Kyungtae Kang
Track-centric Iterative Learning for Global Trajectory Optimization in Autonomous Racing
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:This paper presents a global trajectory optimization framework for minimizing lap time in autonomous racing under uncertain vehicle dynamics. Optimizing the trajectory over the full racing horizon is computationally expensive, and tracking such a trajectory in the real world hardly assures global optimality due to uncertain dynamics. Yet, existing work mostly focuses on dynamics learning at the tracking level, without updating the trajectory itself to account for the learned dynamics. To address these challenges, we propose a track-centric approach that directly learns and optimizes the full-horizon trajectory. We first represent trajectories through a track-agnostic parametric space in light of the wavelet transform. This space is then efficiently explored using Bayesian optimization, where the lap time of each candidate is evaluated by running simulations with the learned dynamics. This optimization is embedded in an iterative learning framework, where the optimized trajectory is deployed to collect real-world data for updating the dynamics, progressively refining the trajectory over the iterations. The effectiveness of the proposed framework is validated through simulations and real-world experiments, demonstrating lap time improvement of up to 20.7% over a nominal baseline and consistently outperforming state-of-the-art methods.
R-TOD: Real-Time Object Detector with Minimized End-to-End Delay for Autonomous Driving
Oct 23, 2020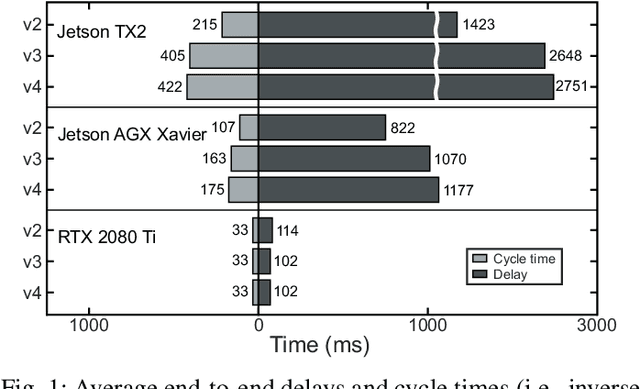
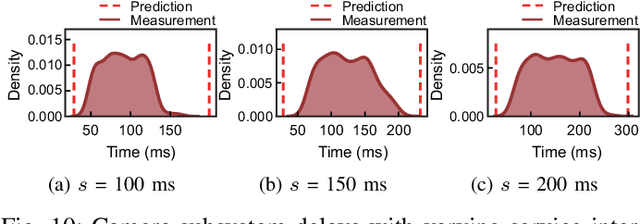
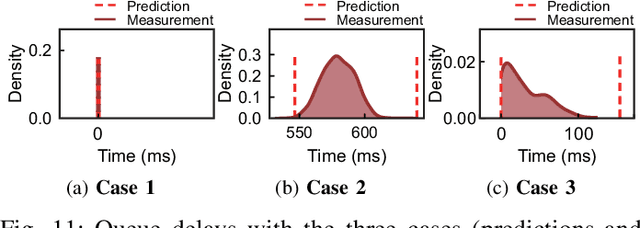
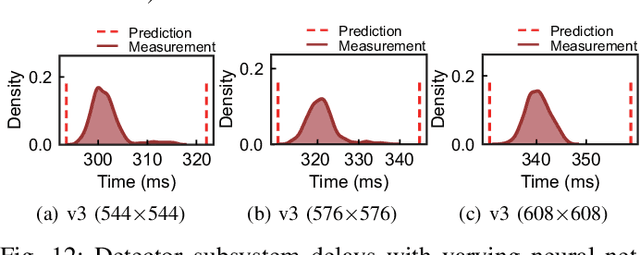
Abstract:For realizing safe autonomous driving, the end-to-end delays of real-time object detection systems should be thoroughly analyzed and minimized. However, despite recent development of neural networks with minimized inference delays, surprisingly little attention has been paid to their end-to-end delays from an object's appearance until its detection is reported. With this motivation, this paper aims to provide more comprehensive understanding of the end-to-end delay, through which precise best- and worst-case delay predictions are formulated, and three optimization methods are implemented: (i) on-demand capture, (ii) zero-slack pipeline, and (iii) contention-free pipeline. Our experimental results show a 76% reduction in the end-to-end delay of Darknet YOLO (You Only Look Once) v3 (from 1070 ms to 261 ms), thereby demonstrating the great potential of exploiting the end-to-end delay analysis for autonomous driving. Furthermore, as we only modify the system architecture and do not change the neural network architecture itself, our approach incurs no penalty on the detection accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge