Kangcheng Hou
Graph Neural Tangent Kernel: Fusing Graph Neural Networks with Graph Kernels
May 30, 2019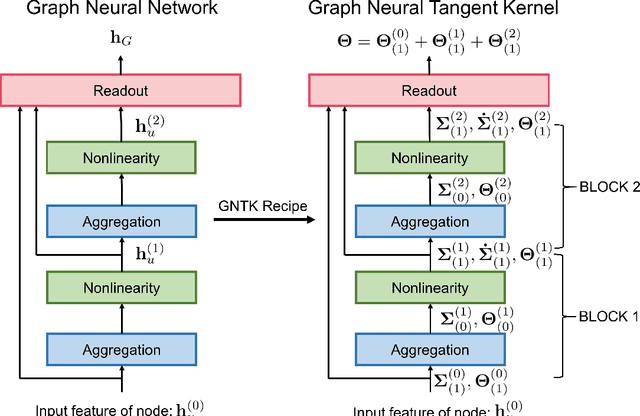
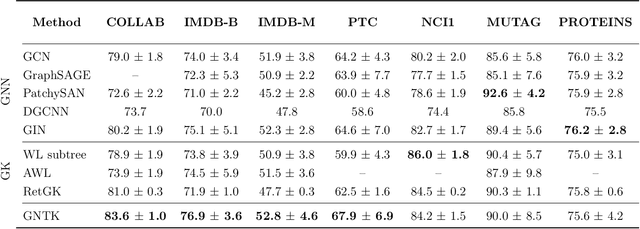
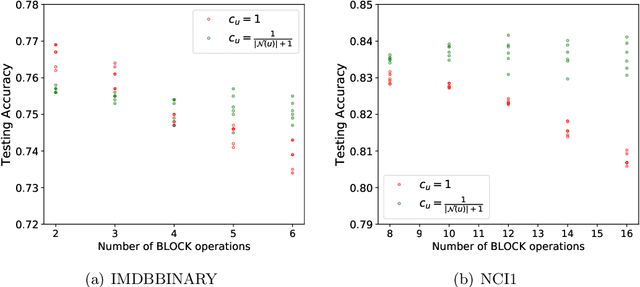
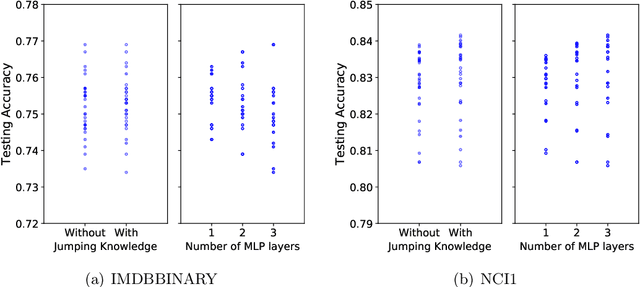
Abstract:While graph kernels (GKs) are easy to train and enjoy provable theoretical guarantees, their practical performances are limited by their expressive power, as the kernel function often depends on hand-crafted combinatorial features of graphs. Compared to graph kernels, graph neural networks (GNNs) usually achieve better practical performance, as GNNs use multi-layer architectures and non-linear activation functions to extract high-order information of graphs as features. However, due to the large number of hyper-parameters and the non-convex nature of the training procedure, GNNs are harder to train. Theoretical guarantees of GNNs are also not well-understood. Furthermore, the expressive power of GNNs scales with the number of parameters, and thus it is hard to exploit the full power of GNNs when computing resources are limited. The current paper presents a new class of graph kernels, Graph Neural Tangent Kernels (GNTKs), which correspond to \emph{infinitely wide} multi-layer GNNs trained by gradient descent. GNTKs enjoy the full expressive power of GNNs and inherit advantages of GKs. Theoretically, we show GNTKs provably learn a class of smooth functions on graphs. Empirically, we test GNTKs on graph classification datasets and show they achieve strong performance.
CaricatureShop: Personalized and Photorealistic Caricature Sketching
Jul 24, 2018



Abstract:In this paper, we propose the first sketching system for interactively personalized and photorealistic face caricaturing. Input an image of a human face, the users can create caricature photos by manipulating its facial feature curves. Our system firstly performs exaggeration on the recovered 3D face model according to the edited sketches, which is conducted by assigning the laplacian of each vertex a scaling factor. To construct the mapping between 2D sketches and a vertex-wise scaling field, a novel deep learning architecture is developed. With the obtained 3D caricature model, two images are generated, one obtained by applying 2D warping guided by the underlying 3D mesh deformation and the other obtained by re-rendering the deformed 3D textured model. These two images are then seamlessly integrated to produce our final output. Due to the severely stretching of meshes, the rendered texture is of blurry appearances. A deep learning approach is exploited to infer the missing details for enhancing these blurry regions. Moreover, a relighting operation is invented to further improve the photorealism of the result. Both quantitative and qualitative experiment results validated the efficiency of our sketching system and the superiority of our proposed techniques against existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge