Julianna Ianni
Using Whole Slide Image Representations from Self-Supervised Contrastive Learning for Melanoma Concordance Regression
Oct 10, 2022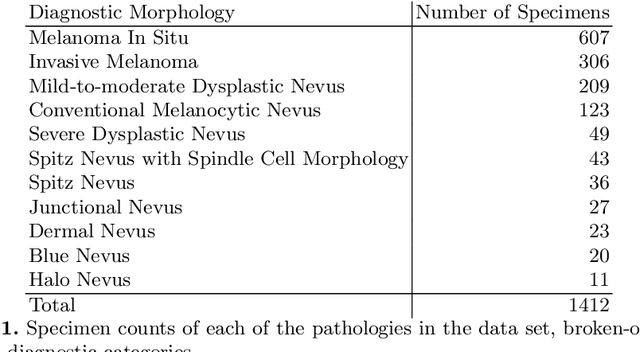
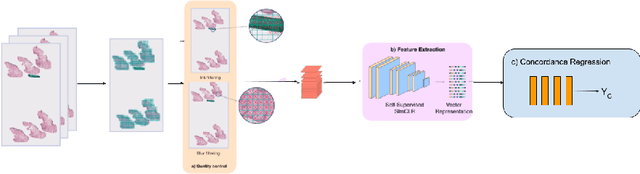
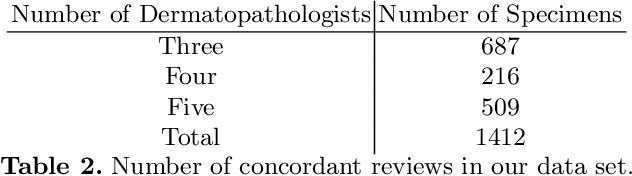
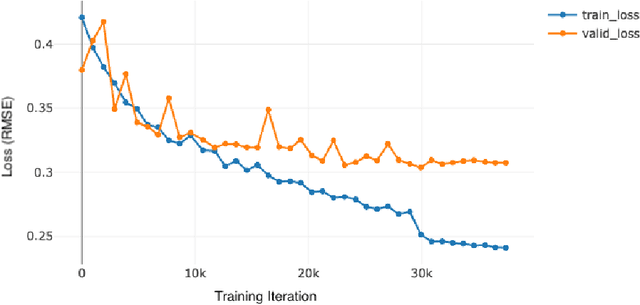
Abstract:Although melanoma occurs more rarely than several other skin cancers, patients' long term survival rate is extremely low if the diagnosis is missed. Diagnosis is complicated by a high discordance rate among pathologists when distinguishing between melanoma and benign melanocytic lesions. A tool that provides potential concordance information to healthcare providers could help inform diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic decision-making for challenging melanoma cases. We present a melanoma concordance regression deep learning model capable of predicting the concordance rate of invasive melanoma or melanoma in-situ from digitized Whole Slide Images (WSIs). The salient features corresponding to melanoma concordance were learned in a self-supervised manner with the contrastive learning method, SimCLR. We trained a SimCLR feature extractor with 83,356 WSI tiles randomly sampled from 10,895 specimens originating from four distinct pathology labs. We trained a separate melanoma concordance regression model on 990 specimens with available concordance ground truth annotations from three pathology labs and tested the model on 211 specimens. We achieved a Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) of 0.28 +/- 0.01 on the test set. We also investigated the performance of using the predicted concordance rate as a malignancy classifier, and achieved a precision and recall of 0.85 +/- 0.05 and 0.61 +/- 0.06, respectively, on the test set. These results are an important first step for building an artificial intelligence (AI) system capable of predicting the results of consulting a panel of experts and delivering a score based on the degree to which the experts would agree on a particular diagnosis. Such a system could be used to suggest additional testing or other action such as ordering additional stains or genetic tests.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge