Jun-Seok Yun
Customizing Segmentation Foundation Model via Prompt Learning for Instance Segmentation
Mar 14, 2024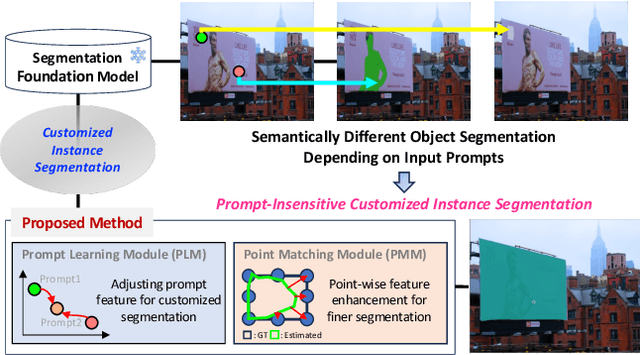
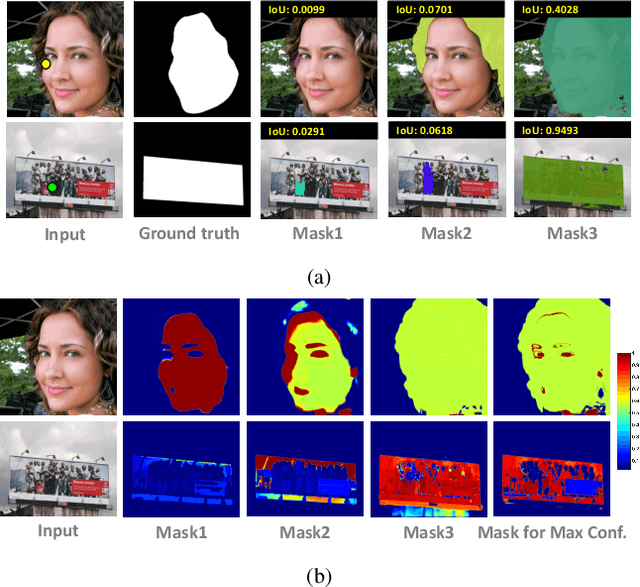


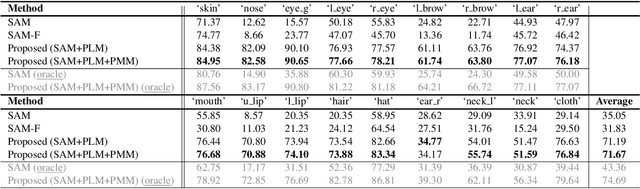
Abstract:Recently, foundation models trained on massive datasets to adapt to a wide range of domains have attracted considerable attention and are actively being explored within the computer vision community. Among these, the Segment Anything Model (SAM) stands out for its remarkable progress in generalizability and flexibility for image segmentation tasks, achieved through prompt-based object mask generation. However, despite its strength, SAM faces two key limitations when applied to customized instance segmentation that segments specific objects or those in unique environments not typically present in the training data: 1) the ambiguity inherent in input prompts and 2) the necessity for extensive additional training to achieve optimal segmentation. To address these challenges, we propose a novel method, customized instance segmentation via prompt learning tailored to SAM. Our method involves a prompt learning module (PLM), which adjusts input prompts into the embedding space to better align with user intentions, thereby enabling more efficient training. Furthermore, we introduce a point matching module (PMM) to enhance the feature representation for finer segmentation by ensuring detailed alignment with ground truth boundaries. Experimental results on various customized instance segmentation scenarios demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
LatentGaze: Cross-Domain Gaze Estimation through Gaze-Aware Analytic Latent Code Manipulation
Sep 21, 2022
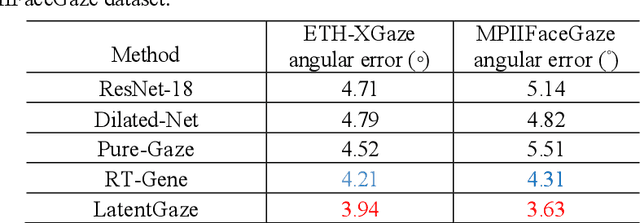
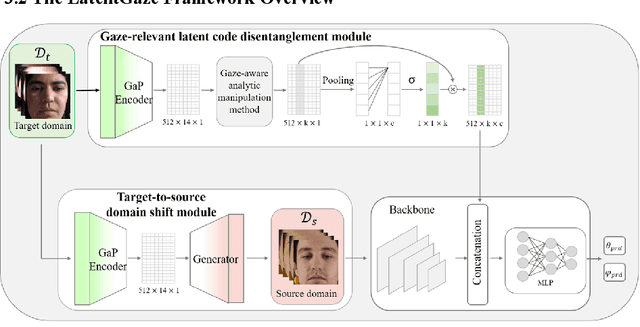
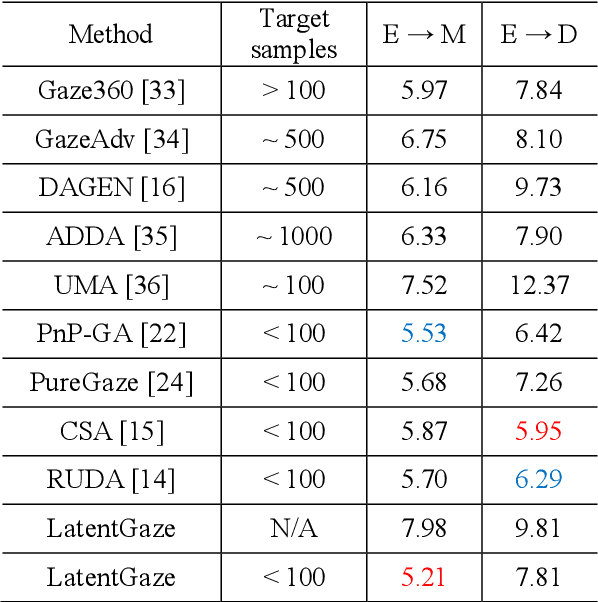
Abstract:Although recent gaze estimation methods lay great emphasis on attentively extracting gaze-relevant features from facial or eye images, how to define features that include gaze-relevant components has been ambiguous. This obscurity makes the model learn not only gaze-relevant features but also irrelevant ones. In particular, it is fatal for the cross-dataset performance. To overcome this challenging issue, we propose a gaze-aware analytic manipulation method, based on a data-driven approach with generative adversarial network inversion's disentanglement characteristics, to selectively utilize gaze-relevant features in a latent code. Furthermore, by utilizing GAN-based encoder-generator process, we shift the input image from the target domain to the source domain image, which a gaze estimator is sufficiently aware. In addition, we propose gaze distortion loss in the encoder that prevents the distortion of gaze information. The experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art gaze estimation accuracy in a cross-domain gaze estimation tasks. This code is available at https://github.com/leeisack/LatentGaze/.
HAZE-Net: High-Frequency Attentive Super-Resolved Gaze Estimation in Low-Resolution Face Images
Sep 21, 2022



Abstract:Although gaze estimation methods have been developed with deep learning techniques, there has been no such approach as aim to attain accurate performance in low-resolution face images with a pixel width of 50 pixels or less. To solve a limitation under the challenging low-resolution conditions, we propose a high-frequency attentive super-resolved gaze estimation network, i.e., HAZE-Net. Our network improves the resolution of the input image and enhances the eye features and those boundaries via a proposed super-resolution module based on a high-frequency attention block. In addition, our gaze estimation module utilizes high-frequency components of the eye as well as the global appearance map. We also utilize the structural location information of faces to approximate head pose. The experimental results indicate that the proposed method exhibits robust gaze estimation performance even in low-resolution face images with 28x28 pixels. The source code of this work is available at https://github.com/dbseorms16/HAZE_Net/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge