Jounghee Kim
K-Wav2vec 2.0: Automatic Speech Recognition based on Joint Decoding of Graphemes and Syllables
Oct 11, 2021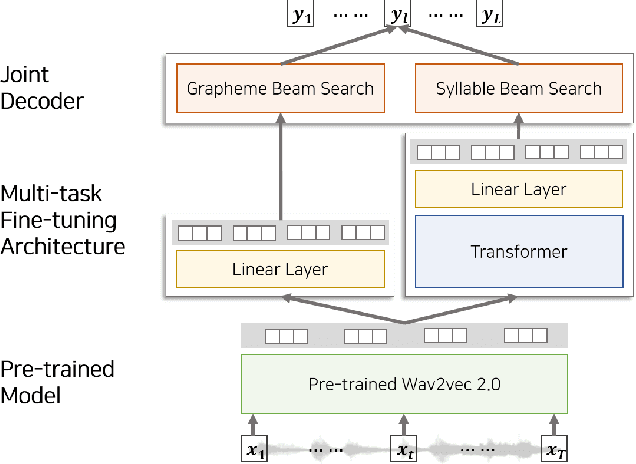


Abstract:Wav2vec 2.0 is an end-to-end framework of self-supervised learning for speech representation that is successful in automatic speech recognition (ASR), but most of the work on the topic has been developed with a single language: English. Therefore, it is unclear whether the self-supervised framework is effective in recognizing other languages with different writing systems, such as Korean which uses the Hangul having a unique writing system. In this paper, we present K-Wav2Vec 2.0, which is a modified version of Wav2vec 2.0 designed for Korean automatic speech recognition by exploring and optimizing various factors of the original Wav2vec 2.0. In fine-tuning, we propose a multi-task hierarchical architecture to reflect the Korean writing structure. Moreover, a joint decoder is applied to alleviate the problem of words existing outside of the vocabulary. In pre-training, we attempted the cross-lingual transfer of the pre-trained model by further pre-training the English Wav2vec 2.0 on a Korean dataset, considering limited resources. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method yields the best performance on both Korean ASR datasets: Ksponspeech (a large-scale Korean speech corpus) and Clovacall (a call-based dialog corpus). Further pre-training is also effective in language adaptation, leading to large improvements without additional data.
Back-Translated Task Adaptive Pretraining: Improving Accuracy and Robustness on Text Classification
Jul 22, 2021



Abstract:Language models (LMs) pretrained on a large text corpus and fine-tuned on a downstream text corpus and fine-tuned on a downstream task becomes a de facto training strategy for several natural language processing (NLP) tasks. Recently, an adaptive pretraining method retraining the pretrained language model with task-relevant data has shown significant performance improvements. However, current adaptive pretraining methods suffer from underfitting on the task distribution owing to a relatively small amount of data to re-pretrain the LM. To completely use the concept of adaptive pretraining, we propose a back-translated task-adaptive pretraining (BT-TAPT) method that increases the amount of task-specific data for LM re-pretraining by augmenting the task data using back-translation to generalize the LM to the target task domain. The experimental results show that the proposed BT-TAPT yields improved classification accuracy on both low- and high-resource data and better robustness to noise than the conventional adaptive pretraining method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge