MIDI-Sandwich: Multi-model Multi-task Hierarchical Conditional VAE-GAN networks for Symbolic Single-track Music Generation
Paper and Code
Jul 04, 2019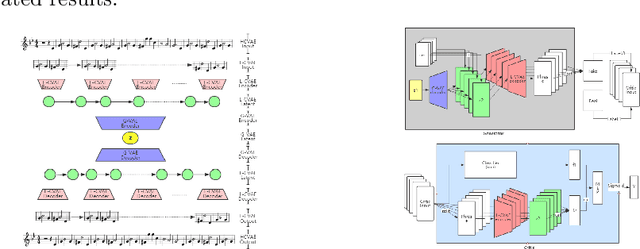
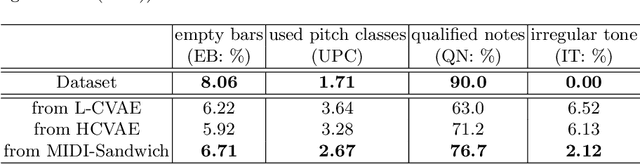
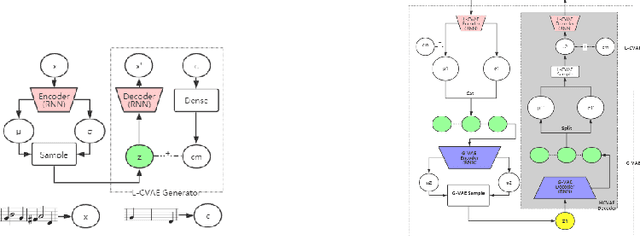
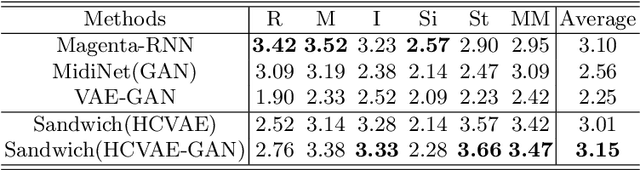
Most existing neural network models for music generation explore how to generate music bars, then directly splice the music bars into a song. However, these methods do not explore the relationship between the bars, and the connected song as a whole has no musical form structure and sense of musical direction. To address this issue, we propose a Multi-model Multi-task Hierarchical Conditional VAE-GAN (Variational Autoencoder-Generative adversarial networks) networks, named MIDI-Sandwich, which combines musical knowledge, such as musical form, tonic, and melodic motion. The MIDI-Sandwich has two submodels: Hierarchical Conditional Variational Autoencoder (HCVAE) and Hierarchical Conditional Generative Adversarial Network (HCGAN). The HCVAE uses hierarchical structure. The underlying layer of HCVAE uses Local Conditional Variational Autoencoder (L-CVAE) to generate a music bar which is pre-specified by the First and Last Notes (FLN). The upper layer of HCVAE uses Global Variational Autoencoder(G-VAE) to analyze the latent vector sequence generated by the L-CVAE encoder, to explore the musical relationship between the bars, and to produce the song pieced together by multiple music bars generated by the L-CVAE decoder, which makes the song both have musical structure and sense of direction. At the same time, the HCVAE shares a part of itself with the HCGAN to further improve the performance of the generated music. The MIDI-Sandwich is validated on the Nottingham dataset and is able to generate a single-track melody sequence (17x8 beats), which is superior to the length of most of the generated models (8 to 32 beats). Meanwhile, by referring to the experimental methods of many classical kinds of literature, the quality evaluation of the generated music is performed. The above experiments prove the validity of the model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge