Joseph E. Burns
Improving Vertebra Segmentation through Joint Vertebra-Rib Atlases
Feb 01, 2016Abstract:Accurate spine segmentation allows for improved identification and quantitative characterization of abnormalities of the vertebra, such as vertebral fractures. However, in existing automated vertebra segmentation methods on computed tomography (CT) images, leakage into nearby bones such as ribs occurs due to the close proximity of these visibly intense structures in a 3D CT volume. To reduce this error, we propose the use of joint vertebra-rib atlases to improve the segmentation of vertebrae via multi-atlas joint label fusion. Segmentation was performed and evaluated on CTs containing 106 thoracic and lumbar vertebrae from 10 pathological and traumatic spine patients on an individual vertebra level basis. Vertebra atlases produced errors where the segmentation leaked into the ribs. The use of joint vertebra-rib atlases produced a statistically significant increase in the Dice coefficient from 92.5 $\pm$ 3.1% to 93.8 $\pm$ 2.1% for the left and right transverse processes and a decrease in the mean and max surface distance from 0.75 $\pm$ 0.60mm and 8.63 $\pm$ 4.44mm to 0.30 $\pm$ 0.27mm and 3.65 $\pm$ 2.87mm, respectively.
Deep convolutional networks for automated detection of posterior-element fractures on spine CT
Jan 29, 2016Abstract:Injuries of the spine, and its posterior elements in particular, are a common occurrence in trauma patients, with potentially devastating consequences. Computer-aided detection (CADe) could assist in the detection and classification of spine fractures. Furthermore, CAD could help assess the stability and chronicity of fractures, as well as facilitate research into optimization of treatment paradigms. In this work, we apply deep convolutional networks (ConvNets) for the automated detection of posterior element fractures of the spine. First, the vertebra bodies of the spine with its posterior elements are segmented in spine CT using multi-atlas label fusion. Then, edge maps of the posterior elements are computed. These edge maps serve as candidate regions for predicting a set of probabilities for fractures along the image edges using ConvNets in a 2.5D fashion (three orthogonal patches in axial, coronal and sagittal planes). We explore three different methods for training the ConvNet using 2.5D patches along the edge maps of 'positive', i.e. fractured posterior-elements and 'negative', i.e. non-fractured elements. An experienced radiologist retrospectively marked the location of 55 displaced posterior-element fractures in 18 trauma patients. We randomly split the data into training and testing cases. In testing, we achieve an area-under-the-curve of 0.857. This corresponds to 71% or 81% sensitivities at 5 or 10 false-positives per patient, respectively. Analysis of our set of trauma patients demonstrates the feasibility of detecting posterior-element fractures in spine CT images using computer vision techniques such as deep convolutional networks.
Osteoporotic and Neoplastic Compression Fracture Classification on Longitudinal CT
Jan 27, 2016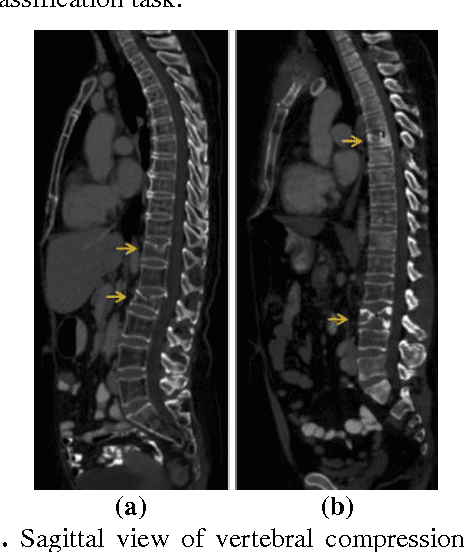
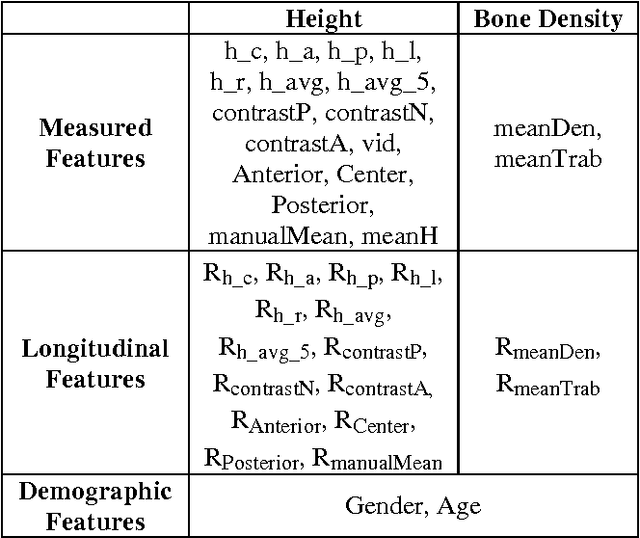
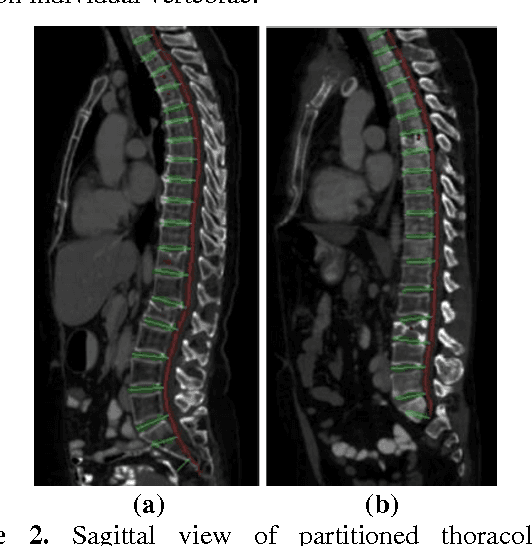

Abstract:Classification of vertebral compression fractures (VCF) having osteoporotic or neoplastic origin is fundamental to the planning of treatment. We developed a fracture classification system by acquiring quantitative morphologic and bone density determinants of fracture progression through the use of automated measurements from longitudinal studies. A total of 250 CT studies were acquired for the task, each having previously identified VCFs with osteoporosis or neoplasm. Thirty-six features or each identified VCF were computed and classified using a committee of support vector machines. Ten-fold cross validation on 695 identified fractured vertebrae showed classification accuracies of 0.812, 0.665, and 0.820 for the measured, longitudinal, and combined feature sets respectively.
Multi-Atlas Segmentation with Joint Label Fusion of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures on CT
Jan 13, 2016



Abstract:The precise and accurate segmentation of the vertebral column is essential in the diagnosis and treatment of various orthopedic, neurological, and oncological traumas and pathologies. Segmentation is especially challenging in the presence of pathology such as vertebral compression fractures. In this paper, we propose a method to produce segmentations for osteoporotic compression fractured vertebrae by applying a multi-atlas joint label fusion technique for clinical CT images. A total of 170 thoracic and lumbar vertebrae were evaluated using atlases from five patients with varying degrees of spinal degeneration. In an osteoporotic cohort of bundled atlases, registration provided an average Dice coefficient and mean absolute surface distance of 2.7$\pm$4.5% and 0.32$\pm$0.13mm for osteoporotic vertebrae, respectively, and 90.9$\pm$3.0% and 0.36$\pm$0.11mm for compression fractured vertebrae.
Detection of Sclerotic Spine Metastases via Random Aggregation of Deep Convolutional Neural Network Classifications
Jul 22, 2014



Abstract:Automated detection of sclerotic metastases (bone lesions) in Computed Tomography (CT) images has potential to be an important tool in clinical practice and research. State-of-the-art methods show performance of 79% sensitivity or true-positive (TP) rate, at 10 false-positives (FP) per volume. We design a two-tiered coarse-to-fine cascade framework to first operate a highly sensitive candidate generation system at a maximum sensitivity of ~92% but with high FP level (~50 per patient). Regions of interest (ROI) for lesion candidates are generated in this step and function as input for the second tier. In the second tier we generate N 2D views, via scale, random translations, and rotations with respect to each ROI centroid coordinates. These random views are used to train a deep Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) classifier. In testing, the CNN is employed to assign individual probabilities for a new set of N random views that are averaged at each ROI to compute a final per-candidate classification probability. This second tier behaves as a highly selective process to reject difficult false positives while preserving high sensitivities. We validate the approach on CT images of 59 patients (49 with sclerotic metastases and 10 normal controls). The proposed method reduces the number of FP/vol. from 4 to 1.2, 7 to 3, and 12 to 9.5 when comparing a sensitivity rates of 60%, 70%, and 80% respectively in testing. The Area-Under-the-Curve (AUC) is 0.834. The results show marked improvement upon previous work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge