Kirill Milintsevich
University of Caen Normandy, University of Tartu
Pantagruel: Unified Self-Supervised Encoders for French Text and Speech
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:We release Pantagruel models, a new family of self-supervised encoder models for French text and speech. Instead of predicting modality-tailored targets such as textual tokens or speech units, Pantagruel learns contextualized target representations in the feature space, allowing modality-specific encoders to capture linguistic and acoustic regularities more effectively. Separate models are pre-trained on large-scale French corpora, including Wikipedia, OSCAR and CroissantLLM for text, together with MultilingualLibriSpeech, LeBenchmark, and INA-100k for speech. INA-100k is a newly introduced 100,000-hour corpus of French audio derived from the archives of the Institut National de l'Audiovisuel (INA), the national repository of French radio and television broadcasts, providing highly diverse audio data. We evaluate Pantagruel across a broad range of downstream tasks spanning both modalities, including those from the standard French benchmarks such as FLUE or LeBenchmark. Across these tasks, Pantagruel models show competitive or superior performance compared to strong French baselines such as CamemBERT, FlauBERT, and LeBenchmark2.0, while maintaining a shared architecture that can seamlessly handle either speech or text inputs. These results confirm the effectiveness of feature-space self-supervised objectives for French representation learning and highlight Pantagruel as a robust foundation for multimodal speech-text understanding.
Evaluating Lexicon Incorporation for Depression Symptom Estimation
Apr 30, 2024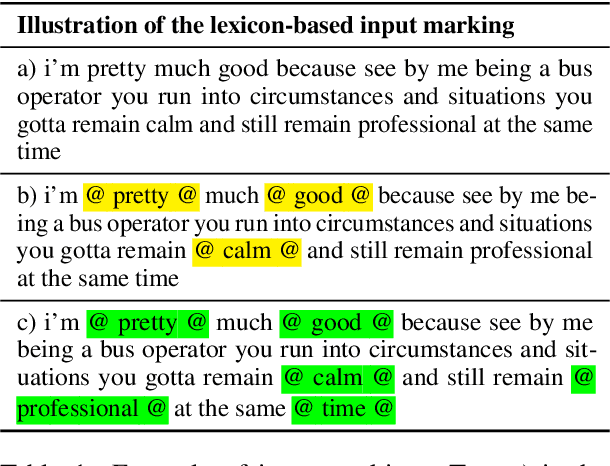
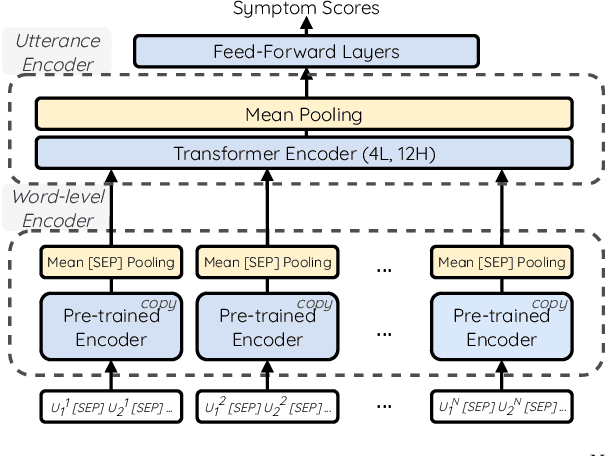
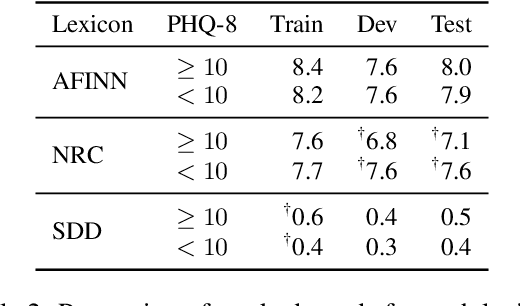
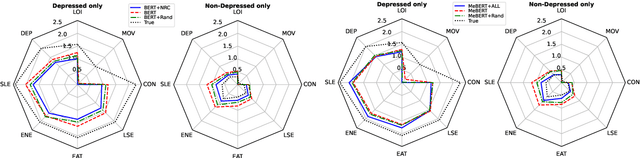
Abstract:This paper explores the impact of incorporating sentiment, emotion, and domain-specific lexicons into a transformer-based model for depression symptom estimation. Lexicon information is added by marking the words in the input transcripts of patient-therapist conversations as well as in social media posts. Overall results show that the introduction of external knowledge within pre-trained language models can be beneficial for prediction performance, while different lexicons show distinct behaviours depending on the targeted task. Additionally, new state-of-the-art results are obtained for the estimation of depression level over patient-therapist interviews.
Your Model Is Not Predicting Depression Well And That Is Why: A Case Study of PRIMATE Dataset
Mar 01, 2024



Abstract:This paper addresses the quality of annotations in mental health datasets used for NLP-based depression level estimation from social media texts. While previous research relies on social media-based datasets annotated with binary categories, i.e. depressed or non-depressed, recent datasets such as D2S and PRIMATE aim for nuanced annotations using PHQ-9 symptoms. However, most of these datasets rely on crowd workers without the domain knowledge for annotation. Focusing on the PRIMATE dataset, our study reveals concerns regarding annotation validity, particularly for the lack of interest or pleasure symptom. Through reannotation by a mental health professional, we introduce finer labels and textual spans as evidence, identifying a notable number of false positives. Our refined annotations, to be released under a Data Use Agreement, offer a higher-quality test set for anhedonia detection. This study underscores the necessity of addressing annotation quality issues in mental health datasets, advocating for improved methodologies to enhance NLP model reliability in mental health assessments.
Enhancing Sequence-to-Sequence Neural Lemmatization with External Resources
Jan 28, 2021



Abstract:We propose a novel hybrid approach to lemmatization that enhances the seq2seq neural model with additional lemmas extracted from an external lexicon or a rule-based system. During training, the enhanced lemmatizer learns both to generate lemmas via a sequential decoder and copy the lemma characters from the external candidates supplied during run-time. Our lemmatizer enhanced with candidates extracted from the Apertium morphological analyzer achieves statistically significant improvements compared to baseline models not utilizing additional lemma information, achieves an average accuracy of 97.25% on a set of 23 UD languages, which is 0.55% higher than obtained with the Stanford Stanza model on the same set of languages. We also compare with other methods of integrating external data into lemmatization and show that our enhanced system performs considerably better than a simple lexicon extension method based on the Stanza system, and it achieves complementary improvements w.r.t. the data augmentation method.
Evaluating Multilingual BERT for Estonian
Oct 01, 2020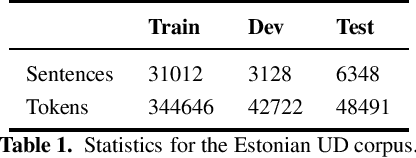
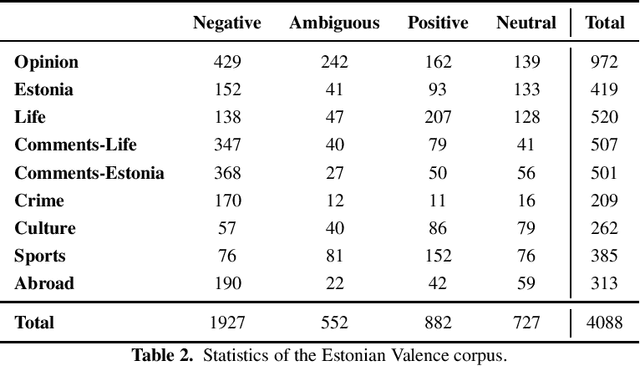
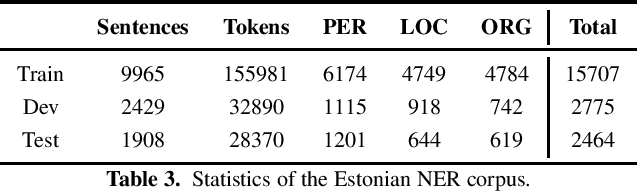
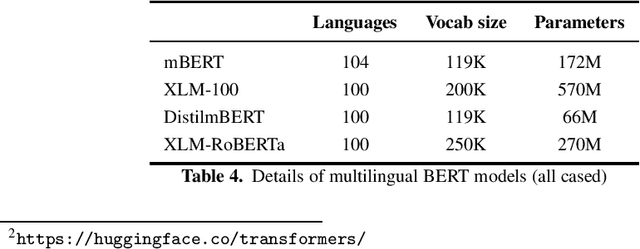
Abstract:Recently, large pre-trained language models, such as BERT, have reached state-of-the-art performance in many natural language processing tasks, but for many languages, including Estonian, BERT models are not yet available. However, there exist several multilingual BERT models that can handle multiple languages simultaneously and that have been trained also on Estonian data. In this paper, we evaluate four multilingual models---multilingual BERT, multilingual distilled BERT, XLM and XLM-RoBERTa---on several NLP tasks including POS and morphological tagging, NER and text classification. Our aim is to establish a comparison between these multilingual BERT models and the existing baseline neural models for these tasks. Our results show that multilingual BERT models can generalise well on different Estonian NLP tasks outperforming all baselines models for POS and morphological tagging and text classification, and reaching the comparable level with the best baseline for NER, with XLM-RoBERTa achieving the highest results compared with other multilingual models.
Automated Word Stress Detection in Russian
Jul 12, 2019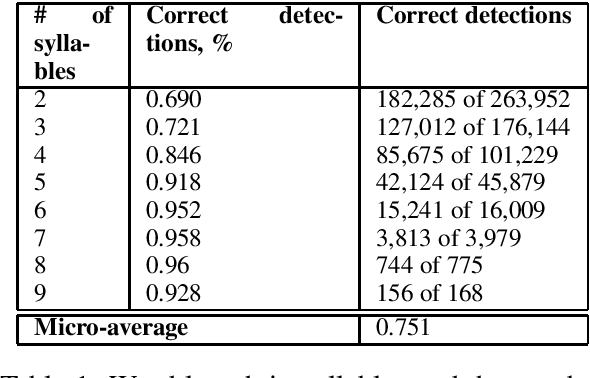
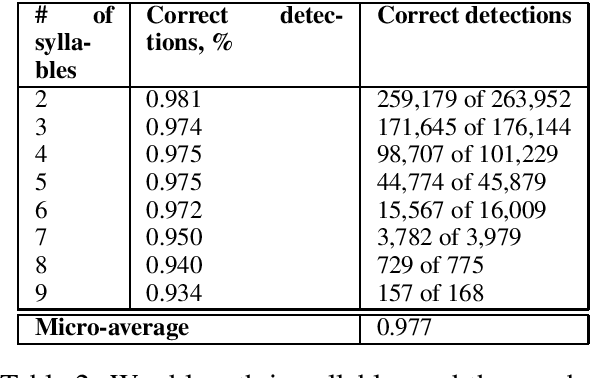
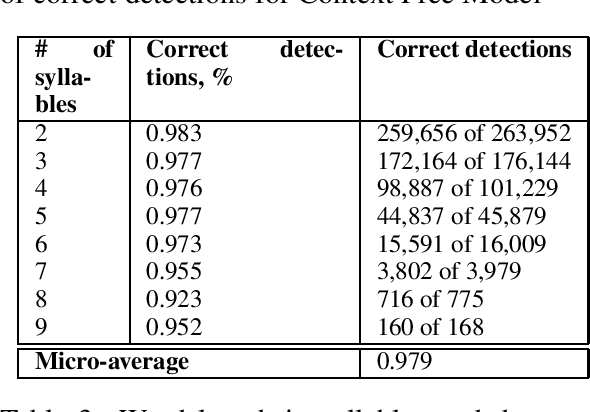
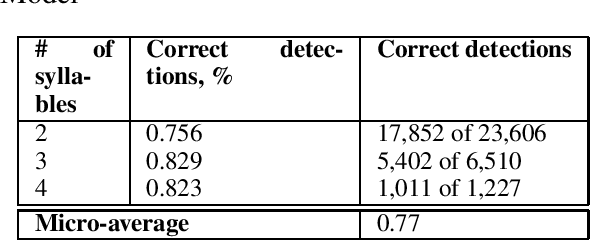
Abstract:In this study we address the problem of automated word stress detection in Russian using character level models and no part-speech-taggers. We use a simple bidirectional RNN with LSTM nodes and achieve the accuracy of 90% or higher. We experiment with two training datasets and show that using the data from an annotated corpus is much more efficient than using a dictionary, since it allows us to take into account word frequencies and the morphological context of the word.
* SCLeM 2017
Char-RNN for Word Stress Detection in East Slavic Languages
Jun 10, 2019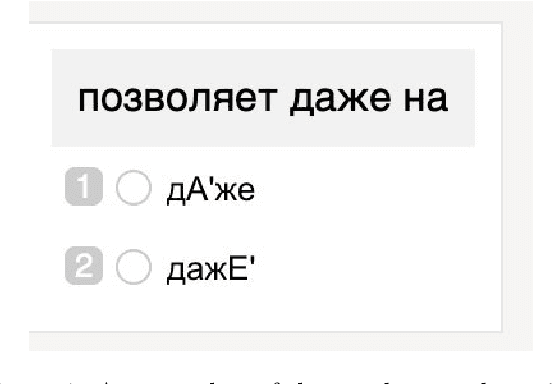
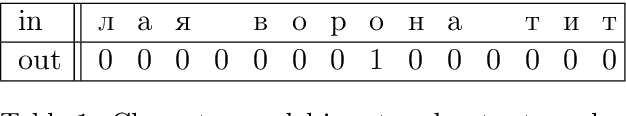
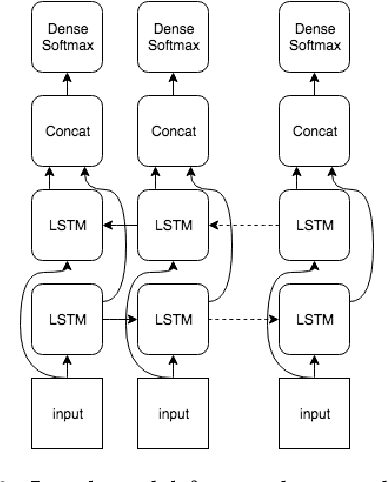
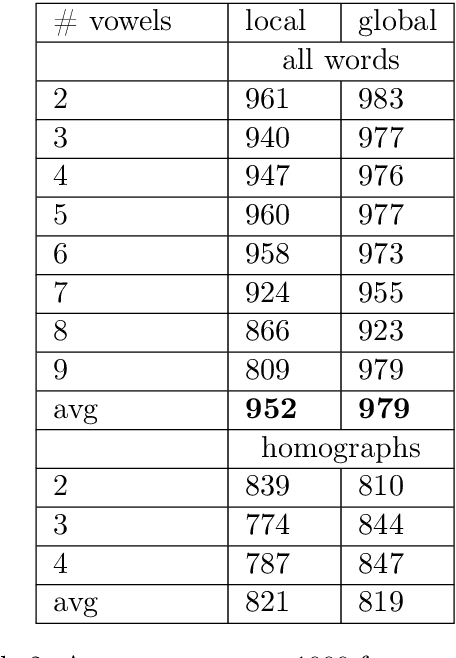
Abstract:We explore how well a sequence labeling approach, namely, recurrent neural network, is suited for the task of resource-poor and POS tagging free word stress detection in the Russian, Ukranian, Belarusian languages. We present new datasets, annotated with the word stress, for the three languages and compare several RNN models trained on three languages and explore possible applications of the transfer learning for the task. We show that it is possible to train a model in a cross-lingual setting and that using additional languages improves the quality of the results.
* Proceedings of the Sixth Workshop on NLP for Similar Languages, Varieties and Dialects at NAACL-2019
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge