Kyle Palko
Maneuver Identification Challenge
Aug 25, 2021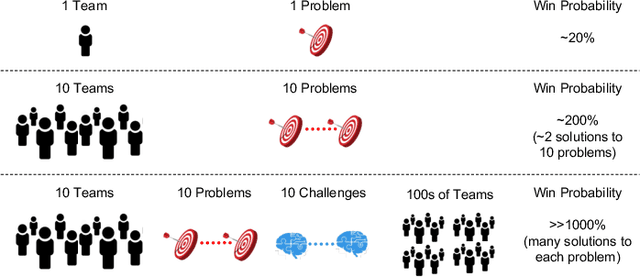
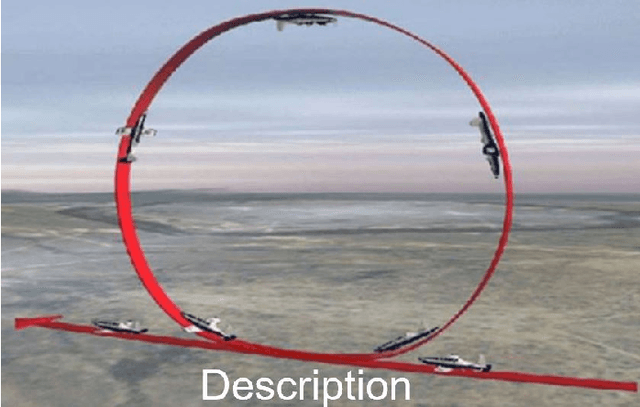
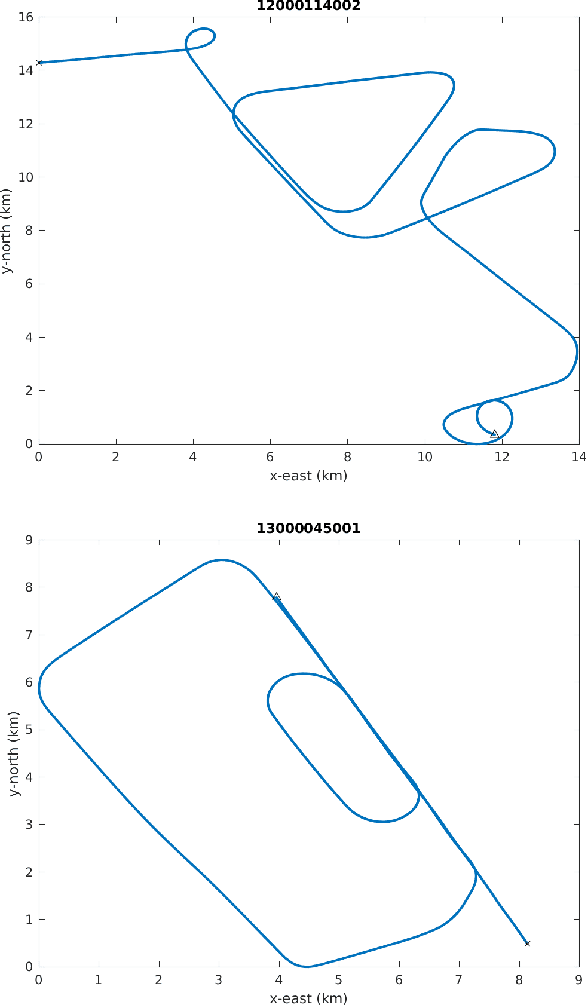
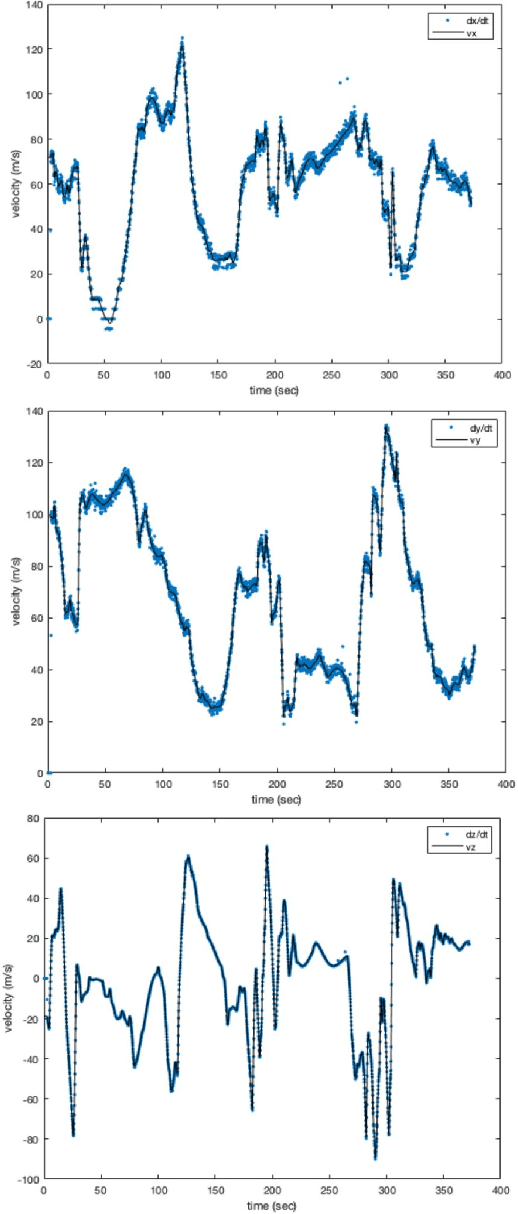

Abstract:AI algorithms that identify maneuvers from trajectory data could play an important role in improving flight safety and pilot training. AI challenges allow diverse teams to work together to solve hard problems and are an effective tool for developing AI solutions. AI challenges are also a key driver of AI computational requirements. The Maneuver Identification Challenge hosted at maneuver-id.mit.edu provides thousands of trajectories collected from pilots practicing in flight simulators, descriptions of maneuvers, and examples of these maneuvers performed by experienced pilots. Each trajectory consists of positions, velocities, and aircraft orientations normalized to a common coordinate system. Construction of the data set required significant data architecture to transform flight simulator logs into AI ready data, which included using a supercomputer for deduplication and data conditioning. There are three proposed challenges. The first challenge is separating physically plausible (good) trajectories from unfeasible (bad) trajectories. Human labeled good and bad trajectories are provided to aid in this task. Subsequent challenges are to label trajectories with their intended maneuvers and to assess the quality of those maneuvers.
Evaluation of Human-AI Teams for Learned and Rule-Based Agents in Hanabi
Jul 20, 2021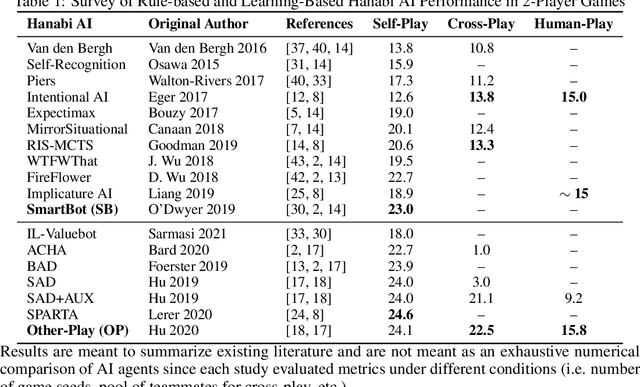
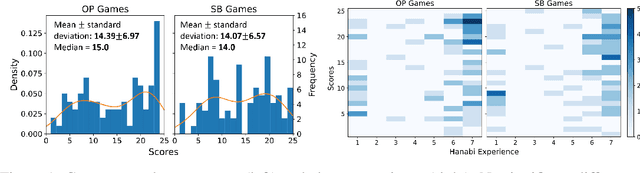
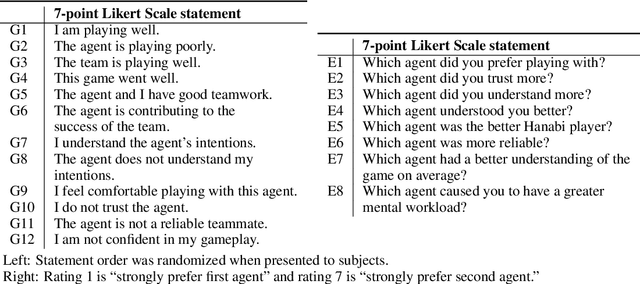
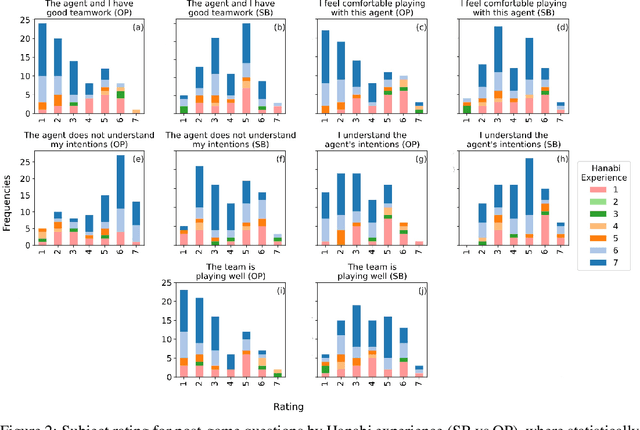
Abstract:Deep reinforcement learning has generated superhuman AI in competitive games such as Go and StarCraft. Can similar learning techniques create a superior AI teammate for human-machine collaborative games? Will humans prefer AI teammates that improve objective team performance or those that improve subjective metrics of trust? In this study, we perform a single-blind evaluation of teams of humans and AI agents in the cooperative card game Hanabi, with both rule-based and learning-based agents. In addition to the game score, used as an objective metric of the human-AI team performance, we also quantify subjective measures of the human's perceived performance, teamwork, interpretability, trust, and overall preference of AI teammate. We find that humans have a clear preference toward a rule-based AI teammate (SmartBot) over a state-of-the-art learning-based AI teammate (Other-Play) across nearly all subjective metrics, and generally view the learning-based agent negatively, despite no statistical difference in the game score. This result has implications for future AI design and reinforcement learning benchmarking, highlighting the need to incorporate subjective metrics of human-AI teaming rather than a singular focus on objective task performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge