Junmin Wu
EdgeNAT: Transformer for Efficient Edge Detection
Aug 20, 2024



Abstract:Transformers, renowned for their powerful feature extraction capabilities, have played an increasingly prominent role in various vision tasks. Especially, recent advancements present transformer with hierarchical structures such as Dilated Neighborhood Attention Transformer (DiNAT), demonstrating outstanding ability to efficiently capture both global and local features. However, transformers' application in edge detection has not been fully exploited. In this paper, we propose EdgeNAT, a one-stage transformer-based edge detector with DiNAT as the encoder, capable of extracting object boundaries and meaningful edges both accurately and efficiently. On the one hand, EdgeNAT captures global contextual information and detailed local cues with DiNAT, on the other hand, it enhances feature representation with a novel SCAF-MLA decoder by utilizing both inter-spatial and inter-channel relationships of feature maps. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on both RGB and depth images. Notably, on the widely used BSDS500 dataset, our L model achieves impressive performances, with ODS F-measure and OIS F-measure of 86.0%, 87.6% for multi-scale input,and 84.9%, and 86.3% for single-scale input, surpassing the current state-of-the-art EDTER by 1.2%, 1.1%, 1.7%, and 1.6%, respectively. Moreover, as for throughput, our approach runs at 20.87 FPS on RTX 4090 GPU with single-scale input. The code for our method will be released soon.
End-to-end Optimized Video Compression with MV-Residual Prediction
May 26, 2020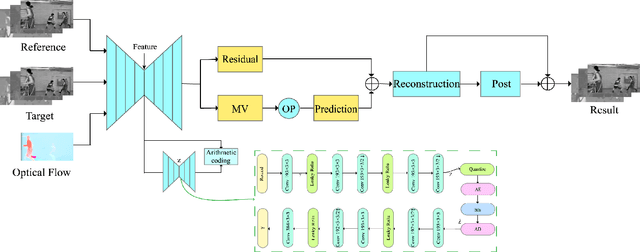
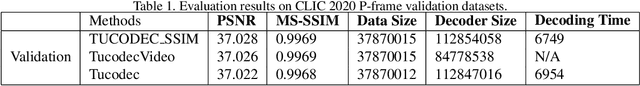
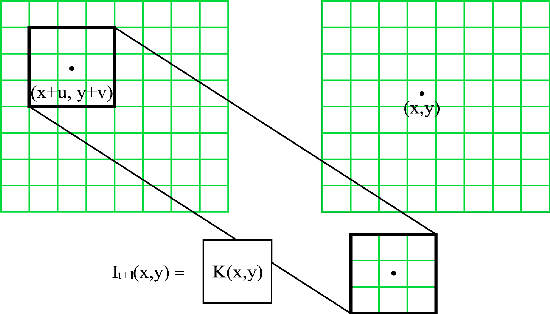
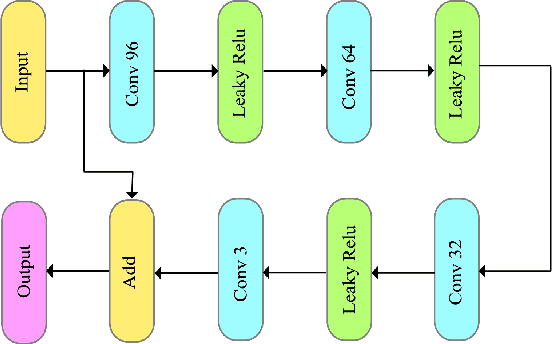
Abstract:We present an end-to-end trainable framework for P-frame compression in this paper. A joint motion vector (MV) and residual prediction network MV-Residual is designed to extract the ensembled features of motion representations and residual information by treating the two successive frames as inputs. The prior probability of the latent representations is modeled by a hyperprior autoencoder and trained jointly with the MV-Residual network. Specially, the spatially-displaced convolution is applied for video frame prediction, in which a motion kernel for each pixel is learned to generate predicted pixel by applying the kernel at a displaced location in the source image. Finally, novel rate allocation and post-processing strategies are used to produce the final compressed bits, considering the bits constraint of the challenge. The experimental results on validation set show that the proposed optimized framework can generate the highest MS-SSIM for P-frame compression competition.
MIDI-Sandwich2: RNN-based Hierarchical Multi-modal Fusion Generation VAE networks for multi-track symbolic music generation
Sep 08, 2019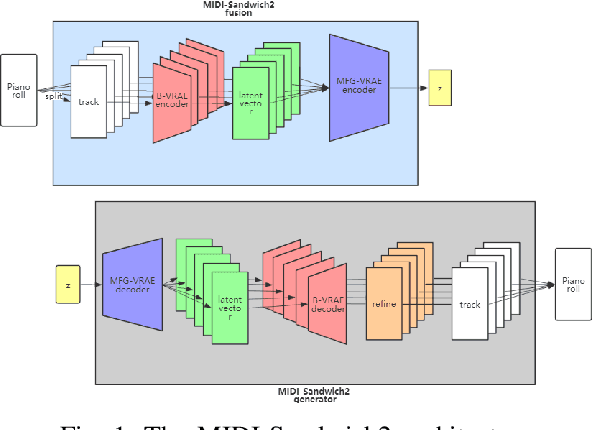
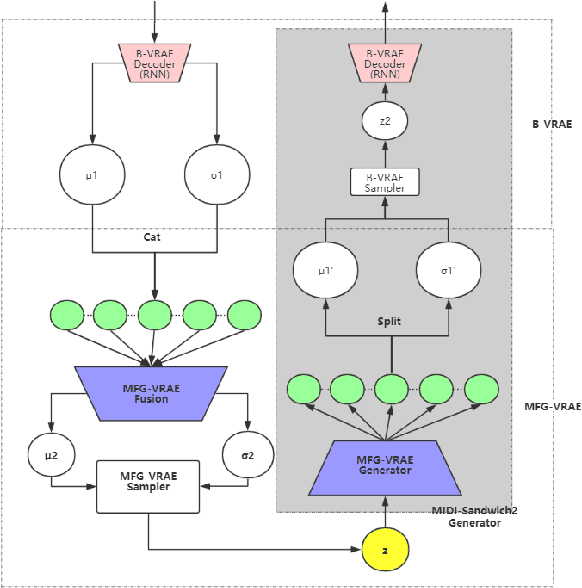
Abstract:Currently, almost all the multi-track music generation models use the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to build the generative model, while the Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) based models can not be applied in this task. In view of the above problem, this paper proposes a RNN-based Hierarchical Multi-modal Fusion Generation Variational Autoencoder (VAE) network, MIDI-Sandwich2, for multi-track symbolic music generation. Inspired by VQ-VAE2, MIDI-Sandwich2 expands the dimension of the original hierarchical model by using multiple independent Binary Variational Autoencoder (BVAE) models without sharing weights to process the information of each track. Then, with multi-modal fusion technology, the upper layer named Multi-modal Fusion Generation VAE (MFG-VAE) combines the latent space vectors generated by the respective tracks, and uses the decoder to perform the ascending dimension reconstruction to simulate the inverse operation of multi-modal fusion, multi-modal generation, so as to realize the RNN-based multi-track symbolic music generation. For the multi-track format pianoroll, we also improve the output binarization method of MuseGAN, which solves the problem that the refinement step of the original scheme is difficult to differentiate and the gradient is hard to descent, making the generated song more expressive. The model is validated on the Lakh Pianoroll Dataset (LPD) multi-track dataset. Compared to the MuseGAN, MIDI-Sandwich2 can not only generate harmonious multi-track music, the generation quality is also close to the state of the art level. At the same time, by using the VAE to restore songs, the semi-generated songs reproduced by the MIDI-Sandwich2 are more beautiful than the pure autogeneration music generated by MuseGAN. Both the code and the audition audio samples are open source on https://github.com/LiangHsia/MIDI-S2.
MIDI-Sandwich: Multi-model Multi-task Hierarchical Conditional VAE-GAN networks for Symbolic Single-track Music Generation
Jul 04, 2019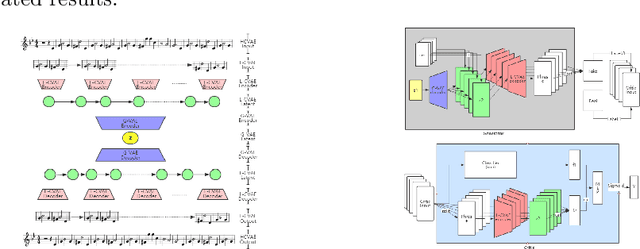
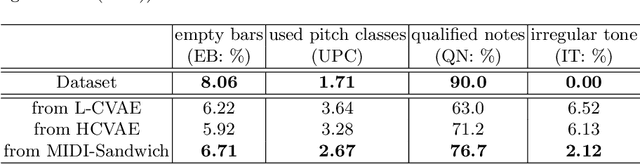
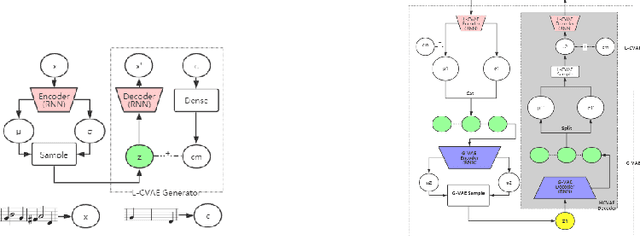
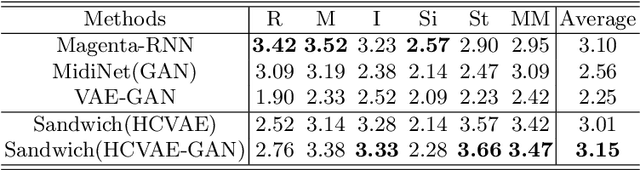
Abstract:Most existing neural network models for music generation explore how to generate music bars, then directly splice the music bars into a song. However, these methods do not explore the relationship between the bars, and the connected song as a whole has no musical form structure and sense of musical direction. To address this issue, we propose a Multi-model Multi-task Hierarchical Conditional VAE-GAN (Variational Autoencoder-Generative adversarial networks) networks, named MIDI-Sandwich, which combines musical knowledge, such as musical form, tonic, and melodic motion. The MIDI-Sandwich has two submodels: Hierarchical Conditional Variational Autoencoder (HCVAE) and Hierarchical Conditional Generative Adversarial Network (HCGAN). The HCVAE uses hierarchical structure. The underlying layer of HCVAE uses Local Conditional Variational Autoencoder (L-CVAE) to generate a music bar which is pre-specified by the First and Last Notes (FLN). The upper layer of HCVAE uses Global Variational Autoencoder(G-VAE) to analyze the latent vector sequence generated by the L-CVAE encoder, to explore the musical relationship between the bars, and to produce the song pieced together by multiple music bars generated by the L-CVAE decoder, which makes the song both have musical structure and sense of direction. At the same time, the HCVAE shares a part of itself with the HCGAN to further improve the performance of the generated music. The MIDI-Sandwich is validated on the Nottingham dataset and is able to generate a single-track melody sequence (17x8 beats), which is superior to the length of most of the generated models (8 to 32 beats). Meanwhile, by referring to the experimental methods of many classical kinds of literature, the quality evaluation of the generated music is performed. The above experiments prove the validity of the model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge