Kijung Yoon
A Comparative Study of Adaptation Strategies for Time Series Foundation Models in Anomaly Detection
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Time series anomaly detection is essential for the reliable operation of complex systems, but most existing methods require extensive task-specific training. We explore whether time series foundation models (TSFMs), pretrained on large heterogeneous data, can serve as universal backbones for anomaly detection. Through systematic experiments across multiple benchmarks, we compare zero-shot inference, full model adaptation, and parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) strategies. Our results demonstrate that TSFMs outperform task-specific baselines, achieving notable gains in AUC-PR and VUS-PR, particularly under severe class imbalance. Moreover, PEFT methods such as LoRA, OFT, and HRA not only reduce computational cost but also match or surpass full fine-tuning in most cases, indicating that TSFMs can be efficiently adapted for anomaly detection, even when pretrained for forecasting. These findings position TSFMs as promising general-purpose models for scalable and efficient time series anomaly detection.
A Multimodal Approach to Alzheimer's Diagnosis: Geometric Insights from Cube Copying and Cognitive Assessments
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Early and accessible detection of Alzheimer's disease (AD) remains a critical clinical challenge, and cube-copying tasks offer a simple yet informative assessment of visuospatial function. This work proposes a multimodal framework that converts hand-drawn cube sketches into graph-structured representations capturing geometric and topological properties, and integrates these features with demographic information and neuropsychological test (NPT) scores for AD classification. Cube drawings are modeled as graphs with node features encoding spatial coordinates, local graphlet-based topology, and angular geometry, which are processed using graph neural networks and fused with age, education, and NPT features in a late-fusion model. Experimental results show that graph-based representations provide a strong unimodal baseline and substantially outperform pixel-based convolutional models, while multimodal integration further improves performance and robustness to class imbalance. SHAP-based interpretability analysis identifies specific graphlet motifs and geometric distortions as key predictors, closely aligning with clinical observations of disorganized cube drawings in AD. Together, these results establish graph-based analysis of cube copying as an interpretable, non-invasive, and scalable approach for Alzheimer's disease screening.
Osteoporosis Prediction from Hand X-ray Images Using Segmentation-for-Classification and Self-Supervised Learning
Dec 06, 2024Abstract:Osteoporosis is a widespread and chronic metabolic bone disease that often remains undiagnosed and untreated due to limited access to bone mineral density (BMD) tests like Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). In response to this challenge, current advancements are pivoting towards detecting osteoporosis by examining alternative indicators from peripheral bone areas, with the goal of increasing screening rates without added expenses or time. In this paper, we present a method to predict osteoporosis using hand and wrist X-ray images, which are both widely accessible and affordable, though their link to DXA-based data is not thoroughly explored. We employ a sophisticated image segmentation model that utilizes a mixture of probabilistic U-Net decoders, specifically designed to capture predictive uncertainty in the segmentation of the ulna, radius, and metacarpal bones. This model is formulated as an optimal transport (OT) problem, enabling it to handle the inherent uncertainties in image segmentation more effectively. Further, we adopt a self-supervised learning (SSL) approach to extract meaningful representations without the need for explicit labels, and move on to classify osteoporosis in a supervised manner. Our method is evaluated on a dataset with 192 individuals, cross-referencing their verified osteoporosis conditions against the standard DXA test. With a notable classification score, this integration of uncertainty-aware segmentation and self-supervised learning represents a pioneering effort in leveraging vision-based techniques for the early detection of osteoporosis from peripheral skeletal sites.
Hierarchical Joint Graph Learning and Multivariate Time Series Forecasting
Nov 30, 2023Abstract:Multivariate time series is prevalent in many scientific and industrial domains. Modeling multivariate signals is challenging due to their long-range temporal dependencies and intricate interactions--both direct and indirect. To confront these complexities, we introduce a method of representing multivariate signals as nodes in a graph with edges indicating interdependency between them. Specifically, we leverage graph neural networks (GNN) and attention mechanisms to efficiently learn the underlying relationships within the time series data. Moreover, we suggest employing hierarchical signal decompositions running over the graphs to capture multiple spatial dependencies. The effectiveness of our proposed model is evaluated across various real-world benchmark datasets designed for long-term forecasting tasks. The results consistently showcase the superiority of our model, achieving an average 23\% reduction in mean squared error (MSE) compared to existing models.
Osteoporosis Prediction from Hand and Wrist X-rays using Image Segmentation and Self-Supervised Learning
Nov 12, 2023Abstract:Osteoporosis is a widespread and chronic metabolic bone disease that often remains undiagnosed and untreated due to limited access to bone mineral density (BMD) tests like Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). In response to this challenge, current advancements are pivoting towards detecting osteoporosis by examining alternative indicators from peripheral bone areas, with the goal of increasing screening rates without added expenses or time. In this paper, we present a method to predict osteoporosis using hand and wrist X-ray images, which are both widely accessible and affordable, though their link to DXA-based data is not thoroughly explored. Initially, our method segments the ulnar, radius, and metacarpal bones using a foundational model for image segmentation. Then, we use a self-supervised learning approach to extract meaningful representations without the need for explicit labels, and move on to classify osteoporosis in a supervised manner. Our method is evaluated on a dataset with 192 individuals, cross-referencing their verified osteoporosis conditions against the standard DXA test. With a notable classification score (AUC=0.83), our model represents a pioneering effort in leveraging vision-based techniques for osteoporosis identification from the peripheral skeleton sites.
Towards Better Generalization with Flexible Representation of Multi-Module Graph Neural Networks
Sep 14, 2022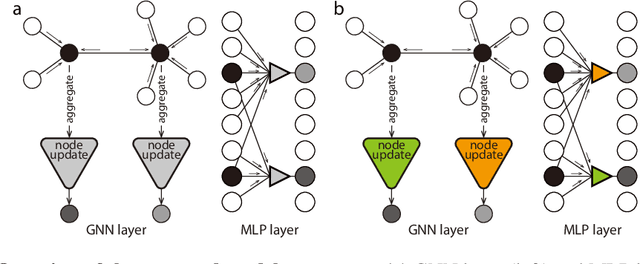
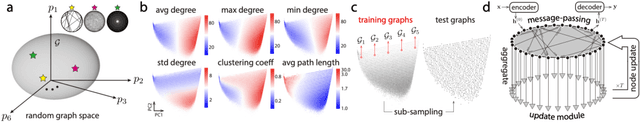
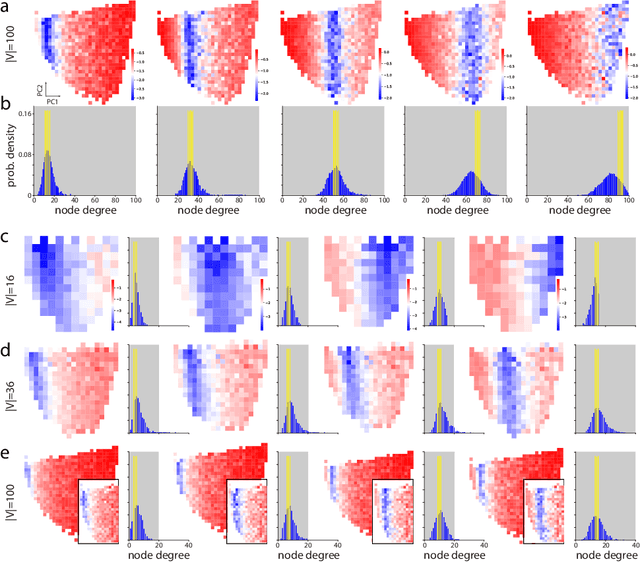
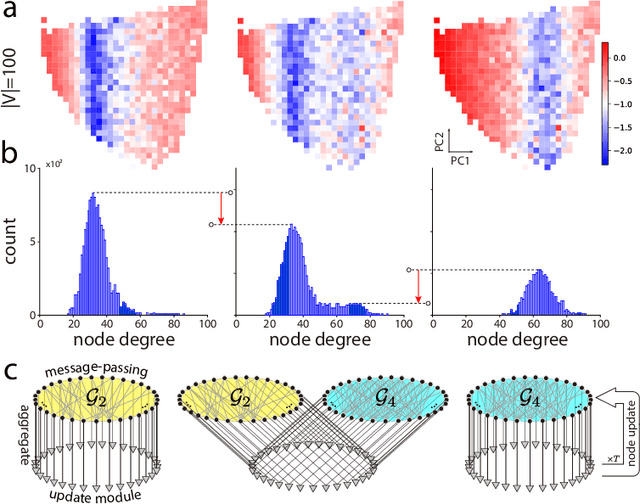
Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) have become compelling models designed to perform learning and inference on graph-structured data, but little work has been done on understanding the fundamental limitations of GNNs to be scalable to larger graphs and generalized to out-of-distribution inputs. In this paper, we use a random graph generator that allows us to systematically investigate how the graph size and structural properties affect the predictive performance of GNNs. We present specific evidence that, among the many graph properties, the mean and modality of the node degree distribution are the key features that determine whether GNNs can generalize to unseen graphs. Accordingly, we propose flexible GNNs (Flex-GNNs), using multiple node update functions and the inner loop optimization as a generalization to the single type of canonical nonlinear transformation over aggregated inputs, allowing the network to adapt flexibly to new graphs. The Flex-GNN framework improves the generalization out of the training set on several inference tasks.
Two-argument activation functions learn soft XOR operations like cortical neurons
Oct 15, 2021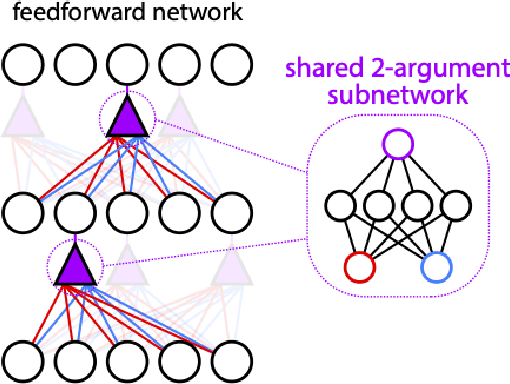
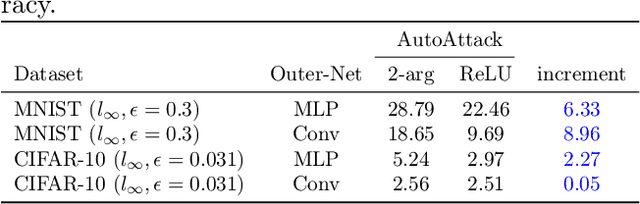
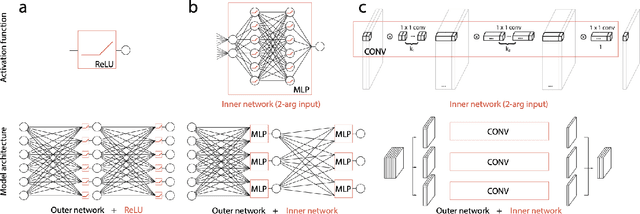
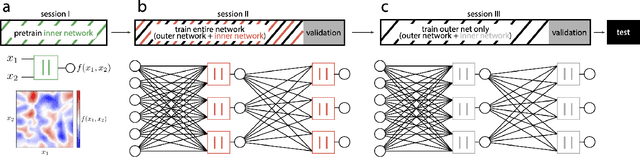
Abstract:Neurons in the brain are complex machines with distinct functional compartments that interact nonlinearly. In contrast, neurons in artificial neural networks abstract away this complexity, typically down to a scalar activation function of a weighted sum of inputs. Here we emulate more biologically realistic neurons by learning canonical activation functions with two input arguments, analogous to basal and apical dendrites. We use a network-in-network architecture where each neuron is modeled as a multilayer perceptron with two inputs and a single output. This inner perceptron is shared by all units in the outer network. Remarkably, the resultant nonlinearities often produce soft XOR functions, consistent with recent experimental observations about interactions between inputs in human cortical neurons. When hyperparameters are optimized, networks with these nonlinearities learn faster and perform better than conventional ReLU nonlinearities with matched parameter counts, and they are more robust to natural and adversarial perturbations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge