Konstantin Ntounas
Generalizability of experimental studies
Jun 25, 2024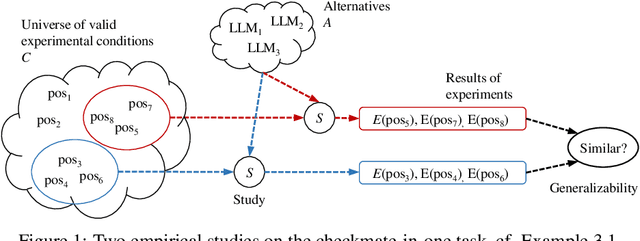
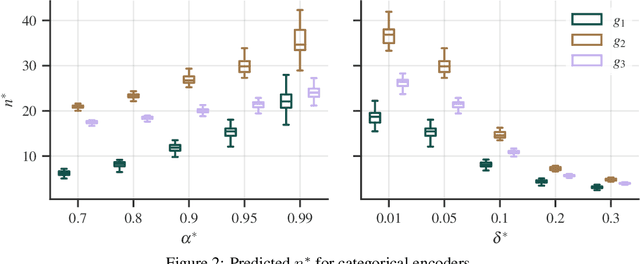
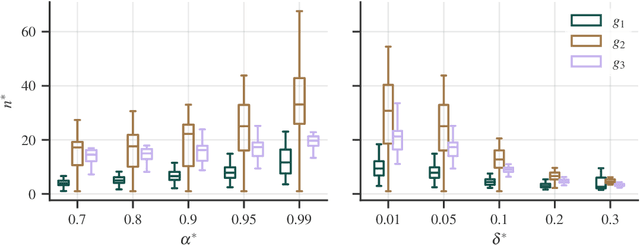
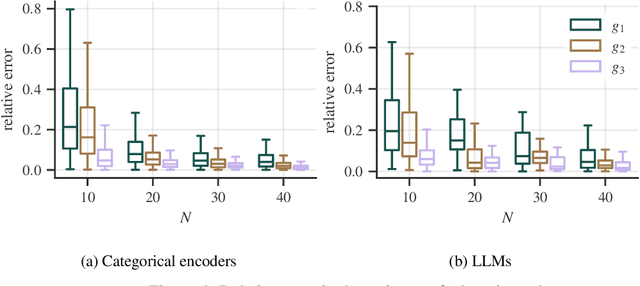
Abstract:Experimental studies are a cornerstone of machine learning (ML) research. A common, but often implicit, assumption is that the results of a study will generalize beyond the study itself, e.g. to new data. That is, there is a high probability that repeating the study under different conditions will yield similar results. Despite the importance of the concept, the problem of measuring generalizability remains open. This is probably due to the lack of a mathematical formalization of experimental studies. In this paper, we propose such a formalization and develop a quantifiable notion of generalizability. This notion allows to explore the generalizability of existing studies and to estimate the number of experiments needed to achieve the generalizability of new studies. To demonstrate its usefulness, we apply it to two recently published benchmarks to discern generalizable and non-generalizable results. We also publish a Python module that allows our analysis to be repeated for other experimental studies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge