Joseph D. Monaco
Bayesian optimization of distributed neurodynamical controller models for spatial navigation
Oct 31, 2021



Abstract:Dynamical systems models for controlling multi-agent swarms have demonstrated advances toward resilient, decentralized navigation algorithms. We previously introduced the NeuroSwarms controller, in which agent-based interactions were modeled by analogy to neuronal network interactions, including attractor dynamics and phase synchrony, that have been theorized to operate within hippocampal place-cell circuits in navigating rodents. This complexity precludes linear analyses of stability, controllability, and performance typically used to study conventional swarm models. Further, tuning dynamical controllers by hand or grid search is often inadequate due to the complexity of objectives, dimensionality of model parameters, and computational costs of simulation-based sampling. Here, we present a framework for tuning dynamical controller models of autonomous multi-agent systems based on Bayesian Optimization (BayesOpt). Our approach utilizes a task-dependent objective function to train Gaussian Processes (GPs) as surrogate models to achieve adaptive and efficient exploration of a dynamical controller model's parameter space. We demonstrate this approach by studying an objective function selecting for NeuroSwarms behaviors that cooperatively localize and capture spatially distributed rewards under time pressure. We generalized task performance across environments by combining scores for simulations in distinct geometries. To validate search performance, we compared high-dimensional clustering for high- vs. low-likelihood parameter points by visualizing sample trajectories in Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) embeddings. Our findings show that adaptive, sample-efficient evaluation of the self-organizing behavioral capacities of complex systems, including dynamical swarm controllers, can accelerate the translation of neuroscientific theory to applied domains.
A brain basis of dynamical intelligence for AI and computational neuroscience
May 21, 2021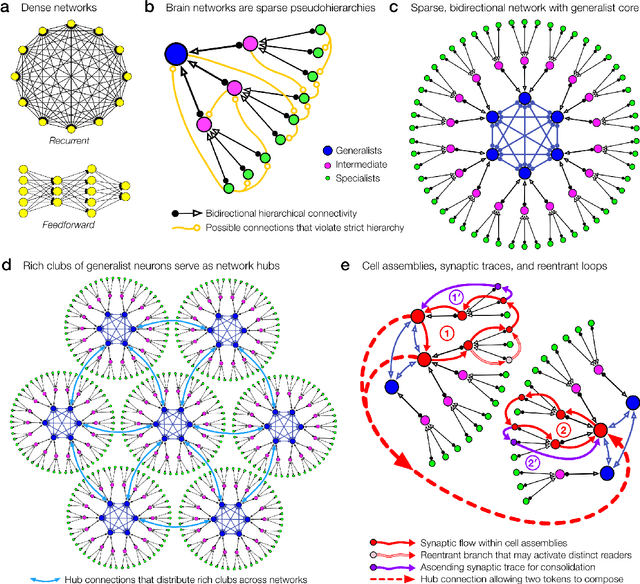
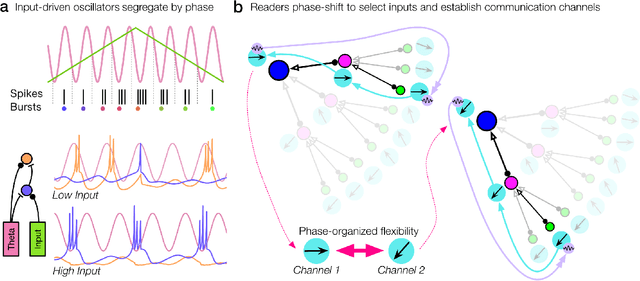
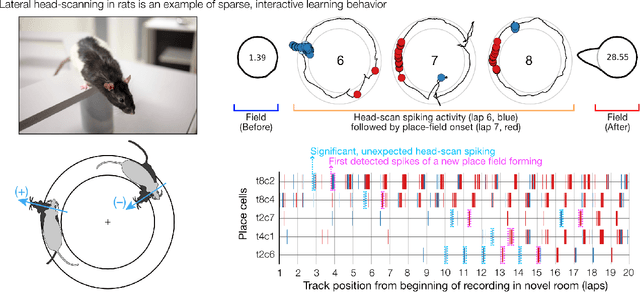
Abstract:The deep neural nets of modern artificial intelligence (AI) have not achieved defining features of biological intelligence, including abstraction, causal learning, and energy-efficiency. While scaling to larger models has delivered performance improvements for current applications, more brain-like capacities may demand new theories, models, and methods for designing artificial learning systems. Here, we argue that this opportunity to reassess insights from the brain should stimulate cooperation between AI research and theory-driven computational neuroscience (CN). To motivate a brain basis of neural computation, we present a dynamical view of intelligence from which we elaborate concepts of sparsity in network structure, temporal dynamics, and interactive learning. In particular, we suggest that temporal dynamics, as expressed through neural synchrony, nested oscillations, and flexible sequences, provide a rich computational layer for reading and updating hierarchical models distributed in long-term memory networks. Moreover, embracing agent-centered paradigms in AI and CN will accelerate our understanding of the complex dynamics and behaviors that build useful world models. A convergence of AI/CN theories and objectives will reveal dynamical principles of intelligence for brains and engineered learning systems. This article was inspired by our symposium on dynamical neuroscience and machine learning at the 6th Annual US/NIH BRAIN Initiative Investigators Meeting.
Cognitive swarming in complex environments with attractor dynamics and oscillatory computing
Sep 15, 2019



Abstract:Neurobiological theories of spatial cognition developed with respect to recording data from relatively small and/or simplistic environments compared to animals' natural habitats. It has been unclear how to extend theoretical models to large or complex spaces. Complementarily, in autonomous systems technology, applications have been growing for distributed control methods that scale to large numbers of low-footprint mobile platforms. Animals and many-robot groups must solve common problems of navigating complex and uncertain environments. Here, we introduce the 'NeuroSwarms' control framework to investigate whether adaptive, autonomous swarm control of minimal artificial agents can be achieved by direct analogy to neural circuits of rodent spatial cognition. NeuroSwarms analogizes agents to neurons and swarming groups to recurrent networks. We implemented neuron-like agent interactions in which mutually visible agents operate as if they were reciprocally-connected place cells in an attractor network. We attributed a phase state to agents to enable patterns of oscillatory synchronization similar to hippocampal models of theta-rhythmic (5-12 Hz) sequence generation. We demonstrate that multi-agent swarming and reward-approach dynamics can be expressed as a mobile form of Hebbian learning and that NeuroSwarms supports a single-entity paradigm that directly informs theoretical models of animal cognition. We present emergent behaviors including phase-organized rings and trajectory sequences that interact with environmental cues and geometry in large, fragmented mazes. Thus, NeuroSwarms is a model artificial spatial system that integrates autonomous control and theoretical neuroscience to potentially uncover common principles to advance both domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge