Federico Marmoreo
Learning without Seeing nor Knowing: Towards Open Zero-Shot Learning
Mar 23, 2021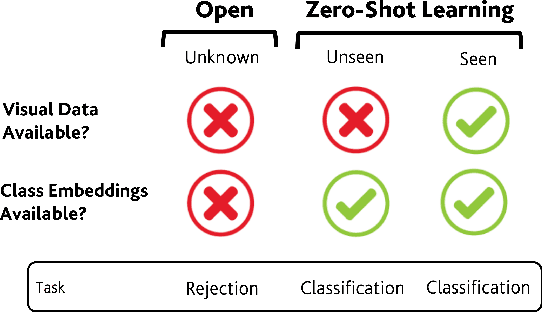
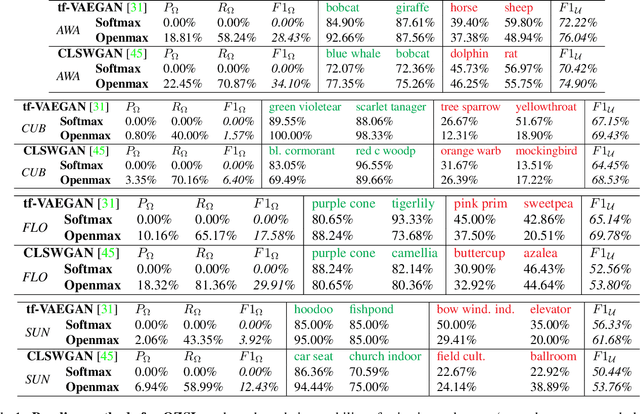
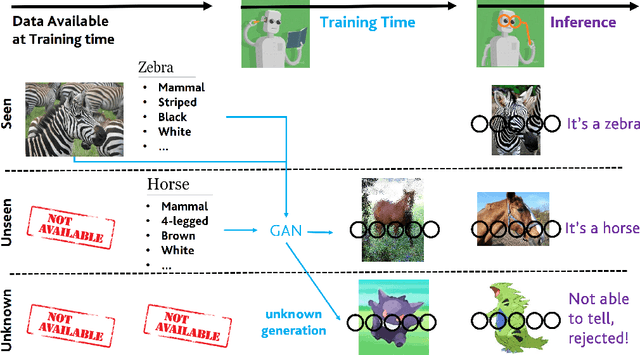
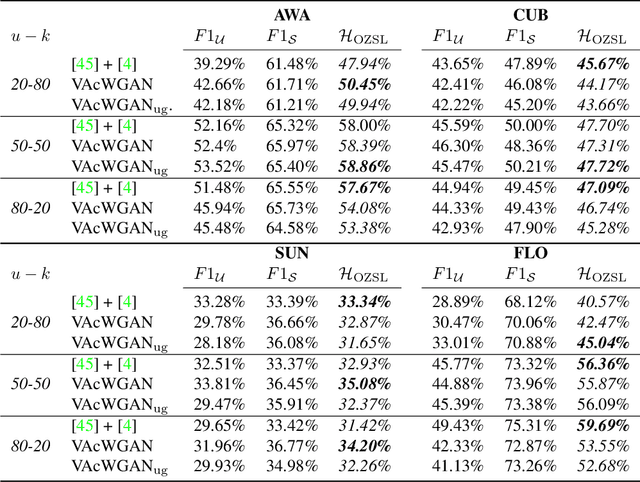
Abstract:In Generalized Zero-Shot Learning (GZSL), unseen categories (for which no visual data are available at training time) can be predicted by leveraging their class embeddings (e.g., a list of attributes describing them) together with a complementary pool of seen classes (paired with both visual data and class embeddings). Despite GZSL is arguably challenging, we posit that knowing in advance the class embeddings, especially for unseen categories, is an actual limit of the applicability of GZSL towards real-world scenarios. To relax this assumption, we propose Open Zero-Shot Learning (OZSL) to extend GZSL towards the open-world settings. We formalize OZSL as the problem of recognizing seen and unseen classes (as in GZSL) while also rejecting instances from unknown categories, for which neither visual data nor class embeddings are provided. We formalize the OZSL problem introducing evaluation protocols, error metrics and benchmark datasets. We also suggest to tackle the OZSL problem by proposing the idea of performing unknown feature generation (instead of only unseen features generation as done in GZSL). We achieve this by optimizing a generative process to sample unknown class embeddings as complementary to the seen and the unseen. We intend these results to be the ground to foster future research, extending the standard closed-world zero-shot learning (GZSL) with the novel open-world counterpart (OZSL).
Transductive Zero-Shot Learning by Decoupled Feature Generation
Feb 23, 2021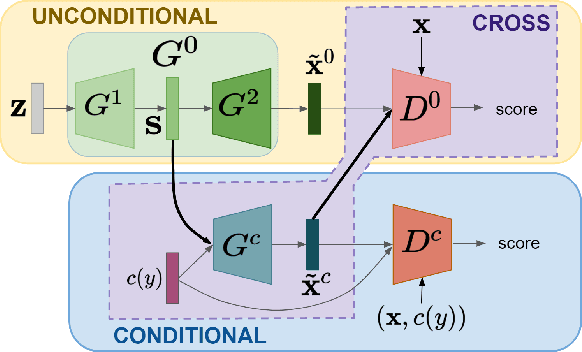
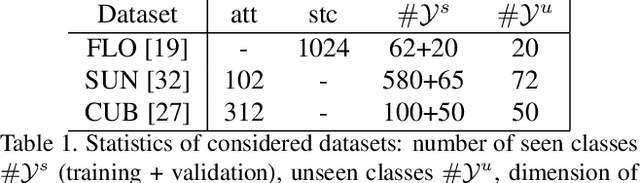
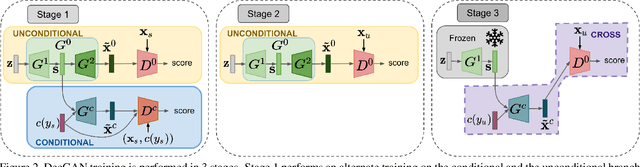
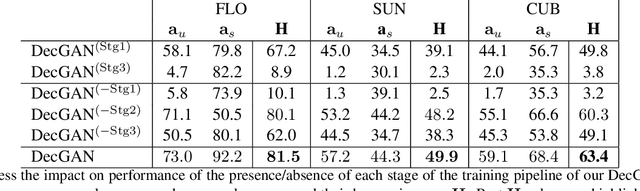
Abstract:In this paper, we address zero-shot learning (ZSL), the problem of recognizing categories for which no labeled visual data are available during training. We focus on the transductive setting, in which unlabelled visual data from unseen classes is available. State-of-the-art paradigms in ZSL typically exploit generative adversarial networks to synthesize visual features from semantic attributes. We posit that the main limitation of these approaches is to adopt a single model to face two problems: 1) generating realistic visual features, and 2) translating semantic attributes into visual cues. Differently, we propose to decouple such tasks, solving them separately. In particular, we train an unconditional generator to solely capture the complexity of the distribution of visual data and we subsequently pair it with a conditional generator devoted to enrich the prior knowledge of the data distribution with the semantic content of the class embeddings. We present a detailed ablation study to dissect the effect of our proposed decoupling approach, while demonstrating its superiority over the related state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge