Kaden Uhlig
Cross-lingual Human-Preference Alignment for Neural Machine Translation with Direct Quality Optimization
Sep 26, 2024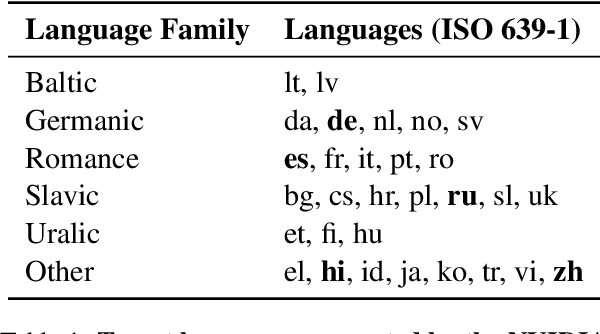
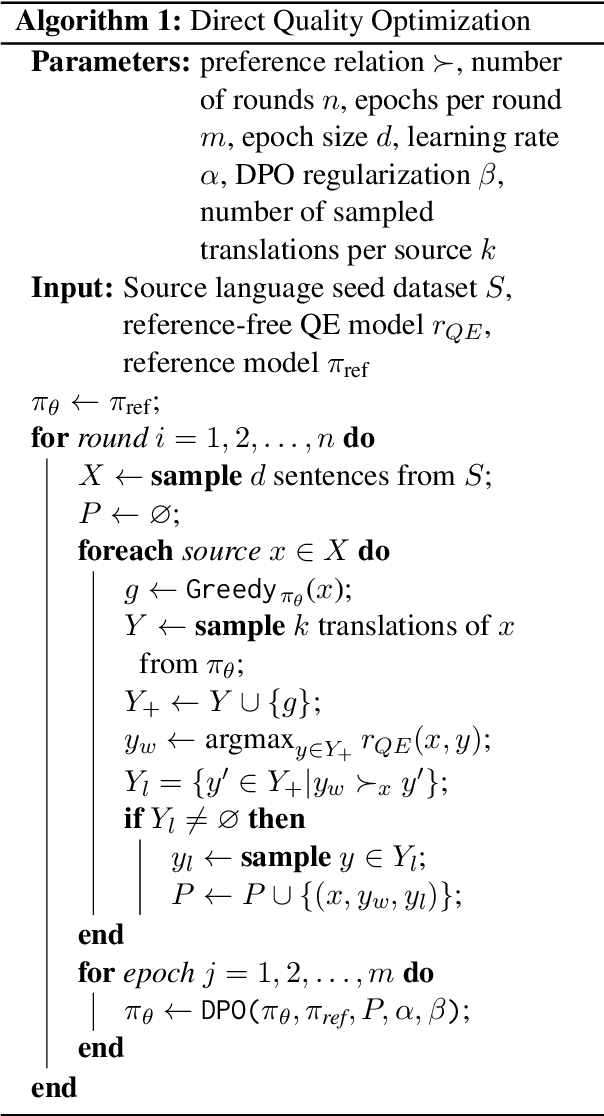

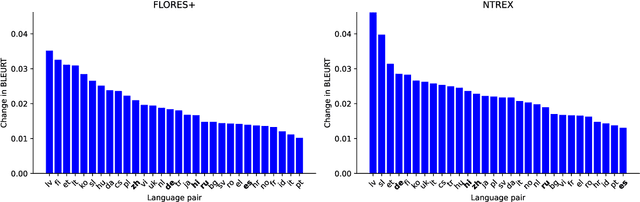
Abstract:Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) and derivative techniques like Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) are task-alignment algorithms used to repurpose general, foundational models for specific tasks. We show that applying task-alignment to neural machine translation (NMT) addresses an existing task--data mismatch in NMT, leading to improvements across all languages of a multilingual model, even when task-alignment is only applied to a subset of those languages. We do so by introducing Direct Quality Optimization (DQO), a variant of DPO leveraging a pre-trained translation quality estimation model as a proxy for human preferences, and verify the improvements with both automatic metrics and human evaluation.
Neural Machine Translation Models Can Learn to be Few-shot Learners
Sep 15, 2023



Abstract:The emergent ability of Large Language Models to use a small number of examples to learn to perform in novel domains and tasks, also called in-context learning (ICL). In this work, we show that a much smaller model can be trained to perform ICL by fine-tuning towards a specialized training objective, exemplified on the task of domain adaptation for neural machine translation. With this capacity for ICL, the model can take advantage of relevant few-shot examples to adapt its output towards the domain. We compare the quality of this domain adaptation to traditional supervised techniques and ICL with a 40B-parameter Large Language Model. Our approach allows efficient batch inference on a mix of domains and outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in terms of both translation quality and immediate adaptation rate, i.e. the ability to reproduce a specific term after being shown a single example.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge