Kexuan Wang
Context-aware Constrained Reinforcement Learning Based Energy-Efficient Power Scheduling for Non-stationary XR Data Traffic
Mar 12, 2025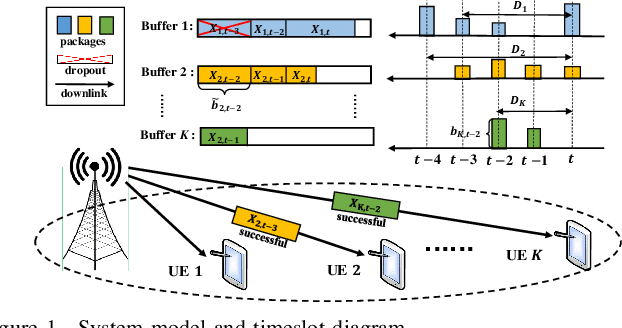
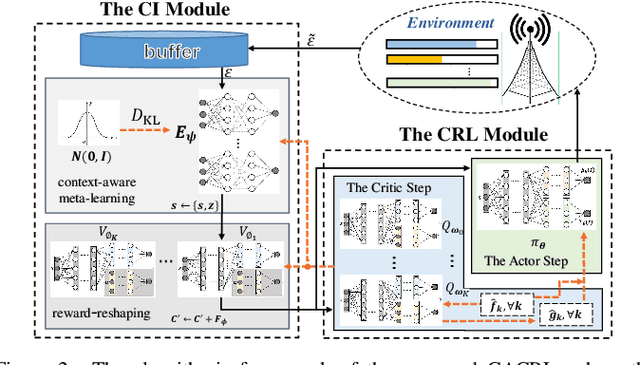
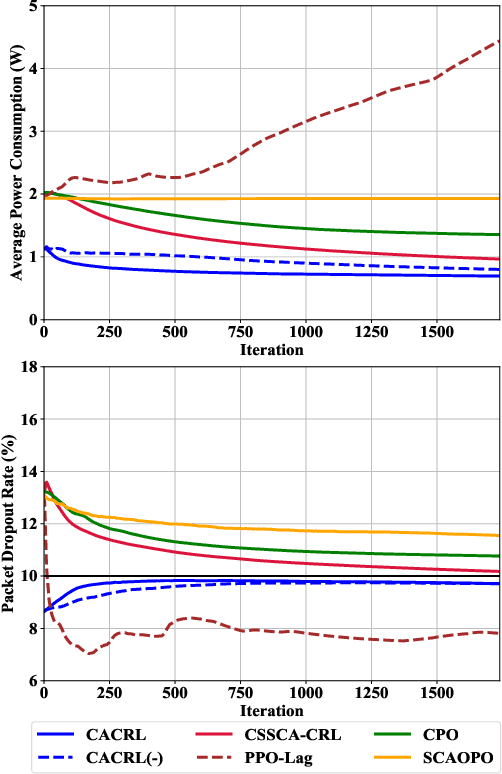
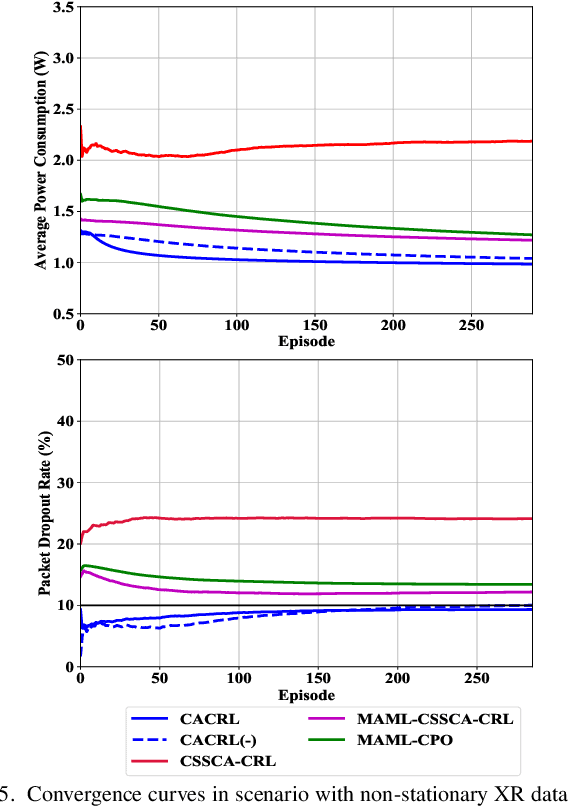
Abstract:In XR downlink transmission, energy-efficient power scheduling (EEPS) is essential for conserving power resource while delivering large data packets within hard-latency constraints. Traditional constrained reinforcement learning (CRL) algorithms show promise in EEPS but still struggle with non-convex stochastic constraints, non-stationary data traffic, and sparse delayed packet dropout feedback (rewards) in XR. To overcome these challenges, this paper models the EEPS in XR as a dynamic parameter-constrained Markov decision process (DP-CMDP) with a varying transition function linked to the non-stationary data traffic and solves it by a proposed context-aware constrained reinforcement learning (CACRL) algorithm, which consists of a context inference (CI) module and a CRL module. The CI module trains an encoder and multiple potential networks to characterize the current transition function and reshape the packet dropout rewards according to the context, transforming the original DP-CMDP into a general CMDP with immediate dense rewards. The CRL module employs a policy network to make EEPS decisions under this CMDP and optimizes the policy using a constrained stochastic successive convex approximation (CSSCA) method, which is better suited for non-convex stochastic constraints. Finally, theoretical analyses provide deep insights into the CADAC algorithm, while extensive simulations demonstrate that it outperforms advanced baselines in both power conservation and satisfying packet dropout constraints.
A Single-Loop Deep Actor-Critic Algorithm for Constrained Reinforcement Learning with Provable Convergence
Jun 10, 2023Abstract:Abstract -- Deep Actor-Critic algorithms, which combine Actor-Critic with deep neural network (DNN), have been among the most prevalent reinforcement learning algorithms for decision-making problems in simulated environments. However, the existing deep Actor-Critic algorithms are still not mature to solve realistic problems with non-convex stochastic constraints and high cost to interact with the environment. In this paper, we propose a single-loop deep Actor-Critic (SLDAC) algorithmic framework for general constrained reinforcement learning (CRL) problems. In the actor step, the constrained stochastic successive convex approximation (CSSCA) method is applied to handle the non-convex stochastic objective and constraints. In the critic step, the critic DNNs are only updated once or a few finite times for each iteration, which simplifies the algorithm to a single-loop framework (the existing works require a sufficient number of updates for the critic step to ensure a good enough convergence of the inner loop for each iteration). Moreover, the variance of the policy gradient estimation is reduced by reusing observations from the old policy. The single-loop design and the observation reuse effectively reduce the agent-environment interaction cost and computational complexity. In spite of the biased policy gradient estimation incurred by the single-loop design and observation reuse, we prove that the SLDAC with a feasible initial point can converge to a Karush-Kuhn-Tuker (KKT) point of the original problem almost surely. Simulations show that the SLDAC algorithm can achieve superior performance with much lower interaction cost.
Lightweight Facial Attractiveness Prediction Using Dual Label Distribution
Dec 04, 2022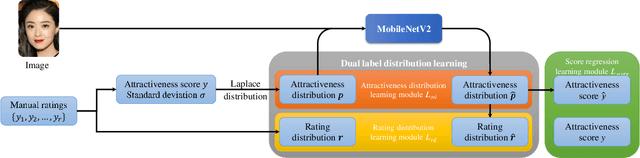
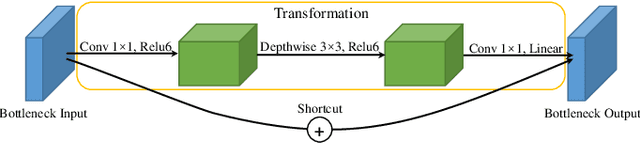
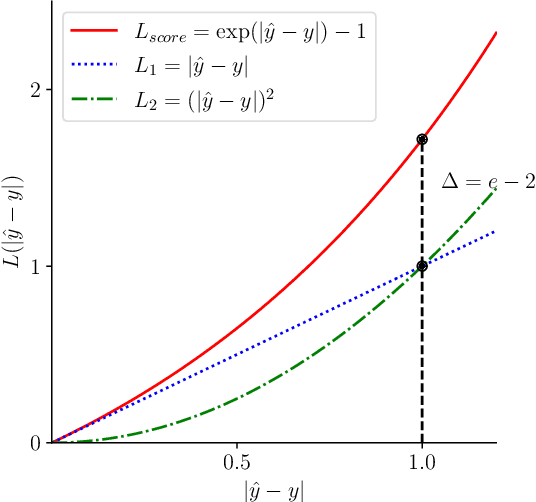
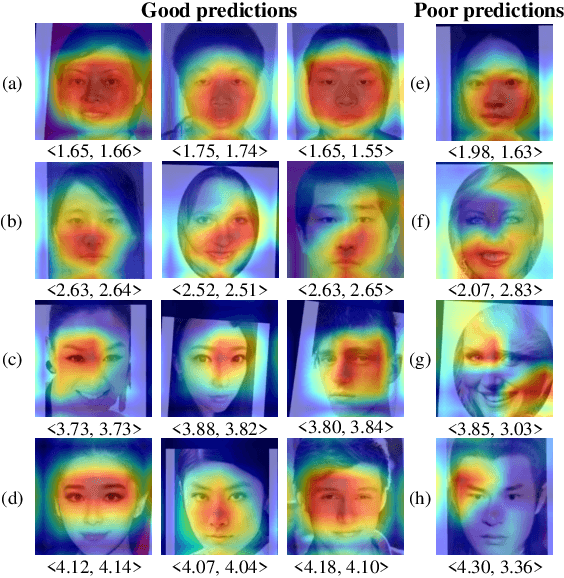
Abstract:Facial attractiveness prediction (FAP) aims to assess the facial attractiveness automatically based on human aesthetic perception. Previous methods using deep convolutional neural networks have boosted the performance, but their giant models lead to a deficiency in flexibility. Besides, most of them fail to take full advantage of the dataset. In this paper, we present a novel end-to-end FAP approach integrating dual label distribution and lightweight design. To make the best use of the dataset, the manual ratings, attractiveness score, and standard deviation are aggregated explicitly to construct a dual label distribution, including the attractiveness distribution and the rating distribution. Such distributions, as well as the attractiveness score, are optimized under a joint learning framework based on the label distribution learning (LDL) paradigm. As for the lightweight design, the data processing is simplified to minimum, and MobileNetV2 is selected as our backbone. Extensive experiments are conducted on two benchmark datasets, where our approach achieves promising results and succeeds in striking a balance between performance and efficiency. Ablation studies demonstrate that our delicately designed learning modules are indispensable and correlated. Additionally, the visualization indicates that our approach is capable of perceiving facial attractiveness and capturing attractive facial regions to facilitate semantic predictions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge