Jung In Lee
ChatGPT Role-play Dataset: Analysis of User Motives and Model Naturalness
Mar 26, 2024Abstract:Recent advances in interactive large language models like ChatGPT have revolutionized various domains; however, their behavior in natural and role-play conversation settings remains underexplored. In our study, we address this gap by deeply investigating how ChatGPT behaves during conversations in different settings by analyzing its interactions in both a normal way and a role-play setting. We introduce a novel dataset of broad range of human-AI conversations annotated with user motives and model naturalness to examine (i) how humans engage with the conversational AI model, and (ii) how natural are AI model responses. Our study highlights the diversity of user motives when interacting with ChatGPT and variable AI naturalness, showing not only the nuanced dynamics of natural conversations between humans and AI, but also providing new avenues for improving the effectiveness of human-AI communication.
On-Device Speaker Anonymization of Acoustic Embeddings for ASR based onFlexible Location Gradient Reversal Layer
Jul 25, 2023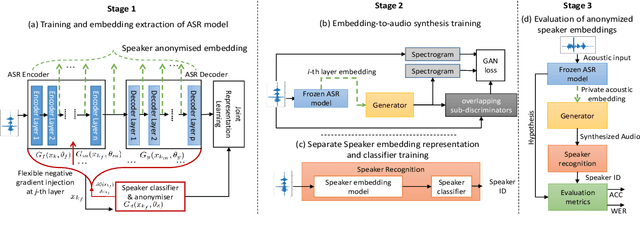
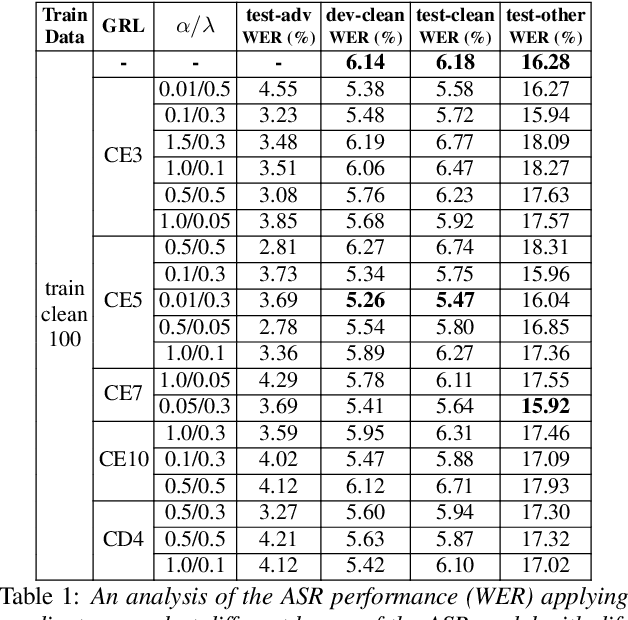

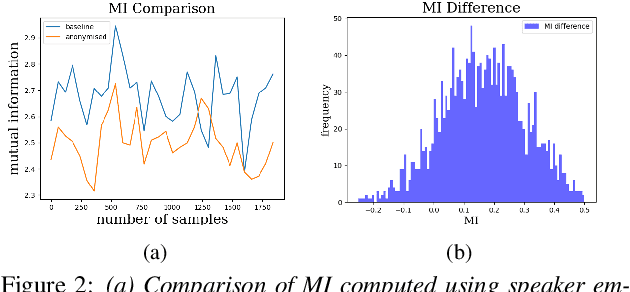
Abstract:Smart devices serviced by large-scale AI models necessitates user data transfer to the cloud for inference. For speech applications, this means transferring private user information, e.g., speaker identity. Our paper proposes a privacy-enhancing framework that targets speaker identity anonymization while preserving speech recognition accuracy for our downstream task~-~Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR). The proposed framework attaches flexible gradient reversal based speaker adversarial layers to target layers within an ASR model, where speaker adversarial training anonymizes acoustic embeddings generated by the targeted layers to remove speaker identity. We propose on-device deployment by execution of initial layers of the ASR model, and transmitting anonymized embeddings to the cloud, where the rest of the model is executed while preserving privacy. Experimental results show that our method efficiently reduces speaker recognition relative accuracy by 33%, and improves ASR performance by achieving 6.2% relative Word Error Rate (WER) reduction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge