Joseph Ngonzi
Optimizing Vital Sign Monitoring in Resource-Constrained Maternal Care: An RL-Based Restless Bandit Approach
Oct 10, 2024

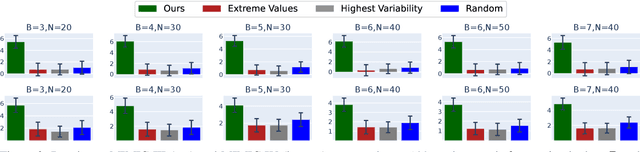
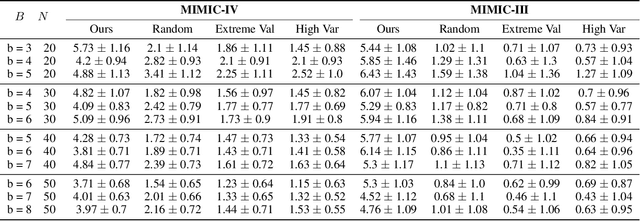
Abstract:Maternal mortality remains a significant global public health challenge. One promising approach to reducing maternal deaths occurring during facility-based childbirth is through early warning systems, which require the consistent monitoring of mothers' vital signs after giving birth. Wireless vital sign monitoring devices offer a labor-efficient solution for continuous monitoring, but their scarcity raises the critical question of how to allocate them most effectively. We devise an allocation algorithm for this problem by modeling it as a variant of the popular Restless Multi-Armed Bandit (RMAB) paradigm. In doing so, we identify and address novel, previously unstudied constraints unique to this domain, which render previous approaches for RMABs unsuitable and significantly increase the complexity of the learning and planning problem. To overcome these challenges, we adopt the popular Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) algorithm from reinforcement learning to learn an allocation policy by training a policy and value function network. We demonstrate in simulations that our approach outperforms the best heuristic baseline by up to a factor of $4$.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge