Kaiyao Miao
Noisy Correspondence Learning with Meta Similarity Correction
Apr 13, 2023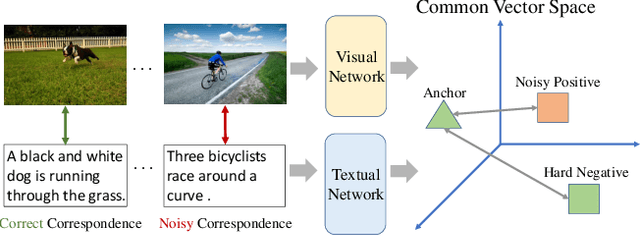
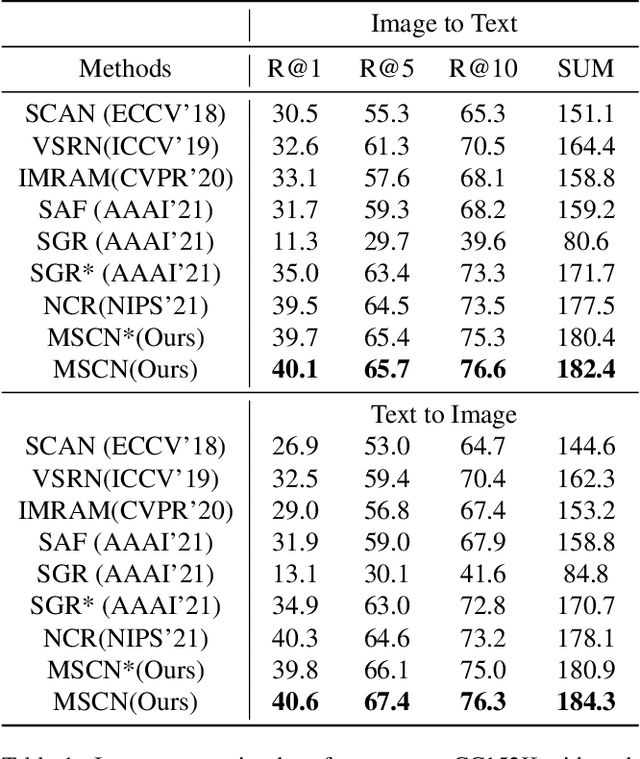
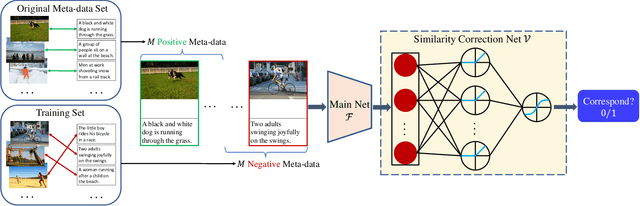
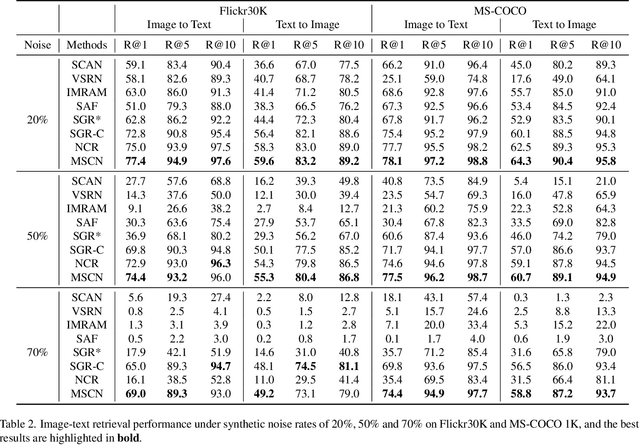
Abstract:Despite the success of multimodal learning in cross-modal retrieval task, the remarkable progress relies on the correct correspondence among multimedia data. However, collecting such ideal data is expensive and time-consuming. In practice, most widely used datasets are harvested from the Internet and inevitably contain mismatched pairs. Training on such noisy correspondence datasets causes performance degradation because the cross-modal retrieval methods can wrongly enforce the mismatched data to be similar. To tackle this problem, we propose a Meta Similarity Correction Network (MSCN) to provide reliable similarity scores. We view a binary classification task as the meta-process that encourages the MSCN to learn discrimination from positive and negative meta-data. To further alleviate the influence of noise, we design an effective data purification strategy using meta-data as prior knowledge to remove the noisy samples. Extensive experiments are conducted to demonstrate the strengths of our method in both synthetic and real-world noises, including Flickr30K, MS-COCO, and Conceptual Captions.
Noise-Tolerant Learning for Audio-Visual Action Recognition
May 20, 2022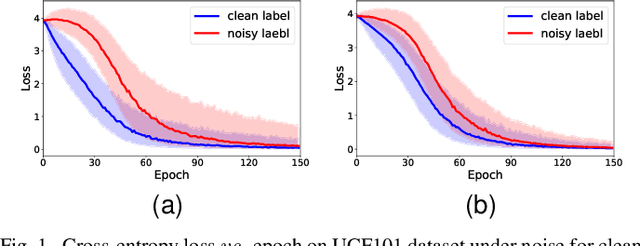
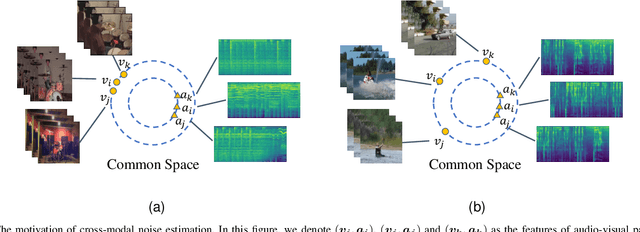
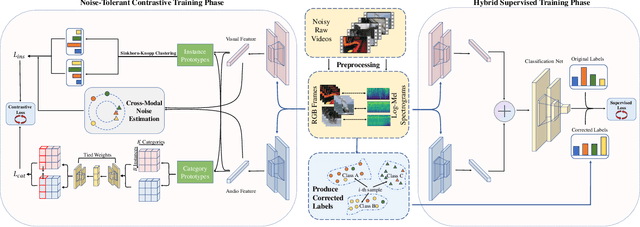
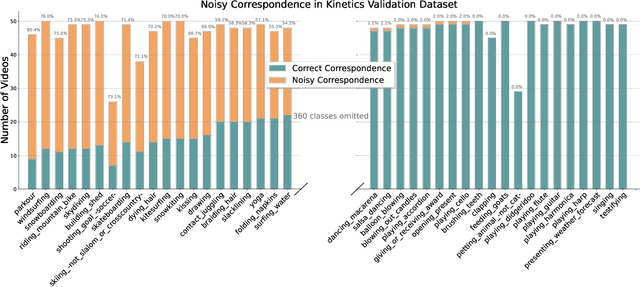
Abstract:Recently, video recognition is emerging with the help of multi-modal learning, which focuses on integrating multiple modalities to improve the performance or robustness of a model. Although various multi-modal learning methods have been proposed and offer remarkable recognition results, almost all of these methods rely on high-quality manual annotations and assume that modalities among multi-modal data provide relevant semantic information. Unfortunately, most widely used video datasets are collected from the Internet and inevitably contain noisy labels and noisy correspondence. To solve this problem, we use the audio-visual action recognition task as a proxy and propose a noise-tolerant learning framework to find anti-interference model parameters to both noisy labels and noisy correspondence. Our method consists of two phases and aims to rectify noise by the inherent correlation between modalities. A noise-tolerant contrastive training phase is performed first to learn robust model parameters unaffected by the noisy labels. To reduce the influence of noisy correspondence, we propose a cross-modal noise estimation component to adjust the consistency between different modalities. Since the noisy correspondence existed at the instance level, a category-level contrastive loss is proposed to further alleviate the interference of noisy correspondence. Then in the hybrid supervised training phase, we calculate the distance metric among features to obtain corrected labels, which are used as complementary supervision. In addition, we investigate the noisy correspondence in real-world datasets and conduct comprehensive experiments with synthetic and real noise data. The results verify the advantageous performance of our method compared to state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge