Juan Dendarieta
DWA-3D: A Reactive Planner for Robust and Efficient Autonomous UAV Navigation
Sep 09, 2024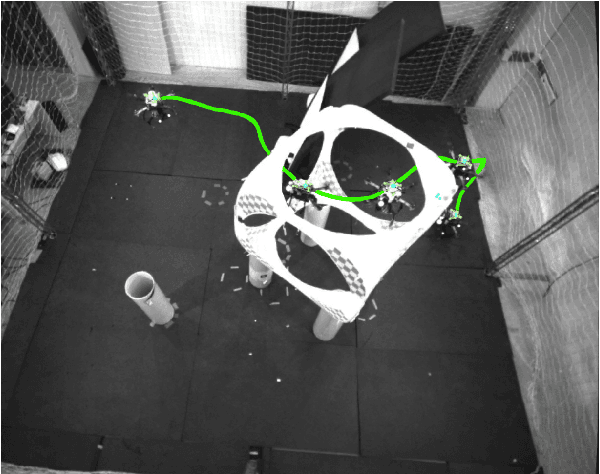
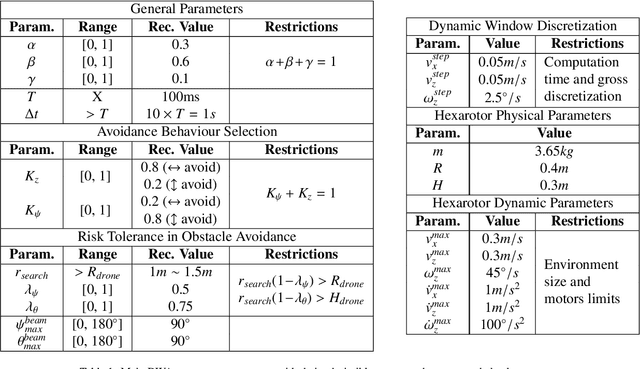
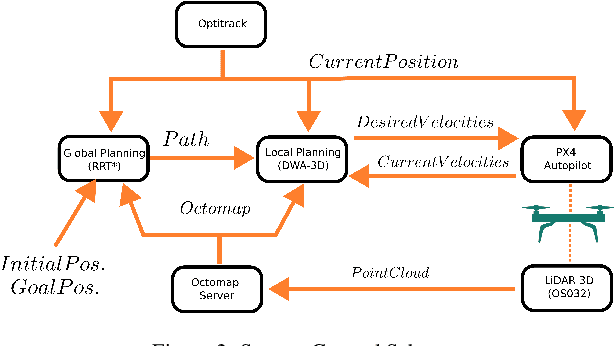

Abstract:Despite the growing impact of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) across various industries, most of current available solutions lack for a robust autonomous navigation system to deal with the appearance of obstacles safely. This work presents an approach to perform autonomous UAV planning and navigation in scenarios in which a safe and high maneuverability is required, due to the cluttered environment and the narrow rooms to move. The system combines an RRT* global planner with a newly proposed reactive planner, DWA-3D, which is the extension of the well known DWA method for 2D robots. We provide a theoretical-empirical method for adjusting the parameters of the objective function to optimize, easing the classical difficulty for tuning them. An onboard LiDAR provides a 3D point cloud, which is projected on an Octomap in which the planning and navigation decisions are made. There is not a prior map; the system builds and updates the map online, from the current and the past LiDAR information included in the Octomap. Extensive real-world experiments were conducted to validate the system and to obtain a fine tuning of the involved parameters. These experiments allowed us to provide a set of values that ensure safe operation across all the tested scenarios. Just by weighting two parameters, it is possible to prioritize either horizontal path alignment or vertical (height) tracking, resulting in enhancing vertical or lateral avoidance, respectively. Additionally, our DWA-3D proposal is able to navigate successfully even in absence of a global planner or with one that does not consider the drone's size. Finally, the conducted experiments show that computation time with the proposed parameters is not only bounded but also remains stable around 40 ms, regardless of the scenario complexity.
CineMPC: A Fully Autonomous Drone Cinematography System Incorporating Zoom, Focus, Pose, and Scene Composition
Jan 10, 2024Abstract:We present CineMPC, a complete cinematographic system that autonomously controls a drone to film multiple targets recording user-specified aesthetic objectives. Existing solutions in autonomous cinematography control only the camera extrinsics, namely its position, and orientation. In contrast, CineMPC is the first solution that includes the camera intrinsic parameters in the control loop, which are essential tools for controlling cinematographic effects like focus, depth-of-field, and zoom. The system estimates the relative poses between the targets and the camera from an RGB-D image and optimizes a trajectory for the extrinsic and intrinsic camera parameters to film the artistic and technical requirements specified by the user. The drone and the camera are controlled in a nonlinear Model Predicted Control (MPC) loop by re-optimizing the trajectory at each time step in response to current conditions in the scene. The perception system of CineMPC can track the targets' position and orientation despite the camera effects. Experiments in a photorealistic simulation and with a real platform demonstrate the capabilities of the system to achieve a full array of cinematographic effects that are not possible without the control of the intrinsics of the camera. Code for CineMPC is implemented following a modular architecture in ROS and released to the community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge