Khalid M. Mosalam
Prediction of the Most Fire-Sensitive Point in Building Structures with Differentiable Agents for Thermal Simulators
Feb 05, 2025



Abstract:Fire safety is a critical area of research in civil and mechanical engineering, particularly in ensuring the structural stability of buildings during fire events. The Most Fire-Sensitive Point (MFSP) in a structure is the location where a fire would cause the greatest impact on structural stability. Accurate prediction of the MFSP is vital for streamlining structural assessments and optimizing the design process. This paper presents a novel framework for MFSP prediction using a neural network-based approach that integrates fire dynamics and finite element analysis through a differentiable agent model. The framework focuses on predicting the Maximum Interstory Drift Ratio (MIDR), a key indicator of structural performance under fire conditions. By leveraging the differentiable agent model, we efficiently generate labeled data for MFSP and directly train a predictor for this critical metric. To achieve this, we generated extensive simulation data encompassing structural and fire scenarios and employed graph neural networks to represent the building structures. Transfer learning was applied to optimize the training process, and an edge update mechanism was introduced to dynamically adjust edge attributes, reflecting property changes under fire conditions. The proposed model was rigorously evaluated on simulation data, demonstrating strong performance in accurately predicting both MIDR and MFSP, thus advancing fire safety analysis for building structures.
Balanced Semi-Supervised Generative Adversarial Network for Damage Assessment from Low-Data Imbalanced-Class Regime
Nov 29, 2022Abstract:In recent years, applying deep learning (DL) to assess structural damages has gained growing popularity in vision-based structural health monitoring (SHM). However, both data deficiency and class-imbalance hinder the wide adoption of DL in practical applications of SHM. Common mitigation strategies include transfer learning, over-sampling, and under-sampling, yet these ad-hoc methods only provide limited performance boost that varies from one case to another. In this work, we introduce one variant of the Generative Adversarial Network (GAN), named the balanced semi-supervised GAN (BSS-GAN). It adopts the semi-supervised learning concept and applies balanced-batch sampling in training to resolve low-data and imbalanced-class problems. A series of computer experiments on concrete cracking and spalling classification were conducted under the low-data imbalanced-class regime with limited computing power. The results show that the BSS-GAN is able to achieve better damage detection in terms of recall and $F_\beta$ score than other conventional methods, indicating its state-of-the-art performance.
Text Analytics for Resilience-Enabled Extreme EventsReconnaissance
Nov 26, 2020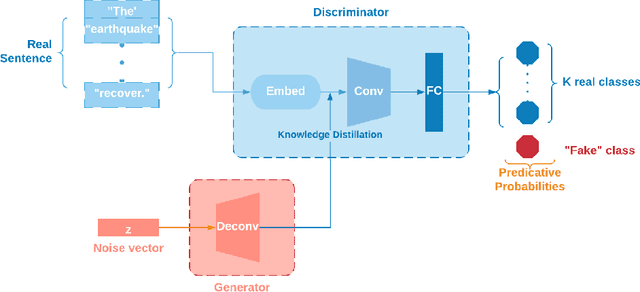
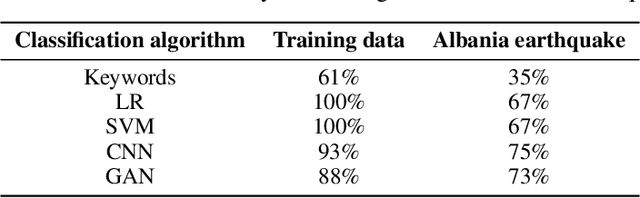
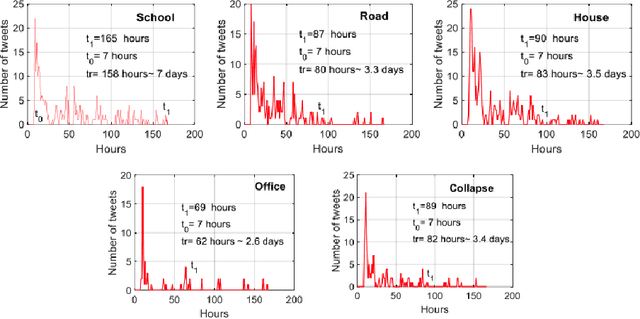

Abstract:Post-hazard reconnaissance for natural disasters (e.g., earthquakes) is important for understanding the performance of the built environment, speeding up the recovery, enhancing resilience and making informed decisions related to current and future hazards. Natural language processing (NLP) is used in this study for the purposes of increasing the accuracy and efficiency of natural hazard reconnaissance through automation. The study particularly focuses on (1) automated data (news and social media) collection hosted by the Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research (PEER) Center server, (2) automatic generation of reconnaissance reports, and (3) use of social media to extract post-hazard information such as the recovery time. Obtained results are encouraging for further development and wider usage of various NLP methods in natural hazard reconnaissance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge