database demonstrate the efficacy of FacEnhance in enhancing low-resolution model outputs to state-of-the-art quality while preserving content and identity consistency. FacEnhance represents significant progress towards resource-efficient, high-fidelity facial expression generation, Renewing outdated low-resolution methods to up-to-date standards.
SpATr: MoCap 3D Human Action Recognition based on Spiral Auto-encoder and Transformer Network
Jun 30, 2023



Abstract:Recent advancements in technology have expanded the possibilities of human action recognition by leveraging 3D data, which offers a richer representation of actions through the inclusion of depth information, enabling more accurate analysis of spatial and temporal characteristics. However, 3D human action recognition is a challenging task due to the irregularity and Disarrangement of the data points in action sequences. In this context, we present our novel model for human action recognition from fixed topology mesh sequences based on Spiral Auto-encoder and Transformer Network, namely SpATr. The proposed method first disentangles space and time in the mesh sequences. Then, an auto-encoder is utilized to extract spatial geometrical features, and tiny transformer is used to capture the temporal evolution of the sequence. Previous methods either use 2D depth images, sample skeletons points or they require a huge amount of memory leading to the ability to process short sequences only. In this work, we show competitive recognition rate and high memory efficiency by building our auto-encoder based on spiral convolutions, which are light weight convolution directly applied to mesh data with fixed topologies, and by modeling temporal evolution using a attention, that can handle large sequences. The proposed method is evaluated on on two 3D human action datasets: MoVi and BMLrub from the Archive of Motion Capture As Surface Shapes (AMASS). The results analysis shows the effectiveness of our method in 3D human action recognition while maintaining high memory efficiency. The code will soon be made publicly available.
Facial Expression Video Generation Based-On Spatio-temporal Convolutional GAN: FEV-GAN
Oct 20, 2022
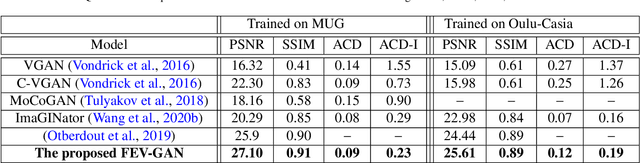


Abstract:Facial expression generation has always been an intriguing task for scientists and researchers all over the globe. In this context, we present our novel approach for generating videos of the six basic facial expressions. Starting from a single neutral facial image and a label indicating the desired facial expression, we aim to synthesize a video of the given identity performing the specified facial expression. Our approach, referred to as FEV-GAN (Facial Expression Video GAN), is based on Spatio-temporal Convolutional GANs, that are known to model both content and motion in the same network. Previous methods based on such a network have shown a good ability to generate coherent videos with smooth temporal evolution. However, they still suffer from low image quality and low identity preservation capability. In this work, we address this problem by using a generator composed of two image encoders. The first one is pre-trained for facial identity feature extraction and the second for spatial feature extraction. We have qualitatively and quantitatively evaluated our model on two international facial expression benchmark databases: MUG and Oulu-CASIA NIR&VIS. The experimental results analysis demonstrates the effectiveness of our approach in generating videos of the six basic facial expressions while preserving the input identity. The analysis also proves that the use of both identity and spatial features enhances the decoder ability to better preserve the identity and generate high-quality videos. The code and the pre-trained model will soon be made publicly available.
* 13 pages, 8 figures, accepted in ISWA journal
Dynamic Facial Expression Generation on Hilbert Hypersphere with Conditional Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Nets
Jul 23, 2019



Abstract:In this work, we propose a novel approach for generating videos of the six basic facial expressions given a neutral face image. We propose to exploit the face geometry by modeling the facial landmarks motion as curves encoded as points on a hypersphere. By proposing a conditional version of manifold-valued Wasserstein generative adversarial network (GAN) for motion generation on the hypersphere, we learn the distribution of facial expression dynamics of different classes, from which we synthesize new facial expression motions. The resulting motions can be transformed to sequences of landmarks and then to images sequences by editing the texture information using another conditional Generative Adversarial Network. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work that explores manifold-valued representations with GAN to address the problem of dynamic facial expression generation. We evaluate our proposed approach both quantitatively and qualitatively on two public datasets; Oulu-CASIA and MUG Facial Expression. Our experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in generating realistic videos with continuous motion, realistic appearance and identity preservation. We also show the efficiency of our framework for dynamic facial expressions generation, dynamic facial expression transfer and data augmentation for training improved emotion recognition models.
Automatic Analysis of Facial Expressions Based on Deep Covariance Trajectories
Oct 25, 2018



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new approach for facial expression recognition. The solution is based on the idea of encoding local and global Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN) features extracted from still images, in compact local and global covariance descriptors. The space geometry of the covariance matrices is that of Symmetric Positive Definite (SPD) matrices. By performing the classification of static facial expressions using a valid Gaussian kernel on the SPD manifold and Support Vector Machine (SVM), we show that the covariance descriptors computed on DCNN features are more effective than the standard classification with fully connected layers and softmax. Besides, we propose a completely new and original solution to model the temporal dynamic of facial expressions as deep trajectories on the SPD manifold. As an extension of the classification pipeline of covariance descriptors, we apply SVM with valid positive definite kernels derived from global alignment for deep covariance trajectories classification. By conducting extensive experiments on the Oulu-CASIA, CK+, and SFEW datasets, we show that both the proposed static and dynamic approaches achieve state-of-the-art performance for facial expression recognition outperforming most recent approaches.
Deep Covariance Descriptors for Facial Expression Recognition
May 10, 2018



Abstract:In this paper, covariance matrices are exploited to encode the deep convolutional neural networks (DCNN) features for facial expression recognition. The space geometry of the covariance matrices is that of Symmetric Positive Definite (SPD) matrices. By performing the classification of the facial expressions using Gaussian kernel on SPD manifold, we show that the covariance descriptors computed on DCNN features are more efficient than the standard classification with fully connected layers and softmax. By implementing our approach using the VGG-face and ExpNet architectures with extensive experiments on the Oulu-CASIA and SFEW datasets, we show that the proposed approach achieves performance at the state of the art for facial expression recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge