Julian Mäder
Assessing Evaluation Metrics for Speech-to-Speech Translation
Oct 26, 2021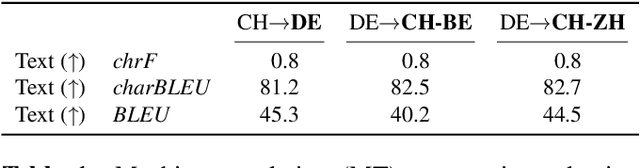
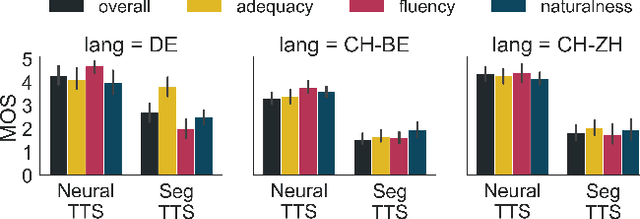
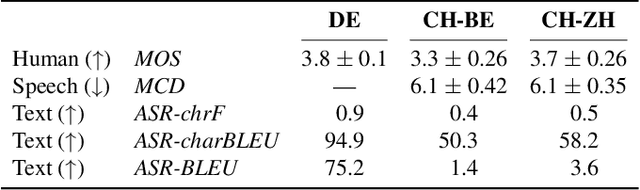
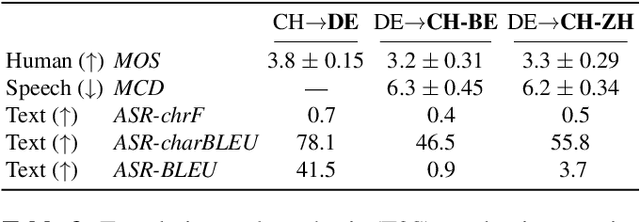
Abstract:Speech-to-speech translation combines machine translation with speech synthesis, introducing evaluation challenges not present in either task alone. How to automatically evaluate speech-to-speech translation is an open question which has not previously been explored. Translating to speech rather than to text is often motivated by unwritten languages or languages without standardized orthographies. However, we show that the previously used automatic metric for this task is best equipped for standardized high-resource languages only. In this work, we first evaluate current metrics for speech-to-speech translation, and second assess how translation to dialectal variants rather than to standardized languages impacts various evaluation methods.
SwissDial: Parallel Multidialectal Corpus of Spoken Swiss German
Mar 21, 2021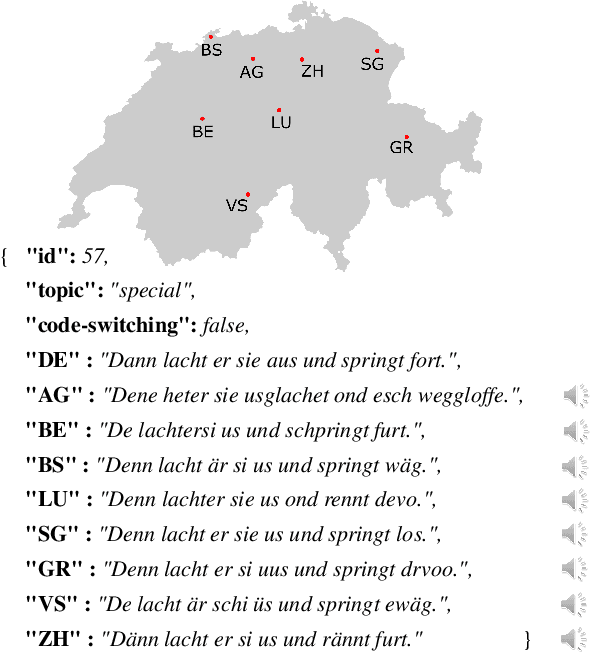
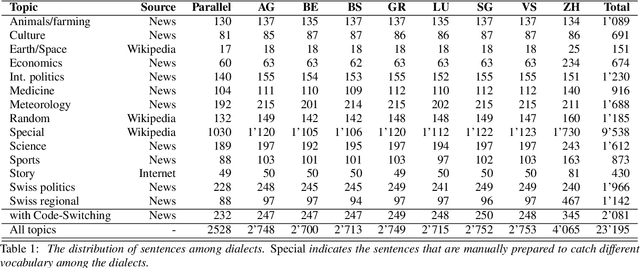
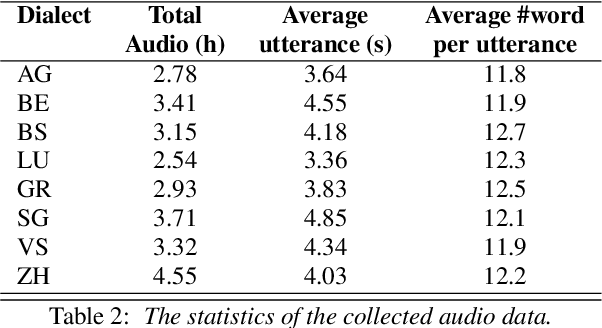
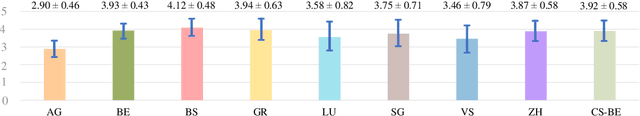
Abstract:Swiss German is a dialect continuum whose natively acquired dialects significantly differ from the formal variety of the language. These dialects are mostly used for verbal communication and do not have standard orthography. This has led to a lack of annotated datasets, rendering the use of many NLP methods infeasible. In this paper, we introduce the first annotated parallel corpus of spoken Swiss German across 8 major dialects, plus a Standard German reference. Our goal has been to create and to make available a basic dataset for employing data-driven NLP applications in Swiss German. We present our data collection procedure in detail and validate the quality of our corpus by conducting experiments with the recent neural models for speech synthesis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge