Kui Xiao
MyGram: Modality-aware Graph Transformer with Global Distribution for Multi-modal Entity Alignment
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:Multi-modal entity alignment aims to identify equivalent entities between two multi-modal Knowledge graphs by integrating multi-modal data, such as images and text, to enrich the semantic representations of entities. However, existing methods may overlook the structural contextual information within each modality, making them vulnerable to interference from shallow features. To address these challenges, we propose MyGram, a modality-aware graph transformer with global distribution for multi-modal entity alignment. Specifically, we develop a modality diffusion learning module to capture deep structural contextual information within modalities and enable fine-grained multi-modal fusion. In addition, we introduce a Gram Loss that acts as a regularization constraint by minimizing the volume of a 4-dimensional parallelotope formed by multi-modal features, thereby achieving global distribution consistency across modalities. We conduct experiments on five public datasets. Results show that MyGram outperforms baseline models, achieving a maximum improvement of 4.8% in Hits@1 on FBDB15K, 9.9% on FBYG15K, and 4.3% on DBP15K.
MacVQA: Adaptive Memory Allocation and Global Noise Filtering for Continual Visual Question Answering
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Visual Question Answering (VQA) requires models to reason over multimodal information, combining visual and textual data. With the development of continual learning, significant progress has been made in retaining knowledge and adapting to new information in the VQA domain. However, current methods often struggle with balancing knowledge retention, adaptation, and robust feature representation. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework with adaptive memory allocation and global noise filtering called MacVQA for visual question answering. MacVQA fuses visual and question information while filtering noise to ensure robust representations, and employs prototype-based memory allocation to optimize feature quality and memory usage. These designs enable MacVQA to balance knowledge acquisition, retention, and compositional generalization in continual VQA learning. Experiments on ten continual VQA tasks show that MacVQA outperforms existing baselines, achieving 43.38% average accuracy and 2.32% average forgetting on standard tasks, and 42.53% average accuracy and 3.60% average forgetting on novel composition tasks.
KeenKT: Knowledge Mastery-State Disambiguation for Knowledge Tracing
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Knowledge Tracing (KT) aims to dynamically model a student's mastery of knowledge concepts based on their historical learning interactions. Most current methods rely on single-point estimates, which cannot distinguish true ability from outburst or carelessness, creating ambiguity in judging mastery. To address this issue, we propose a Knowledge Mastery-State Disambiguation for Knowledge Tracing model (KeenKT), which represents a student's knowledge state at each interaction using a Normal-Inverse-Gaussian (NIG) distribution, thereby capturing the fluctuations in student learning behaviors. Furthermore, we design an NIG-distance-based attention mechanism to model the dynamic evolution of the knowledge state. In addition, we introduce a diffusion-based denoising reconstruction loss and a distributional contrastive learning loss to enhance the model's robustness. Extensive experiments on six public datasets demonstrate that KeenKT outperforms SOTA KT models in terms of prediction accuracy and sensitivity to behavioral fluctuations. The proposed method yields the maximum AUC improvement of 5.85% and the maximum ACC improvement of 6.89%.
Disentangling Heterogeneous Knowledge Concept Embedding for Cognitive Diagnosis on Untested Knowledge
May 25, 2024



Abstract:Cognitive diagnosis is a fundamental and critical task in learning assessment, which aims to infer students' proficiency on knowledge concepts from their response logs. Current works assume each knowledge concept will certainly be tested and covered by multiple exercises. However, whether online or offline courses, it's hardly feasible to completely cover all knowledge concepts in several exercises. Restricted tests lead to undiscovered knowledge deficits, especially untested knowledge concepts(UKCs). In this paper, we propose a novel \underline{Dis}entangling Heterogeneous \underline{K}nowledge \underline{C}ognitive \underline{D}iagnosis framework on untested knowledge(DisKCD). Specifically, we leverage course grades, exercise questions, and resources to learn the potential representations of students, exercises, and knowledge concepts. In particular, knowledge concepts are disentangled into tested and untested based on the limiting actual exercises. We construct a heterogeneous relation graph network via students, exercises, tested knowledge concepts(TKCs), and UKCs. Then, through a hierarchical heterogeneous message-passing mechanism, the fine-grained relations are incorporated into the embeddings of the entities. Finally, the embeddings will be applied to multiple existing cognitive diagnosis models to infer students' proficiency on UKCs. Experimental results on real-world datasets show that the proposed model can effectively improve the performance of the task of diagnosing students' proficiency on UKCs. Our anonymous code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DisKCD.
Delve into Base-Novel Confusion: Redundancy Exploration for Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning
May 08, 2024
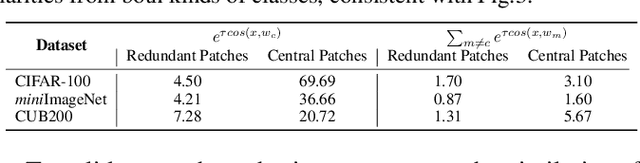

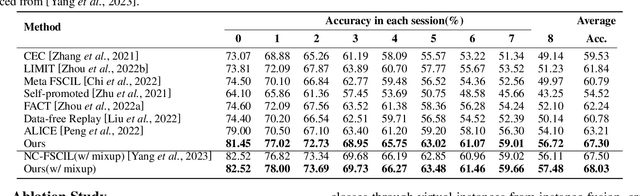
Abstract:Few-shot class-incremental learning (FSCIL) aims to acquire knowledge from novel classes with limited samples while retaining information about base classes. Existing methods address catastrophic forgetting and overfitting by freezing the feature extractor during novel-class learning. However, these methods usually tend to cause the confusion between base and novel classes, i.e., classifying novel-class samples into base classes. In this paper, we delve into this phenomenon to study its cause and solution. We first interpret the confusion as the collision between the novel-class and the base-class region in the feature space. Then, we find the collision is caused by the label-irrelevant redundancies within the base-class feature and pixel space. Through qualitative and quantitative experiments, we identify this redundancy as the shortcut in the base-class training, which can be decoupled to alleviate the collision. Based on this analysis, to alleviate the collision between base and novel classes, we propose a method for FSCIL named Redundancy Decoupling and Integration (RDI). RDI first decouples redundancies from base-class space to shrink the intra-base-class feature space. Then, it integrates the redundancies as a dummy class to enlarge the inter-base-class feature space. This process effectively compresses the base-class feature space, creating buffer space for novel classes and alleviating the model's confusion between the base and novel classes. Extensive experiments across benchmark datasets, including CIFAR-100, miniImageNet, and CUB-200-2011 demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge