Junchi Chu
ESNI: Domestic Robots Design for Elderly and Disabled People
Mar 30, 2022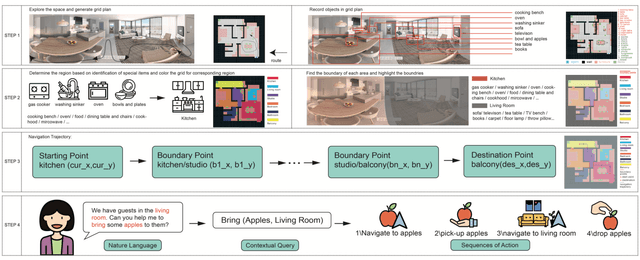
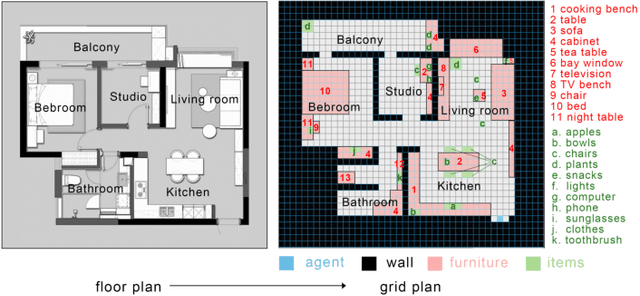
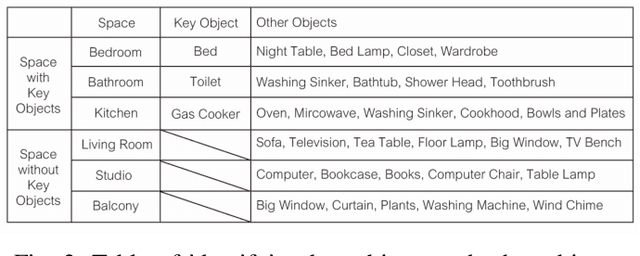
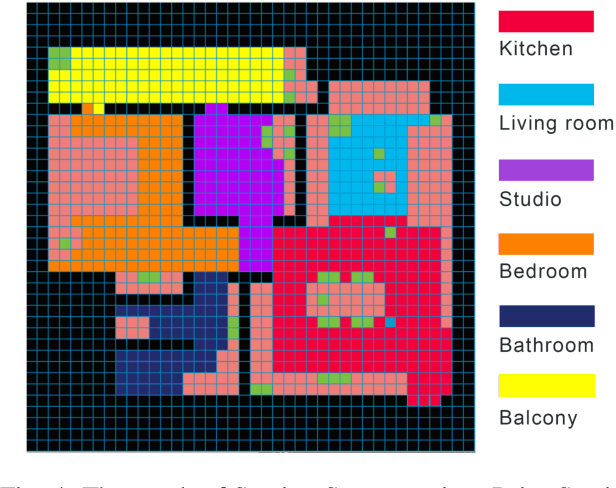
Abstract:Our paper focuses on the research of the possibility for speech recognition intelligent agents to assist the elderly and disabled people's lives, to improve their life quality by utilizing cutting-edge technologies. After researching the attitude of elderly and disabled people toward the household agent, we propose a design framework: ESNI(Exploration, Segmentation, Navigation, Instruction) that apply to mobile agent, achieve some functionalities such as processing human commands, picking up a specified object, and moving an object to another location. The agent starts the exploration in an unseen environment, stores each item's information in the grid cells to his memory and analyzes the corresponding features for each section. We divided our indoor environment into 6 sections: Kitchen, Living room, Bedroom, Studio, Bathroom, Balcony. The agent uses algorithms to assign sections for each grid cell then generates a navigation trajectory base on the section segmentation. When the user gives a command to the agent, feature words will be extracted and processed into a sequence of sub-tasks.
Generalizing to New Domains by Mapping Natural Language to Lifted LTL
Oct 11, 2021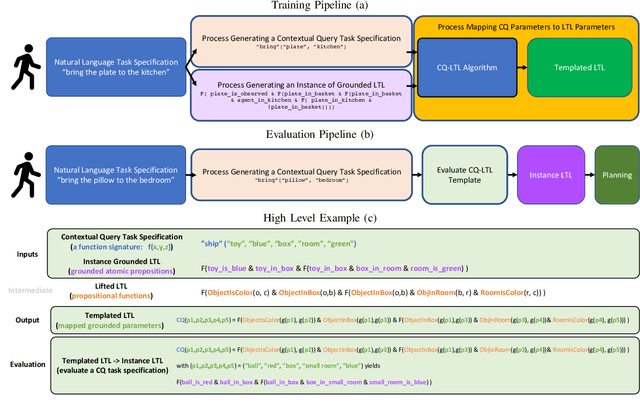
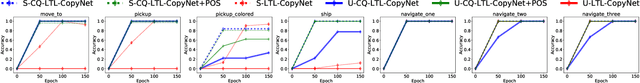
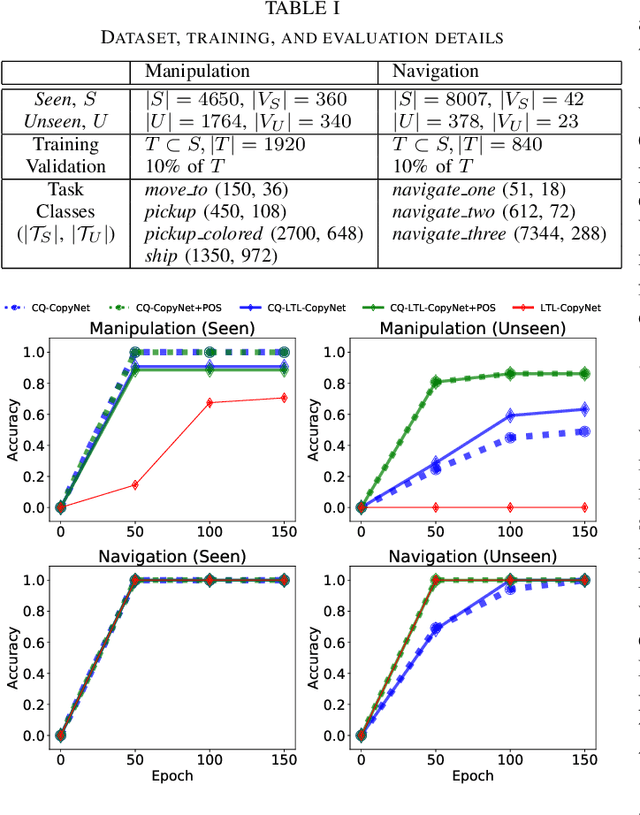
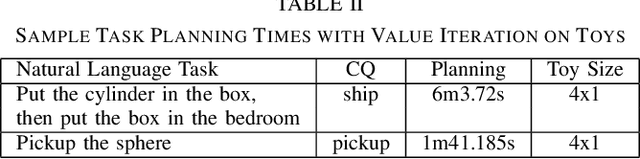
Abstract:Recent work on using natural language to specify commands to robots has grounded that language to LTL. However, mapping natural language task specifications to LTL task specifications using language models require probability distributions over finite vocabulary. Existing state-of-the-art methods have extended this finite vocabulary to include unseen terms from the input sequence to improve output generalization. However, novel out-of-vocabulary atomic propositions cannot be generated using these methods. To overcome this, we introduce an intermediate contextual query representation which can be learned from single positive task specification examples, associating a contextual query with an LTL template. We demonstrate that this intermediate representation allows for generalization over unseen object references, assuming accurate groundings are available. We compare our method of mapping natural language task specifications to intermediate contextual queries against state-of-the-art CopyNet models capable of translating natural language to LTL, by evaluating whether correct LTL for manipulation and navigation task specifications can be output, and show that our method outperforms the CopyNet model on unseen object references. We demonstrate that the grounded LTL our method outputs can be used for planning in a simulated OO-MDP environment. Finally, we discuss some common failure modes encountered when translating natural language task specifications to grounded LTL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge