Osteoporotic and Neoplastic Compression Fracture Classification on Longitudinal CT
Paper and Code
Jan 27, 2016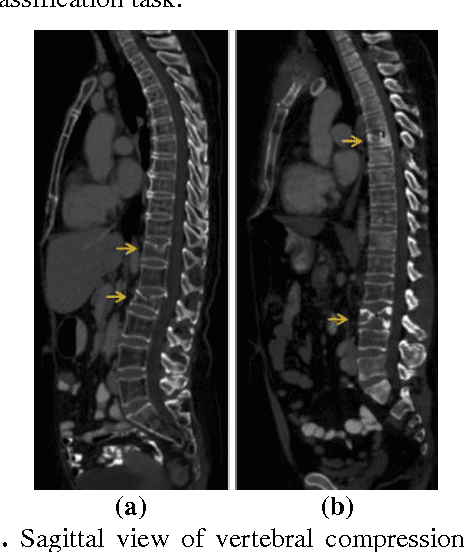
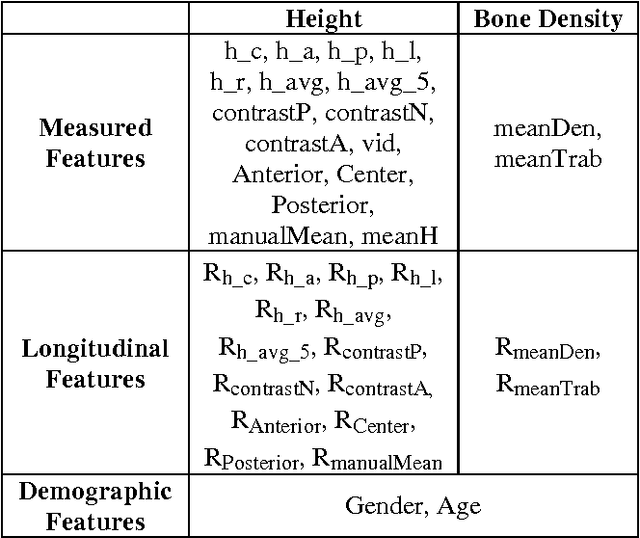
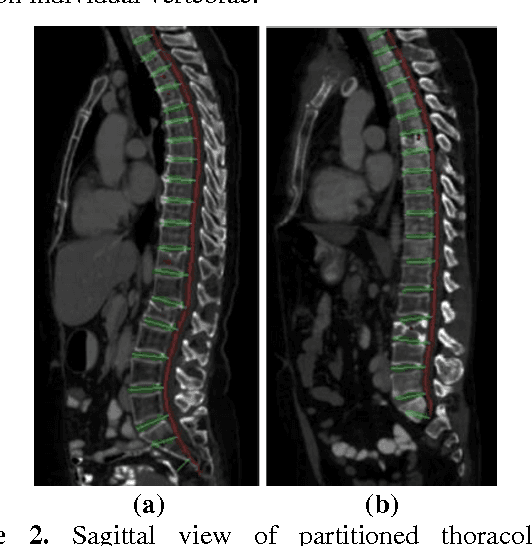

Classification of vertebral compression fractures (VCF) having osteoporotic or neoplastic origin is fundamental to the planning of treatment. We developed a fracture classification system by acquiring quantitative morphologic and bone density determinants of fracture progression through the use of automated measurements from longitudinal studies. A total of 250 CT studies were acquired for the task, each having previously identified VCFs with osteoporosis or neoplasm. Thirty-six features or each identified VCF were computed and classified using a committee of support vector machines. Ten-fold cross validation on 695 identified fractured vertebrae showed classification accuracies of 0.812, 0.665, and 0.820 for the measured, longitudinal, and combined feature sets respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge