Karli Gillette
Explainable Deep Learning-based Classification of Wolff-Parkinson-White Electrocardiographic Signals
Nov 08, 2025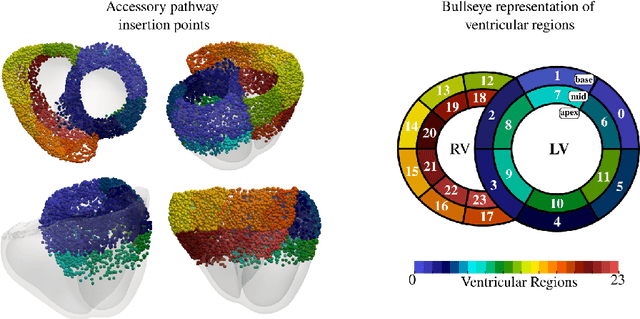
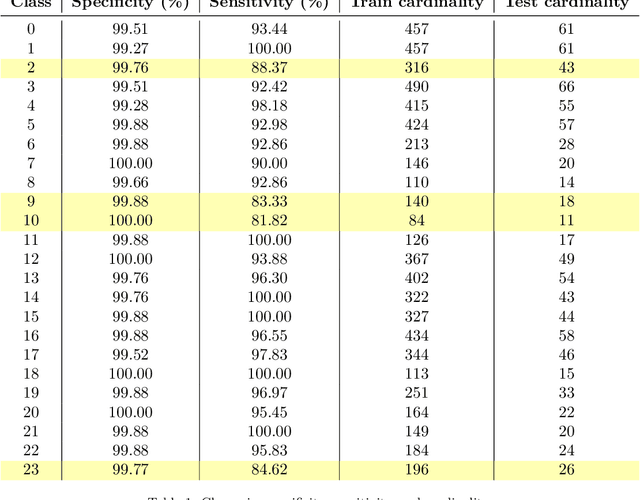
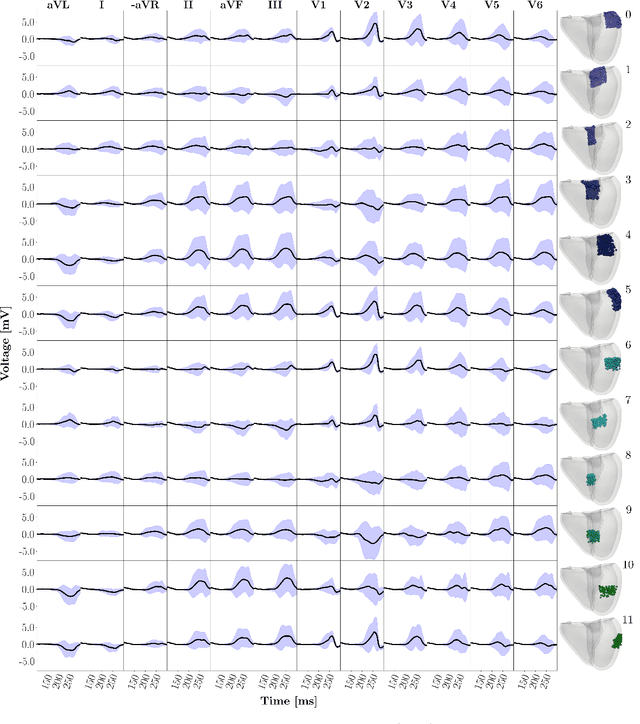
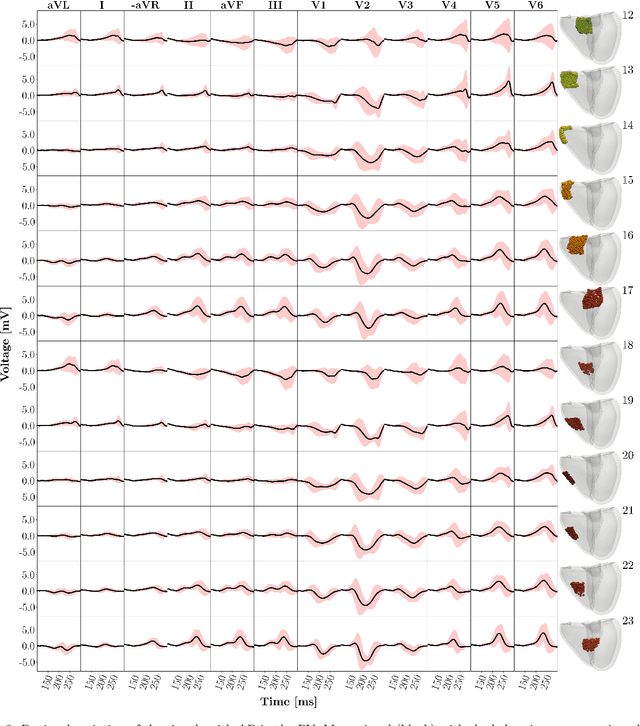
Abstract:Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome is a cardiac electrophysiology (EP) disorder caused by the presence of an accessory pathway (AP) that bypasses the atrioventricular node, faster ventricular activation rate, and provides a substrate for atrio-ventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT). Accurate localization of the AP is critical for planning and guiding catheter ablation procedures. While traditional diagnostic tree (DT) methods and more recent machine learning (ML) approaches have been proposed to predict AP location from surface electrocardiogram (ECG), they are often constrained by limited anatomical localization resolution, poor interpretability, and the use of small clinical datasets. In this study, we present a Deep Learning (DL) model for the localization of single manifest APs across 24 cardiac regions, trained on a large, physiologically realistic database of synthetic ECGs generated using a personalized virtual heart model. We also integrate eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) methods, Guided Backpropagation, Grad-CAM, and Guided Grad-CAM, into the pipeline. This enables interpretation of DL decision-making and addresses one of the main barriers to clinical adoption: lack of transparency in ML predictions. Our model achieves localization accuracy above 95%, with a sensitivity of 94.32% and specificity of 99.78%. XAI outputs are physiologically validated against known depolarization patterns, and a novel index is introduced to identify the most informative ECG leads for AP localization. Results highlight lead V2 as the most critical, followed by aVF, V1, and aVL. This work demonstrates the potential of combining cardiac digital twins with explainable DL to enable accurate, transparent, and non-invasive AP localization.
MedalCare-XL: 16,900 healthy and pathological 12 lead ECGs obtained through electrophysiological simulations
Nov 29, 2022Abstract:Mechanistic cardiac electrophysiology models allow for personalized simulations of the electrical activity in the heart and the ensuing electrocardiogram (ECG) on the body surface. As such, synthetic signals possess known ground truth labels of the underlying disease and can be employed for validation of machine learning ECG analysis tools in addition to clinical signals. Recently, synthetic ECGs were used to enrich sparse clinical data or even replace them completely during training leading to improved performance on real-world clinical test data. We thus generated a novel synthetic database comprising a total of 16,900 12 lead ECGs based on electrophysiological simulations equally distributed into healthy control and 7 pathology classes. The pathological case of myocardial infraction had 6 sub-classes. A comparison of extracted features between the virtual cohort and a publicly available clinical ECG database demonstrated that the synthetic signals represent clinical ECGs for healthy and pathological subpopulations with high fidelity. The ECG database is split into training, validation, and test folds for development and objective assessment of novel machine learning algorithms.
Comparison of propagation models and forward calculation methods on cellular, tissue and organ scale atrial electrophysiology
Mar 15, 2022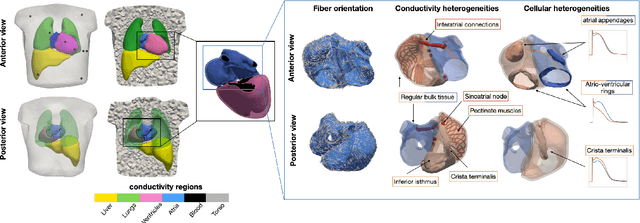
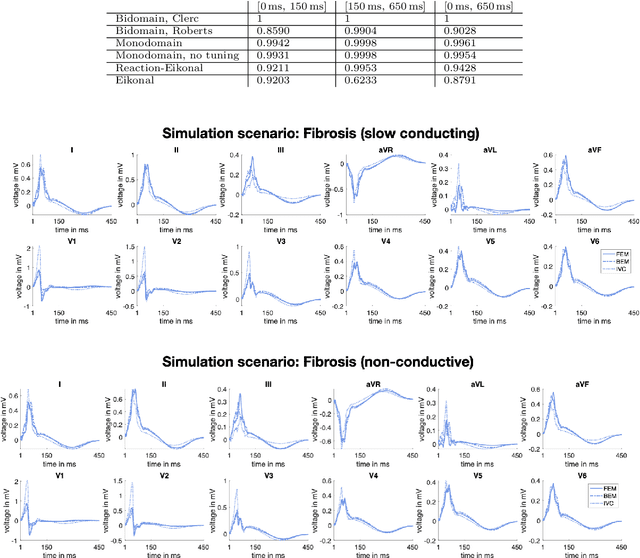
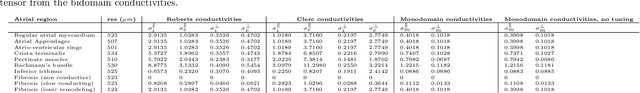
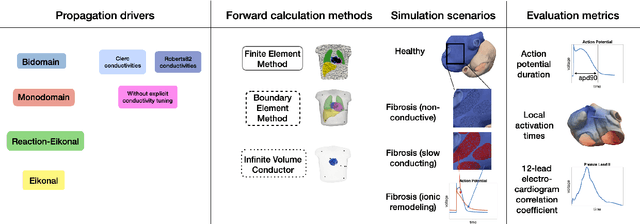
Abstract:Objective: The bidomain model and the finite element method are an established standard to mathematically describe cardiac electrophysiology, but are both suboptimal choices for fast and large-scale simulations due to high computational costs. We investigate to what extent simplified approaches for propagation models (monodomain, reaction-eikonal and eikonal) and forward calculation (boundary element and infinite volume conductor) deliver markedly accelerated, yet physiologically accurate simulation results in atrial electrophysiology. Methods: We compared action potential durations, local activation times (LATs), and electrocardiograms (ECGs) for sinus rhythm simulations on healthy and fibrotically infiltrated atrial models. Results: All simplified model solutions yielded LATs and P waves in accurate accordance with the bidomain results. Only for the eikonal model with pre-computed action potential templates shifted in time to derive transmembrane voltages, repolarization behavior notably deviated from the bidomain results. ECGs calculated with the boundary element method were characterized by correlation coefficients >0.9 compared to the finite element method. The infinite volume conductor method led to lower correlation coefficients caused predominantly by systematic overestimations of P wave amplitudes in the precordial leads. Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that the eikonal model yields accurate LATs and combined with the boundary element method precise ECGs compared to markedly more expensive full bidomain simulations. However, for an accurate representation of atrial repolarization dynamics, diffusion terms must be accounted for in simplified models. Significance: Simulations of atrial LATs and ECGs can be notably accelerated to clinically feasible time frames at high accuracy by resorting to the eikonal and boundary element methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge