Junyang Huang
Relation Aware Semi-autoregressive Semantic Parsing for NL2SQL
Aug 02, 2021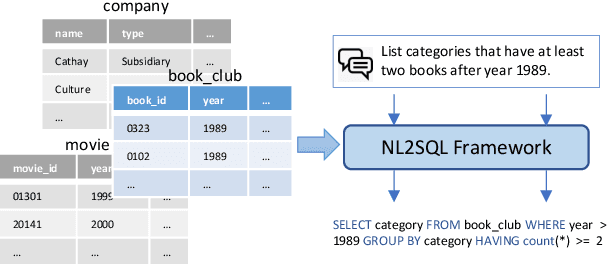
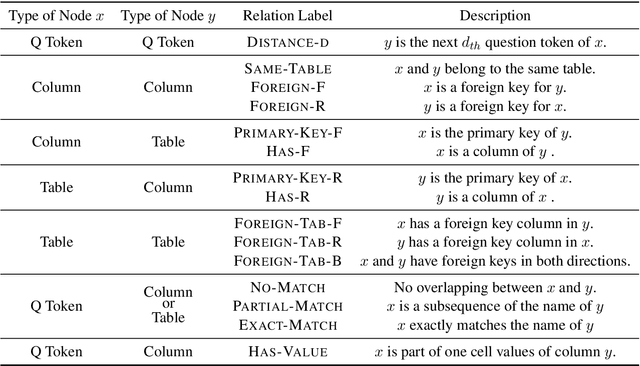
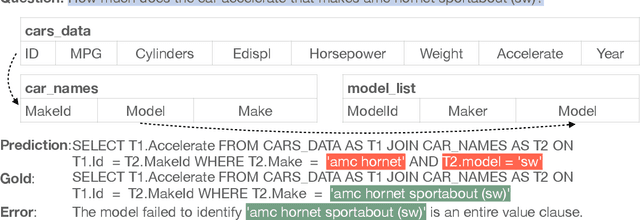
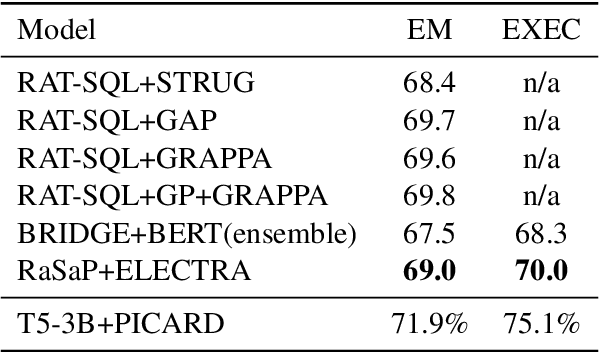
Abstract:Natural language to SQL (NL2SQL) aims to parse a natural language with a given database into a SQL query, which widely appears in practical Internet applications. Jointly encode database schema and question utterance is a difficult but important task in NL2SQL. One solution is to treat the input as a heterogeneous graph. However, it failed to learn good word representation in question utterance. Learning better word representation is important for constructing a well-designed NL2SQL system. To solve the challenging task, we present a Relation aware Semi-autogressive Semantic Parsing (\MODN) ~framework, which is more adaptable for NL2SQL. It first learns relation embedding over the schema entities and question words with predefined schema relations with ELECTRA and relation aware transformer layer as backbone. Then we decode the query SQL with a semi-autoregressive parser and predefined SQL syntax. From empirical results and case study, our model shows its effectiveness in learning better word representation in NL2SQL.
Attention-guided Progressive Mapping for Profile Face Recognition
Jun 29, 2021
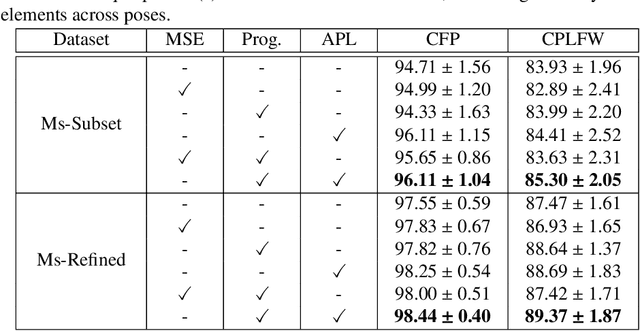
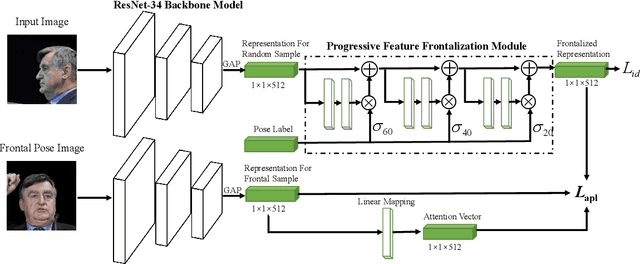

Abstract:The past few years have witnessed great progress in the domain of face recognition thanks to advances in deep learning. However, cross pose face recognition remains a significant challenge. It is difficult for many deep learning algorithms to narrow the performance gap caused by pose variations; the main reasons for this relate to the intra-class discrepancy between face images in different poses and the pose imbalances of training datasets. Learning pose-robust features by traversing to the feature space of frontal faces provides an effective and cheap way to alleviate this problem. In this paper, we present a method for progressively transforming profile face representations to the canonical pose with an attentive pair-wise loss. Firstly, to reduce the difficulty of directly transforming the profile face features into a frontal pose, we propose to learn the feature residual between the source pose and its nearby pose in a block-byblock fashion, and thus traversing to the feature space of a smaller pose by adding the learned residual. Secondly, we propose an attentive pair-wise loss to guide the feature transformation progressing in the most effective direction. Finally, our proposed progressive module and attentive pair-wise loss are light-weight and easy to implement, adding only about 7:5% extra parameters. Evaluations on the CFP and CPLFW datasets demonstrate the superiority of our proposed method. Code is available at https://github.com/hjy1312/AGPM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge