Juan D. S. Ortega
Multimodal Fusion with Deep Neural Networks for Audio-Video Emotion Recognition
Jul 06, 2019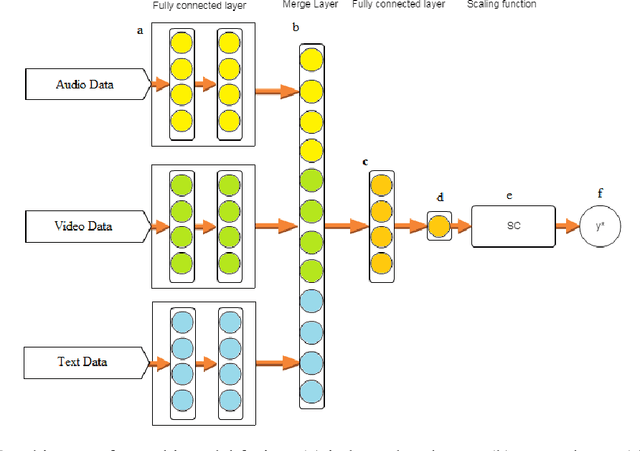
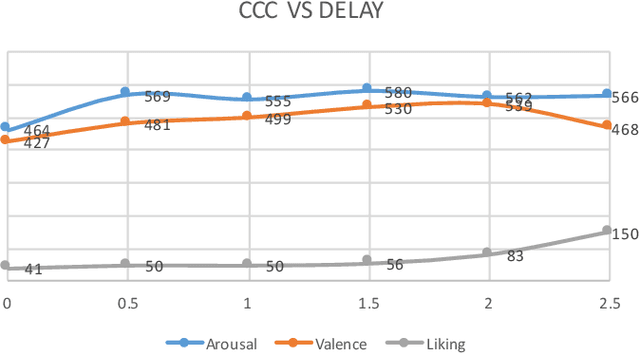
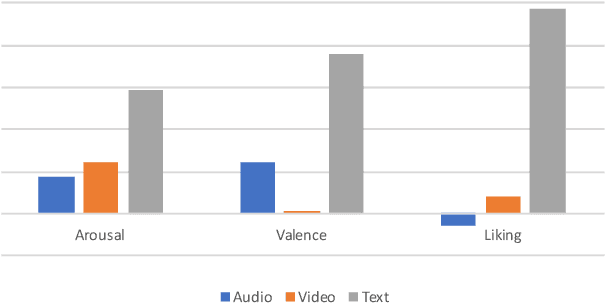
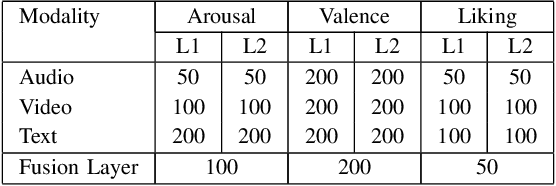
Abstract:This paper presents a novel deep neural network (DNN) for multimodal fusion of audio, video and text modalities for emotion recognition. The proposed DNN architecture has independent and shared layers which aim to learn the representation for each modality, as well as the best combined representation to achieve the best prediction. Experimental results on the AVEC Sentiment Analysis in the Wild dataset indicate that the proposed DNN can achieve a higher level of Concordance Correlation Coefficient (CCC) than other state-of-the-art systems that perform early fusion of modalities at feature-level (i.e., concatenation) and late fusion at score-level (i.e., weighted average) fusion. The proposed DNN has achieved CCCs of 0.606, 0.534, and 0.170 on the development partition of the dataset for predicting arousal, valence and liking, respectively.
Emotion Recognition Using Fusion of Audio and Video Features
Jun 25, 2019



Abstract:In this paper we propose a fusion approach to continuous emotion recognition that combines visual and auditory modalities in their representation spaces to predict the arousal and valence levels. The proposed approach employs a pre-trained convolution neural network and transfer learning to extract features from video frames that capture the emotional content. For the auditory content, a minimalistic set of parameters such as prosodic, excitation, vocal tract, and spectral descriptors are used as features. The fusion of these two modalities is carried out at a feature level, before training a single support vector regressor (SVR) or at a prediction level, after training one SVR for each modality. The proposed approach also includes preprocessing and post-processing techniques which contribute favorably to improving the concordance correlation coefficient (CCC). Experimental results for predicting spontaneous and natural emotions on the RECOLA dataset have shown that the proposed approach takes advantage of the complementary information of visual and auditory modalities and provides CCCs of 0.749 and 0.565 for arousal and valence, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge