Julio Ivan Davila Carrazco
Learnable Data Augmentation for One-Shot Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Oct 03, 2023Abstract:This paper presents a classification framework based on learnable data augmentation to tackle the One-Shot Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (OS-UDA) problem. OS-UDA is the most challenging setting in Domain Adaptation, as only one single unlabeled target sample is assumed to be available for model adaptation. Driven by such single sample, our method LearnAug-UDA learns how to augment source data, making it perceptually similar to the target. As a result, a classifier trained on such augmented data will generalize well for the target domain. To achieve this, we designed an encoder-decoder architecture that exploits a perceptual loss and style transfer strategies to augment the source data. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on two well-known Domain Adaptation benchmarks, DomainNet and VisDA. The project code is available at https://github.com/IIT-PAVIS/LearnAug-UDA
Target-driven One-Shot Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
May 08, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a novel framework for the challenging problem of One-Shot Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (OSUDA), which aims to adapt to a target domain with only a single unlabeled target sample. Unlike existing approaches that rely on large labeled source and unlabeled target data, our Target-driven One-Shot UDA (TOS-UDA) approach employs a learnable augmentation strategy guided by the target sample's style to align the source distribution with the target distribution. Our method consists of three modules: an augmentation module, a style alignment module, and a classifier. Unlike existing methods, our augmentation module allows for strong transformations of the source samples, and the style of the single target sample available is exploited to guide the augmentation by ensuring perceptual similarity. Furthermore, our approach integrates augmentation with style alignment, eliminating the need for separate pre-training on additional datasets. Our method outperforms or performs comparably to existing OS-UDA methods on the Digits and DomainNet benchmarks.
Learning without Seeing nor Knowing: Towards Open Zero-Shot Learning
Mar 23, 2021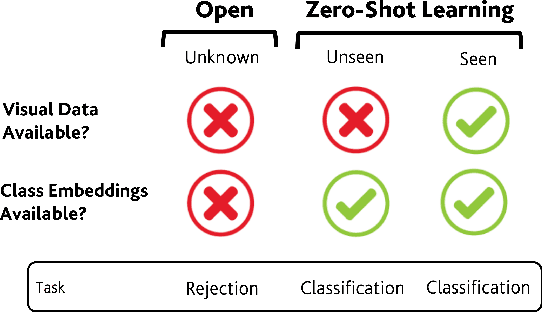
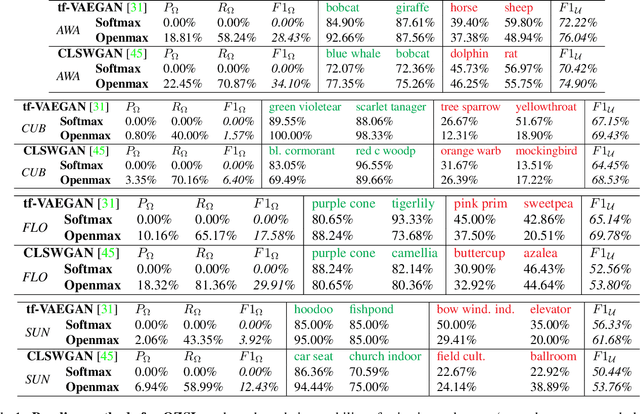
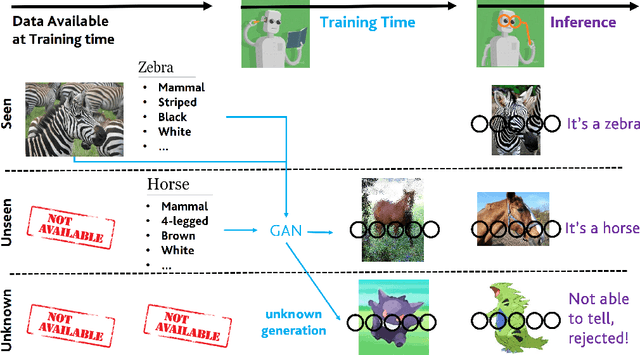
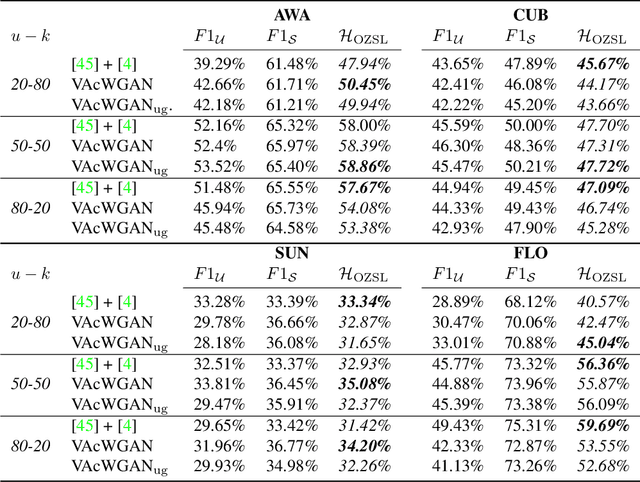
Abstract:In Generalized Zero-Shot Learning (GZSL), unseen categories (for which no visual data are available at training time) can be predicted by leveraging their class embeddings (e.g., a list of attributes describing them) together with a complementary pool of seen classes (paired with both visual data and class embeddings). Despite GZSL is arguably challenging, we posit that knowing in advance the class embeddings, especially for unseen categories, is an actual limit of the applicability of GZSL towards real-world scenarios. To relax this assumption, we propose Open Zero-Shot Learning (OZSL) to extend GZSL towards the open-world settings. We formalize OZSL as the problem of recognizing seen and unseen classes (as in GZSL) while also rejecting instances from unknown categories, for which neither visual data nor class embeddings are provided. We formalize the OZSL problem introducing evaluation protocols, error metrics and benchmark datasets. We also suggest to tackle the OZSL problem by proposing the idea of performing unknown feature generation (instead of only unseen features generation as done in GZSL). We achieve this by optimizing a generative process to sample unknown class embeddings as complementary to the seen and the unseen. We intend these results to be the ground to foster future research, extending the standard closed-world zero-shot learning (GZSL) with the novel open-world counterpart (OZSL).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge