Karthik Krishnamurthy
One Agent Too Many: User Perspectives on Approaches to Multi-agent Conversational AI
Jan 13, 2024Abstract:Conversational agents have been gaining increasing popularity in recent years. Influenced by the widespread adoption of task-oriented agents such as Apple Siri and Amazon Alexa, these agents are being deployed into various applications to enhance user experience. Although these agents promote "ask me anything" functionality, they are typically built to focus on a single or finite set of expertise. Given that complex tasks often require more than one expertise, this results in the users needing to learn and adopt multiple agents. One approach to alleviate this is to abstract the orchestration of agents in the background. However, this removes the option of choice and flexibility, potentially harming the ability to complete tasks. In this paper, we explore these different interaction experiences (one agent for all) vs (user choice of agents) for conversational AI. We design prototypes for each, systematically evaluating their ability to facilitate task completion. Through a series of conducted user studies, we show that users have a significant preference for abstracting agent orchestration in both system usability and system performance. Additionally, we demonstrate that this mode of interaction is able to provide quality responses that are rated within 1% of human-selected answers.
One Agent To Rule Them All: Towards Multi-agent Conversational AI
Mar 15, 2022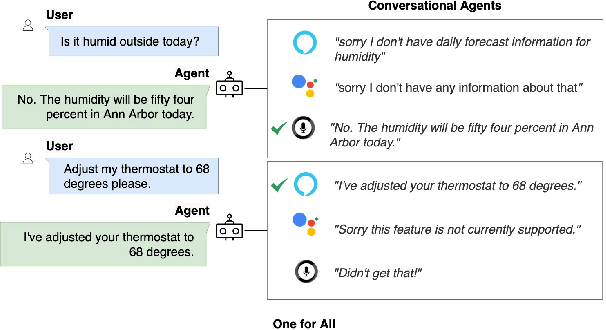
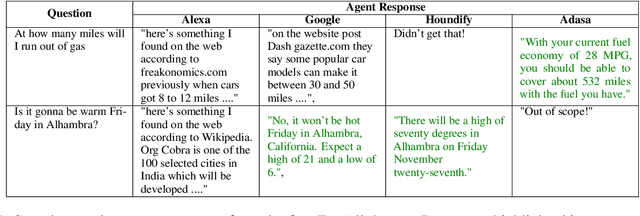
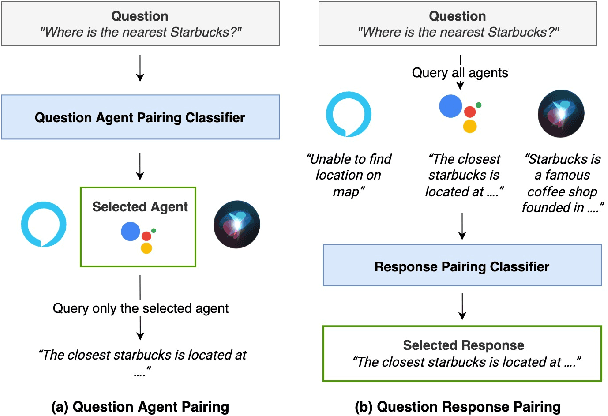
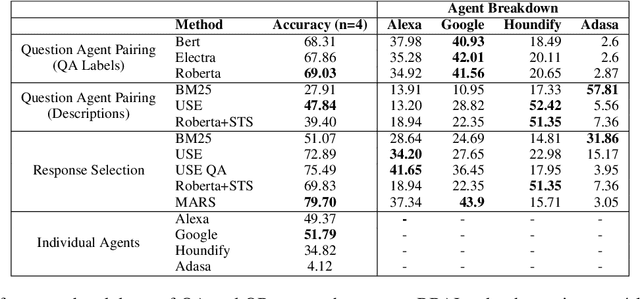
Abstract:The increasing volume of commercially available conversational agents (CAs) on the market has resulted in users being burdened with learning and adopting multiple agents to accomplish their tasks. Though prior work has explored supporting a multitude of domains within the design of a single agent, the interaction experience suffers due to the large action space of desired capabilities. To address these problems, we introduce a new task BBAI: Black-Box Agent Integration, focusing on combining the capabilities of multiple black-box CAs at scale. We explore two techniques: question agent pairing and question response pairing aimed at resolving this task. Leveraging these techniques, we design One For All (OFA), a scalable system that provides a unified interface to interact with multiple CAs. Additionally, we introduce MARS: Multi-Agent Response Selection, a new encoder model for question response pairing that jointly encodes user question and agent response pairs. We demonstrate that OFA is able to automatically and accurately integrate an ensemble of commercially available CAs spanning disparate domains. Specifically, using the MARS encoder we achieve the highest accuracy on our BBAI task, outperforming strong baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge