Justin Ley
Diffusion Generative Models in Infinite Dimensions
Dec 01, 2022Abstract:Diffusion generative models have recently been applied to domains where the available data can be seen as a discretization of an underlying function, such as audio signals or time series. However, these models operate directly on the discretized data, and there are no semantics in the modeling process that relate the observed data to the underlying functional forms. We generalize diffusion models to operate directly in function space by developing the foundational theory for such models in terms of Gaussian measures on Hilbert spaces. A significant benefit of our function space point of view is that it allows us to explicitly specify the space of functions we are working in, leading us to develop methods for diffusion generative modeling in Sobolev spaces. Our approach allows us to perform both unconditional and conditional generation of function-valued data. We demonstrate our methods on several synthetic and real-world benchmarks.
Location Leakage in Federated Signal Maps
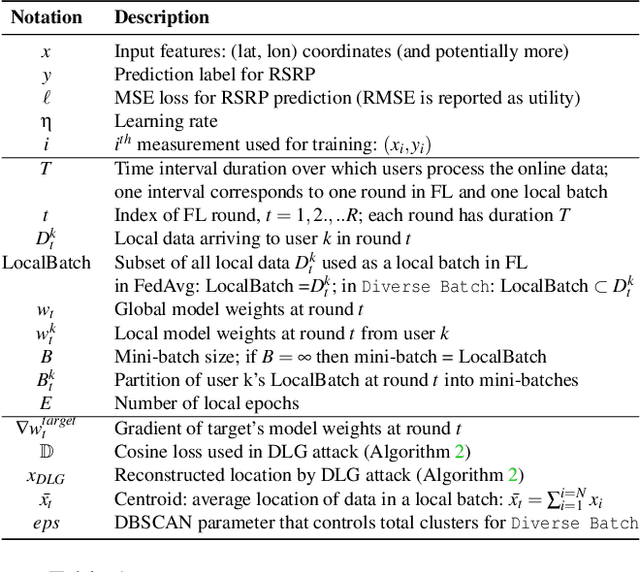
Dec 07, 2021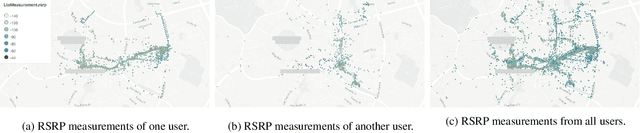
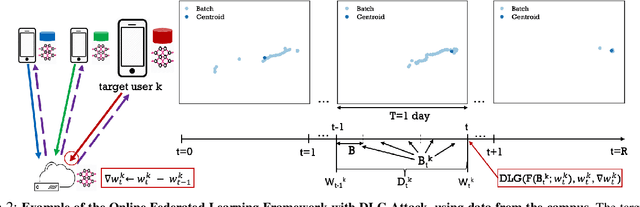

Abstract:We consider the problem of predicting cellular network performance (signal maps) from measurements collected by several mobile devices. We formulate the problem within the online federated learning framework: (i) federated learning (FL) enables users to collaboratively train a model, while keeping their training data on their devices; (ii) measurements are collected as users move around over time and are used for local training in an online fashion. We consider an honest-but-curious server, who observes the updates from target users participating in FL and infers their location using a deep leakage from gradients (DLG) type of attack, originally developed to reconstruct training data of DNN image classifiers. We make the key observation that a DLG attack, applied to our setting, infers the average location of a batch of local data, and can thus be used to reconstruct the target users' trajectory at a coarse granularity. We show that a moderate level of privacy protection is already offered by the averaging of gradients, which is inherent to Federated Averaging. Furthermore, we propose an algorithm that devices can apply locally to curate the batches used for local updates, so as to effectively protect their location privacy without hurting utility. Finally, we show that the effect of multiple users participating in FL depends on the similarity of their trajectories. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study of DLG attacks in the setting of FL from crowdsourced spatio-temporal data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge