Joseph A. Izatt
Computational 3D microscopy with optical coherence refraction tomography
Feb 24, 2022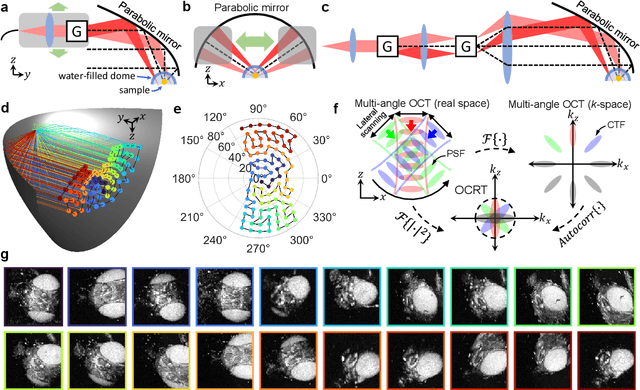
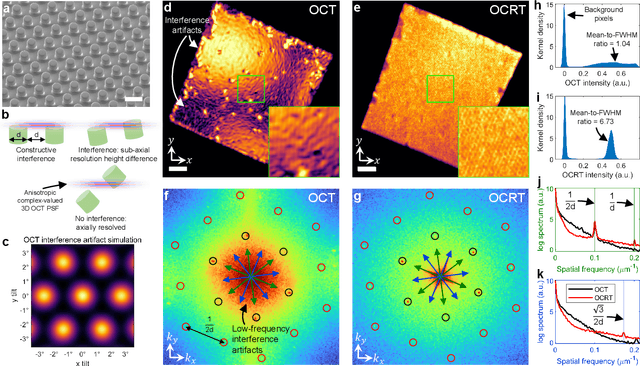
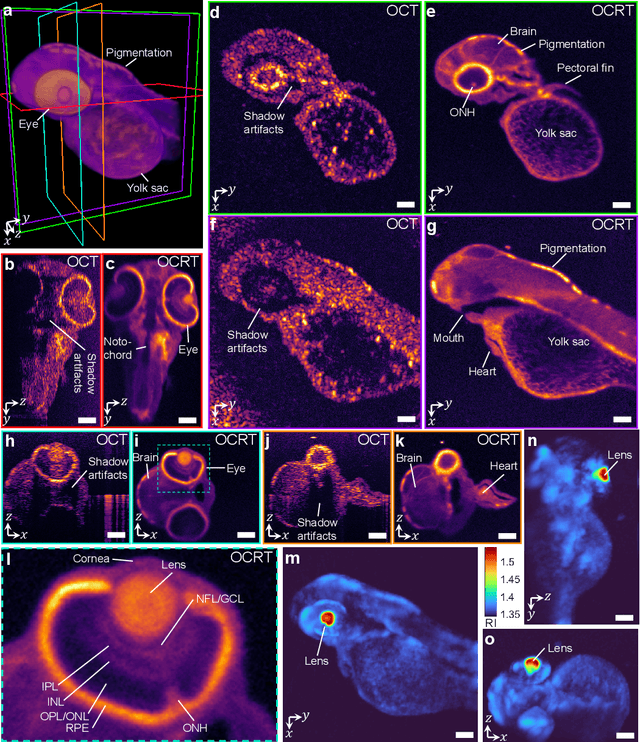
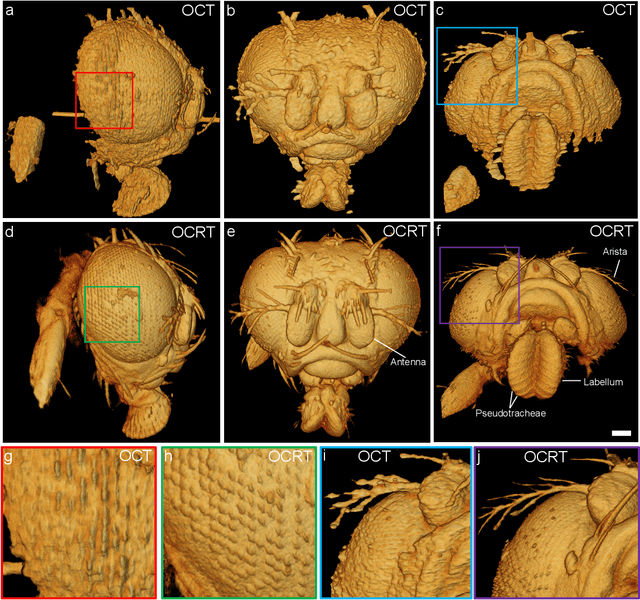
Abstract:Optical coherence tomography (OCT) has seen widespread success as an in vivo clinical diagnostic 3D imaging modality, impacting areas including ophthalmology, cardiology, and gastroenterology. Despite its many advantages, such as high sensitivity, speed, and depth penetration, OCT suffers from several shortcomings that ultimately limit its utility as a 3D microscopy tool, such as its pervasive coherent speckle noise and poor lateral resolution required to maintain millimeter-scale imaging depths. Here, we present 3D optical coherence refraction tomography (OCRT), a computational extension of OCT which synthesizes an incoherent contrast mechanism by combining multiple OCT volumes, acquired across two rotation axes, to form a resolution-enhanced, speckle-reduced, refraction-corrected 3D reconstruction. Our label-free computational 3D microscope features a novel optical design incorporating a parabolic mirror to enable the capture of 5D plenoptic datasets, consisting of millimetric 3D fields of view over up to $\pm75^\circ$ without moving the sample. We demonstrate that 3D OCRT reveals 3D features unobserved by conventional OCT in fruit fly, zebrafish, and mouse samples.
Mesoscopic photogrammetry with an unstabilized phone camera
Dec 11, 2020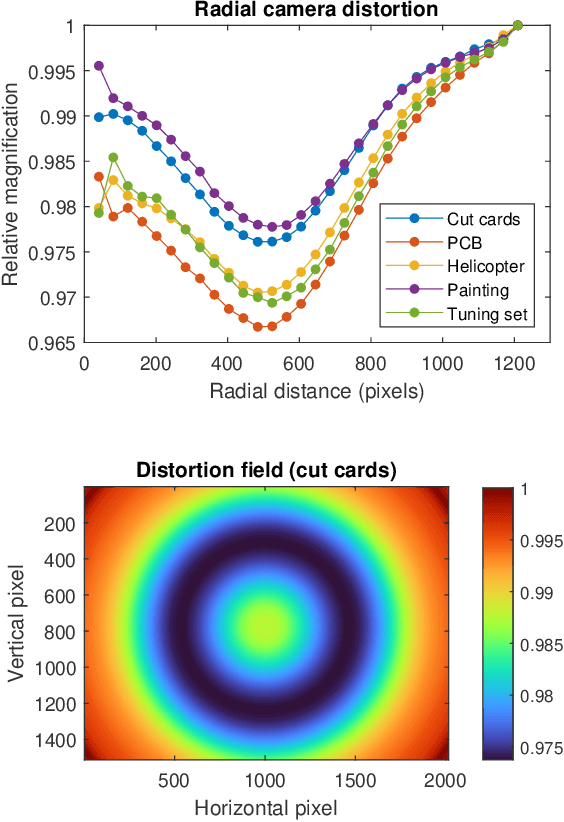
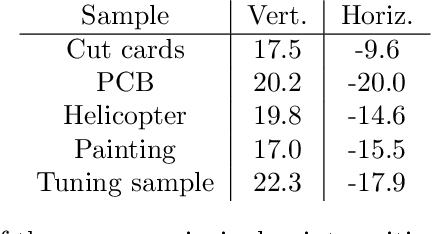
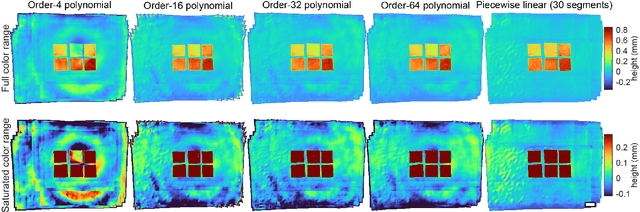
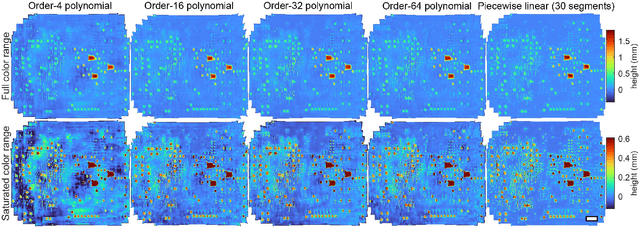
Abstract:We present a feature-free photogrammetric technique that enables quantitative 3D mesoscopic (mm-scale height variation) imaging with tens-of-micron accuracy from sequences of images acquired by a smartphone at close range (several cm) under freehand motion without additional hardware. Our end-to-end, pixel-intensity-based approach jointly registers and stitches all the images by estimating a coaligned height map, which acts as a pixel-wise radial deformation field that orthorectifies each camera image to allow homographic registration. The height maps themselves are reparameterized as the output of an untrained encoder-decoder convolutional neural network (CNN) with the raw camera images as the input, which effectively removes many reconstruction artifacts. Our method also jointly estimates both the camera's dynamic 6D pose and its distortion using a nonparametric model, the latter of which is especially important in mesoscopic applications when using cameras not designed for imaging at short working distances, such as smartphone cameras. We also propose strategies for reducing computation time and memory, applicable to other multi-frame registration problems. Finally, we demonstrate our method using sequences of multi-megapixel images captured by an unstabilized smartphone on a variety of samples (e.g., painting brushstrokes, circuit board, seeds).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge