Jules Vidal
Principal Geodesic Analysis of Merge Trees (and Persistence Diagrams)
Jul 22, 2022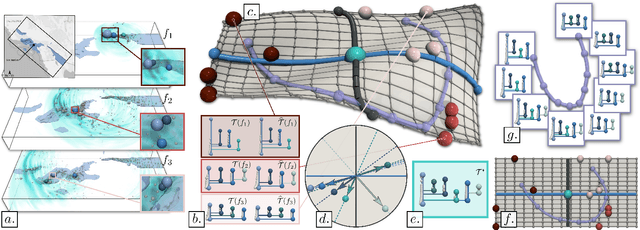
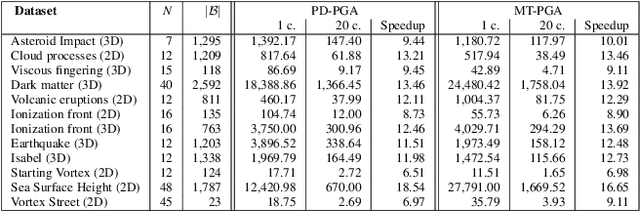
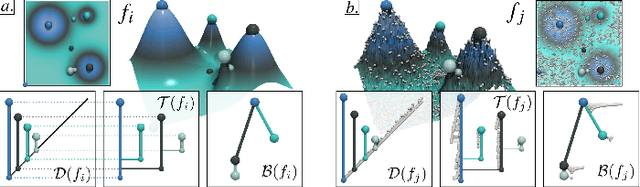
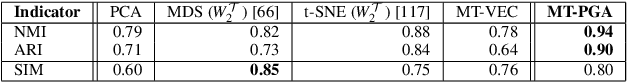
Abstract:This paper presents a computational framework for the Principal Geodesic Analysis of merge trees (MT-PGA), a novel adaptation of the celebrated Principal Component Analysis (PCA) framework [87] to the Wasserstein metric space of merge trees [92]. We formulate MT-PGA computation as a constrained optimization problem, aiming at adjusting a basis of orthogonal geodesic axes, while minimizing a fitting energy. We introduce an efficient, iterative algorithm which exploits shared-memory parallelism, as well as an analytic expression of the fitting energy gradient, to ensure fast iterations. Our approach also trivially extends to extremum persistence diagrams. Extensive experiments on public ensembles demonstrate the efficiency of our approach - with MT-PGA computations in the orders of minutes for the largest examples. We show the utility of our contributions by extending to merge trees two typical PCA applications. First, we apply MT-PGA to data reduction and reliably compress merge trees by concisely representing them by their first coordinates in the MT-PGA basis. Second, we present a dimensionality reduction framework exploiting the first two directions of the MT-PGA basis to generate two-dimensional layouts of the ensemble. We augment these layouts with persistence correlation views, enabling global and local visual inspections of the feature variability in the ensemble. In both applications, quantitative experiments assess the relevance of our framework. Finally, we provide a lightweight C++ implementation that can be used to reproduce our results.
Discrete Morse Sandwich: Fast Computation of Persistence Diagrams for Scalar Data -- An Algorithm and A Benchmark
Jun 27, 2022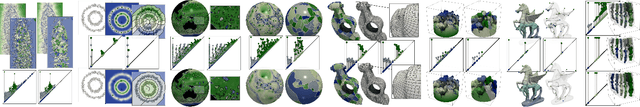
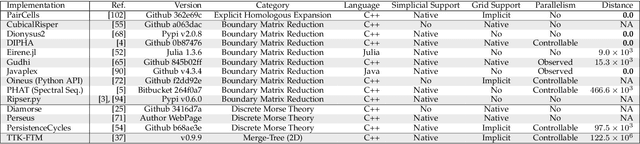
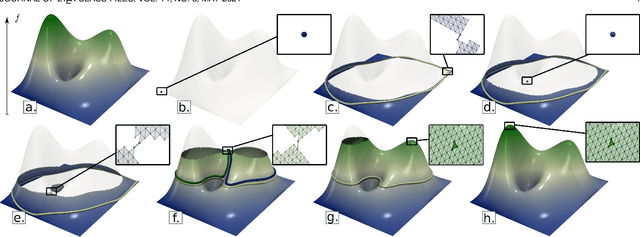
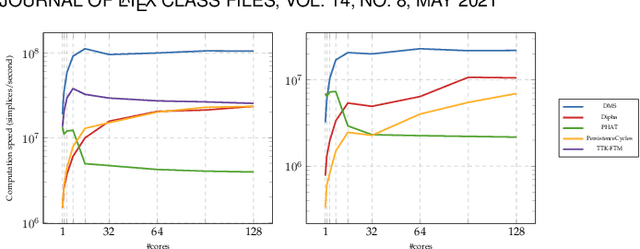
Abstract:This paper introduces an efficient algorithm for persistence diagram computation, given an input piecewise linear scalar field f defined on a d-dimensional simplicial complex K, with $d \leq 3$. Our method extends the seminal "PairCells" algorithm by introducing three main accelerations. First, we express this algorithm within the setting of discrete Morse theory, which considerably reduces the number of input simplices to consider. Second, we introduce a stratification approach to the problem, that we call "sandwiching". Specifically, minima-saddle persistence pairs ($D_0(f)$) and saddle-maximum persistence pairs ($D_{d-1}(f)$) are efficiently computed by respectively processing with a Union-Find the unstable sets of 1-saddles and the stable sets of (d-1)-saddles. This fast processing of the dimensions 0 and (d-1) further reduces, and drastically, the number of critical simplices to consider for the computation of $D_1(f)$, the intermediate layer of the sandwich. Third, we document several performance improvements via shared-memory parallelism. We provide an open-source implementation of our algorithm for reproducibility purposes. We also contribute a reproducible benchmark package, which exploits three-dimensional data from a public repository and compares our algorithm to a variety of publicly available implementations. Extensive experiments indicate that our algorithm improves by two orders of magnitude the time performance of the seminal "PairCells" algorithm it extends. Moreover, it also improves memory footprint and time performance over a selection of 14 competing approaches, with a substantial gain over the fastest available approaches, while producing a strictly identical output. We illustrate the utility of our contributions with an application to the fast and robust extraction of persistent 1-dimensional generators on surfaces, volume data and high-dimensional point clouds.
Wasserstein Distances, Geodesics and Barycenters of Merge Trees
Jul 16, 2021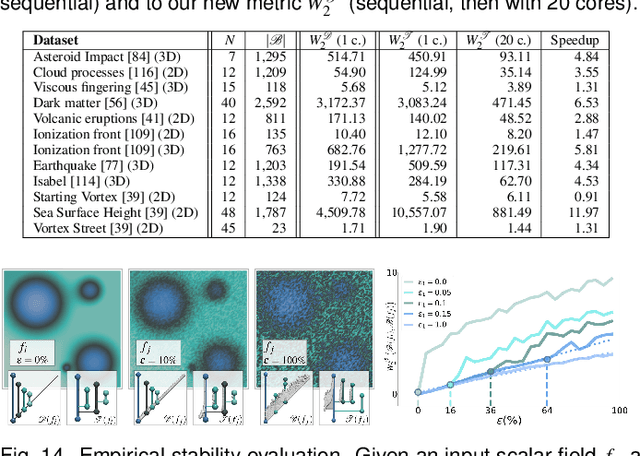
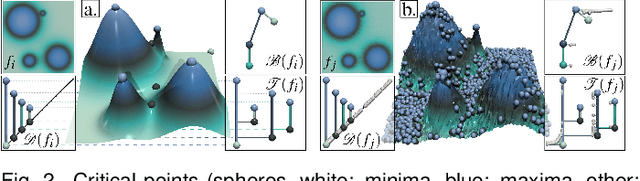
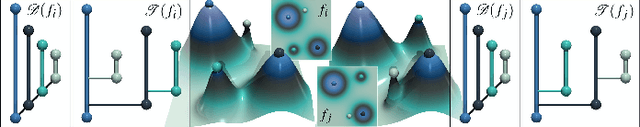
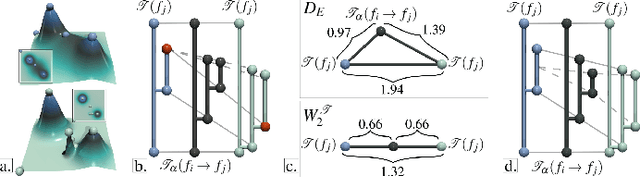
Abstract:This paper presents a unified computational framework for the estimation of distances, geodesics and barycenters of merge trees. We extend recent work on the edit distance [106] and introduce a new metric, called the Wasserstein distance between merge trees, which is purposely designed to enable efficient computations of geodesics and barycenters. Specifically, our new distance is strictly equivalent to the L2-Wasserstein distance between extremum persistence diagrams, but it is restricted to a smaller solution space, namely, the space of rooted partial isomorphisms between branch decomposition trees. This enables a simple extension of existing optimization frameworks [112] for geodesics and barycenters from persistence diagrams to merge trees. We introduce a task-based algorithm which can be generically applied to distance, geodesic, barycenter or cluster computation. The task-based nature of our approach enables further accelerations with shared-memory parallelism. Extensive experiments on public ensembles and SciVis contest benchmarks demonstrate the efficiency of our approach -- with barycenter computations in the orders of minutes for the largest examples -- as well as its qualitative ability to generate representative barycenter merge trees, visually summarizing the features of interest found in the ensemble. We show the utility of our contributions with dedicated visualization applications: feature tracking, temporal reduction and ensemble clustering. We provide a lightweight C++ implementation that can be used to reproduce our results.
Statistical Parameter Selection for Clustering Persistence Diagrams
Oct 17, 2019



Abstract:In urgent decision making applications, ensemble simulations are an important way to determine different outcome scenarios based on currently available data. In this paper, we will analyze the output of ensemble simulations by considering so-called persistence diagrams, which are reduced representations of the original data, motivated by the extraction of topological features. Based on a recently published progressive algorithm for the clustering of persistence diagrams, we determine the optimal number of clusters, and therefore the number of significantly different outcome scenarios, by the minimization of established statistical score functions. Furthermore, we present a proof-of-concept prototype implementation of the statistical selection of the number of clusters and provide the results of an experimental study, where this implementation has been applied to real-world ensemble data sets.
Progressive Wasserstein Barycenters of Persistence Diagrams
Jul 10, 2019



Abstract:This paper presents an efficient algorithm for the progressive approximation of Wasserstein barycenters of persistence diagrams, with applications to the visual analysis of ensemble data. Given a set of scalar fields, our approach enables the computation of a persistence diagram which is representative of the set, and which visually conveys the number, data ranges and saliences of the main features of interest found in the set. Such representative diagrams are obtained by computing explicitly the discrete Wasserstein barycenter of the set of persistence diagrams, a notoriously computationally intensive task. In particular, we revisit efficient algorithms for Wasserstein distance approximation [12,51] to extend previous work on barycenter estimation [94]. We present a new fast algorithm, which progressively approximates the barycenter by iteratively increasing the computation accuracy as well as the number of persistent features in the output diagram. Such a progressivity drastically improves convergence in practice and allows to design an interruptible algorithm, capable of respecting computation time constraints. This enables the approximation of Wasserstein barycenters within interactive times. We present an application to ensemble clustering where we revisit the k-means algorithm to exploit our barycenters and compute, within execution time constraints, meaningful clusters of ensemble data along with their barycenter diagram. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-life data sets report that our algorithm converges to barycenters that are qualitatively meaningful with regard to the applications, and quantitatively comparable to previous techniques, while offering an order of magnitude speedup when run until convergence (without time constraint). Our algorithm can be trivially parallelized to provide additional speedups in practice on standard workstations. [...]
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge