Kailin Koch
Few-Shot Detection of Machine-Generated Text using Style Representations
Jan 12, 2024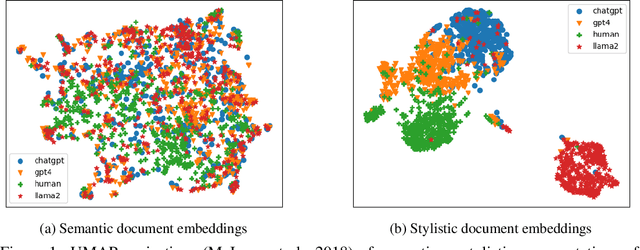
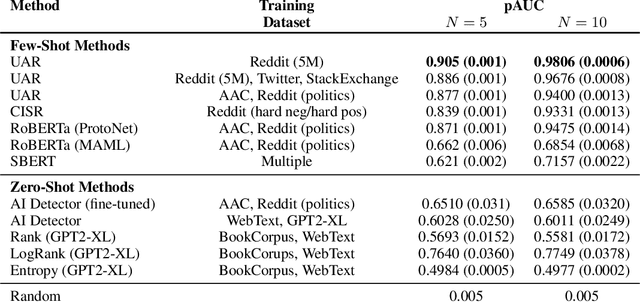
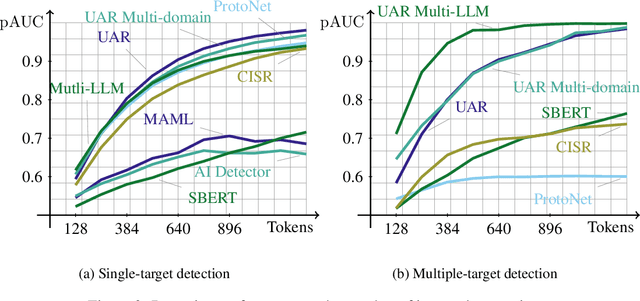
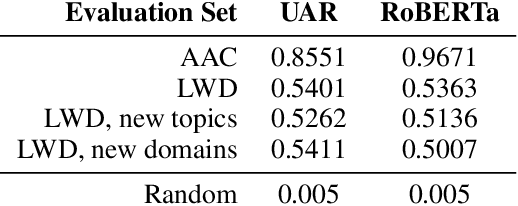
Abstract:The advent of instruction-tuned language models that convincingly mimic human writing poses a significant risk of abuse. For example, such models could be used for plagiarism, disinformation, spam, or phishing. However, such abuse may be counteracted with the ability to detect whether a piece of text was composed by a language model rather than a human. Some previous approaches to this problem have relied on supervised methods trained on corpora of confirmed human and machine-written documents. Unfortunately, model under-specification poses an unavoidable challenge for neural network-based detectors, making them brittle in the face of data shifts, such as the release of further language models producing still more fluent text than the models used to train the detectors. Other previous approaches require access to the models that may have generated a document in question at inference or detection time, which is often impractical. In light of these challenges, we pursue a fundamentally different approach not relying on samples from language models of concern at training time. Instead, we propose to leverage representations of writing style estimated from human-authored text. Indeed, we find that features effective at distinguishing among human authors are also effective at distinguishing human from machine authors, including state of the art large language models like Llama 2, ChatGPT, and GPT-4. Furthermore, given a handful of examples composed by each of several specific language models of interest, our approach affords the ability to predict which model generated a given document.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge