Kyoung Jin Noh
Extraction of Coronary Vessels in Fluoroscopic X-Ray Sequences Using Vessel Correspondence Optimization
Jul 28, 2022Abstract:We present a method to extract coronary vessels from fluoroscopic x-ray sequences. Given the vessel structure for the source frame, vessel correspondence candidates in the subsequent frame are generated by a novel hierarchical search scheme to overcome the aperture problem. Optimal correspondences are determined within a Markov random field optimization framework. Post-processing is performed to extract vessel branches newly visible due to the inflow of contrast agent. Quantitative and qualitative evaluation conducted on a dataset of 18 sequences demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Scale Space Approximation in Convolutional Neural Networks for Retinal Vessel Segmentation
Oct 18, 2018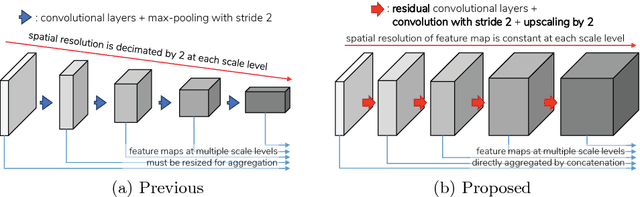
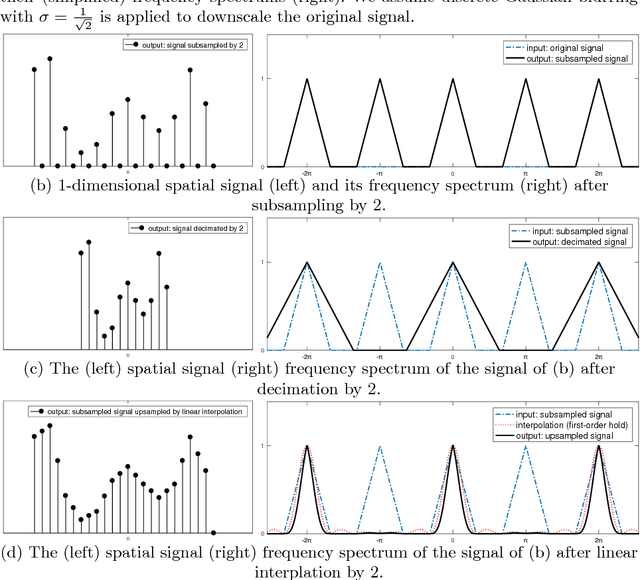
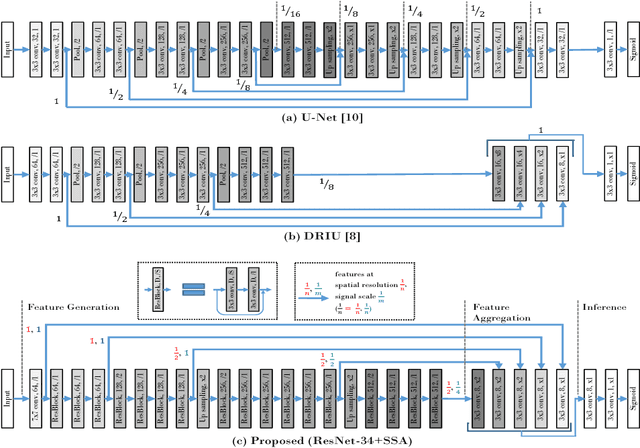
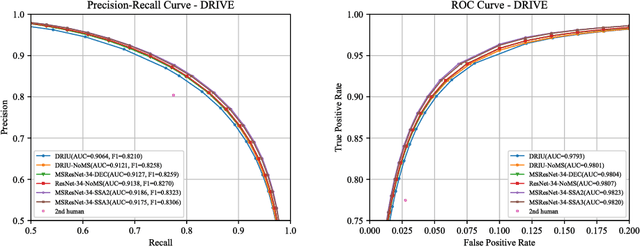
Abstract:Retinal images have the highest resolution and clarity among medical images. Thus, vessel analysis in retinal images may facilitate early diagnosis and treatment of many chronic diseases. In this paper, we propose a novel multi-scale residual convolutional neural network structure based on a \emph{scale-space approximation (SSA)} block of layers, comprising subsampling and subsequent upsampling, for multi-scale representation. Through analysis in the frequency domain, we show that this block structure is a close approximation of Gaussian filtering, the operation to achieve scale variations in scale-space theory. Experimental evaluations demonstrate that the proposed network outperforms current state-of-the-art methods. Ablative analysis shows that the SSA is indeed an important factor in performance improvement.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge