Jui-Yi Tsai
CDGraph: Dual Conditional Social Graph Synthesizing via Diffusion Model
Nov 06, 2023Abstract:The social graphs synthesized by the generative models are increasingly in demand due to data scarcity and concerns over user privacy. One of the key performance criteria for generating social networks is the fidelity to specified conditionals, such as users with certain membership and financial status. While recent diffusion models have shown remarkable performance in generating images, their effectiveness in synthesizing graphs has not yet been explored in the context of conditional social graphs. In this paper, we propose the first kind of conditional diffusion model for social networks, CDGraph, which trains and synthesizes graphs based on two specified conditions. We propose the co-evolution dependency in the denoising process of CDGraph to capture the mutual dependencies between the dual conditions and further incorporate social homophily and social contagion to preserve the connectivity between nodes while satisfying the specified conditions. Moreover, we introduce a novel classifier loss, which guides the training of the diffusion process through the mutual dependency of dual conditions. We evaluate CDGraph against four existing graph generative methods, i.e., SPECTRE, GSM, EDGE, and DiGress, on four datasets. Our results show that the generated graphs from CDGraph achieve much higher dual-conditional validity and lower discrepancy in various social network metrics than the baselines, thus demonstrating its proficiency in generating dual-conditional social graphs.
Live Multi-Streaming and Donation Recommendations via Coupled Donation-Response Tensor Factorization
Oct 05, 2021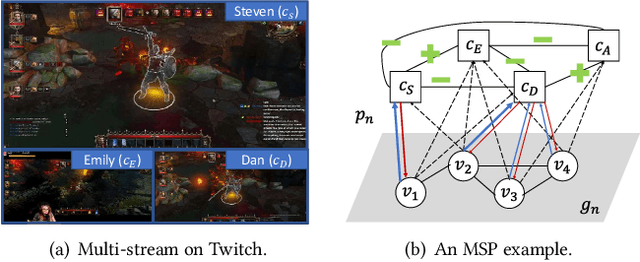
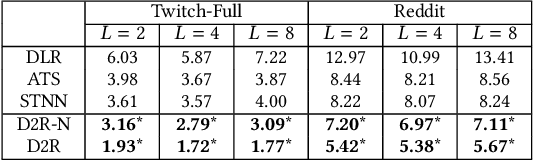
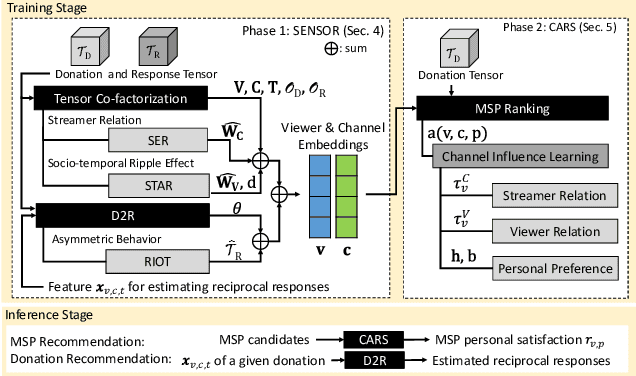

Abstract:In contrast to traditional online videos, live multi-streaming supports real-time social interactions between multiple streamers and viewers, such as donations. However, donation and multi-streaming channel recommendations are challenging due to complicated streamer and viewer relations, asymmetric communications, and the tradeoff between personal interests and group interactions. In this paper, we introduce Multi-Stream Party (MSP) and formulate a new multi-streaming recommendation problem, called Donation and MSP Recommendation (DAMRec). We propose Multi-stream Party Recommender System (MARS) to extract latent features via socio-temporal coupled donation-response tensor factorization for donation and MSP recommendations. Experimental results on Twitch and Douyu manifest that MARS significantly outperforms existing recommenders by at least 38.8% in terms of hit ratio and mean average precision.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge