Junseok Kim
Persona Switch: Mixing Distinct Perspectives in Decoding Time
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Role-play prompting is known to steer the behavior of language models by injecting a persona into the prompt, improving their zero-shot reasoning capabilities. However, such improvements are inconsistent across different tasks or instances. This inconsistency suggests that zero-shot and role-play prompting may offer complementary strengths rather than one being universally superior. Building on this insight, we propose Persona Switch, a novel decoding method that dynamically combines the benefits of both prompting strategies. Our method proceeds step-by-step, selecting the better output between zero-shot and role-play prompting at each step by comparing their output confidence, as measured by the logit gap. Experiments with widely-used LLMs demonstrate that Persona Switch consistently outperforms competitive baselines, achieving up to 5.13% accuracy improvement. Furthermore, we show that output confidence serves as an informative measure for selecting the more reliable output.
Reliability-Aware Adaptive Self-Consistency for Efficient Sampling in LLM Reasoning
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Self-Consistency improves reasoning reliability through multi-sample aggregation, but incurs substantial inference cost. Adaptive self-consistency methods mitigate this issue by adjusting the sampling budget; however, they rely on count-based stopping rules that treat all responses equally, often leading to unnecessary sampling. We propose Reliability-Aware Adaptive Self-Consistency (ReASC), which addresses this limitation by reframing adaptive sampling from response counting to evidence sufficiency, leveraging response-level confidence for principled information aggregation. ReASC operates in two stages: a single-sample decision stage that resolves instances confidently answerable from a single response, and a reliability-aware accumulation stage that aggregates responses by jointly leveraging their frequency and confidence. Across five models and four datasets, ReASC consistently achieves the best accuracy-cost trade-off compared to existing baselines, yielding improved inference efficiency across model scales from 3B to 27B parameters. As a concrete example, ReASC reduces inference cost by up to 70\% relative to self-consistency while preserving accuracy on GSM8K using Gemma-3-4B-it.
Persona is a Double-edged Sword: Enhancing the Zero-shot Reasoning by Ensembling the Role-playing and Neutral Prompts
Aug 16, 2024Abstract:Recent studies demonstrate that prompting an appropriate role-playing persona to an LLM improves its reasoning capability. However, assigning a proper persona is difficult since an LLM's performance is extremely sensitive to assigned prompts; therefore, personas sometimes hinder LLMs and degrade their reasoning capabilities. In this paper, we propose a novel framework, Jekyll \& Hyde, which ensembles the results of role-playing and neutral prompts to eradicate performance degradation via unilateral use of role-playing prompted LLM and enhance the robustness of an LLM's reasoning ability. Specifically, Jekyll \& Hyde collects two potential solutions from both role-playing and neutral prompts and selects a better solution after cross-checking via an LLM evaluator. However, LLM-based evaluators tend to be affected by the order of those potential solutions within the prompt when selecting the proper solution; thus, we also propose a robust LLM evaluator to mitigate the position bias. The experimental analysis demonstrates that role-playing prompts distract LLMs and degrade their reasoning abilities in 4 out of 12 datasets, even when using GPT-4. In addition, we reveal that Jekyll \& Hyde improves reasoning capabilities by selecting better choices among the potential solutions on twelve widely-used reasoning datasets. We further show that our proposed LLM evaluator outperforms other baselines, proving the LLMs' position bias is successfully mitigated.
SKIP: Skill-Localized Prompt Tuning for Inference Speed Boost-Up
Apr 18, 2024Abstract:Prompt-tuning methods have shown comparable performance as parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods in various natural language understanding tasks. However, existing prompt tuning methods still utilize the entire model architecture; thus, they fail to accelerate inference speed in the application. In this paper, we propose a novel approach called SKIll-localized Prompt tuning (SKIP), which is extremely efficient in inference time. Our method significantly enhances inference efficiency by investigating and utilizing a skill-localized subnetwork in a language model. Surprisingly, our method improves the inference speed up to 160% while pruning 52% of the parameters. Furthermore, we demonstrate that our method is applicable across various transformer-based architectures, thereby confirming its practicality and scalability.
Simultaneous Recognition of Horizontal and Vertical Text in Natural Images
Dec 06, 2018
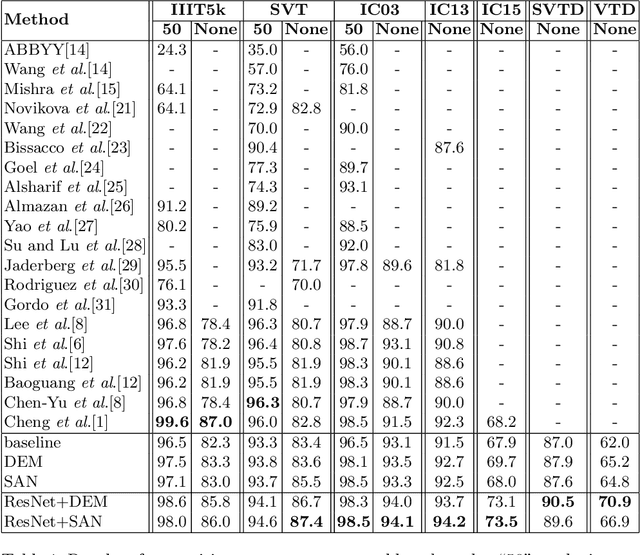
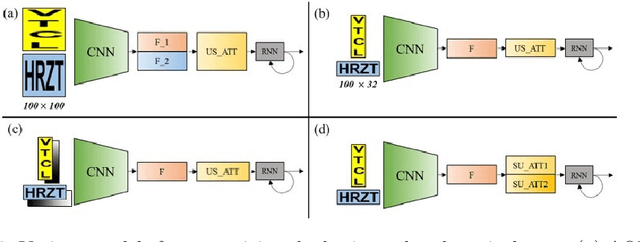

Abstract:Recent state-of-the-art scene text recognition methods have primarily focused on horizontal text in images. However, in several Asian countries, including China, large amounts of text in signs, books, and TV commercials are vertically directed. Because the horizontal and vertical texts exhibit different characteristics, developing an algorithm that can simultaneously recognize both types of text in real environments is necessary. To address this problem, we adopted the direction encoding mask (DEM) and selective attention network (SAN) methods based on supervised learning. DEM contains directional information to compensate in cases that lack text direction; therefore, our network is trained using this information to handle the vertical text. The SAN method is designed to work individually for both types of text. To train the network to recognize both types of text and to evaluate the effectiveness of the designed model, we prepared a new synthetic vertical text dataset and collected an actual vertical text dataset (VTD142) from the Web. Using these datasets, we proved that our proposed model can accurately recognize both vertical and horizontal text and can achieve state-of-the-art results in experiments using benchmark datasets, including the street view test (SVT), IIIT-5k, and ICDAR. Although our model is relatively simple as compared to its predecessors, it maintains the accuracy and is trained in an end-to-end manner.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge