José Antonio Hernández López
The Power of Types: Exploring the Impact of Type Checking on Neural Bug Detection in Dynamically Typed Languages
Nov 22, 2024



Abstract:Motivation: Automated bug detection in dynamically typed languages such as Python is essential for maintaining code quality. The lack of mandatory type annotations in such languages can lead to errors that are challenging to identify early with traditional static analysis tools. Recent progress in deep neural networks has led to increased use of neural bug detectors. In statically typed languages, a type checker is integrated into the compiler and thus taken into consideration when the neural bug detector is designed for these languages. Problem: However, prior studies overlook this aspect during the training and testing of neural bug detectors for dynamically typed languages. When an optional type checker is used, assessing existing neural bug detectors on bugs easily detectable by type checkers may impact their performance estimation. Moreover, including these bugs in the training set of neural bug detectors can shift their detection focus toward the wrong type of bugs. Contribution: We explore the impact of type checking on various neural bug detectors for variable misuse bugs, a common type targeted by neural bug detectors. Existing synthetic and real-world datasets are type-checked to evaluate the prevalence of type-related bugs. Then, we investigate how type-related bugs influence the training and testing of the neural bug detectors. Findings: Our findings indicate that existing bug detection datasets contain a significant proportion of type-related bugs. Building on this insight, we discover integrating the neural bug detector with a type checker can be beneficial, especially when the code is annotated with types. Further investigation reveals neural bug detectors perform better on type-related bugs than other bugs. Moreover, removing type-related bugs from the training data helps improve neural bug detectors' ability to identify bugs beyond the scope of type checkers.
AST-Probe: Recovering abstract syntax trees from hidden representations of pre-trained language models
Jun 23, 2022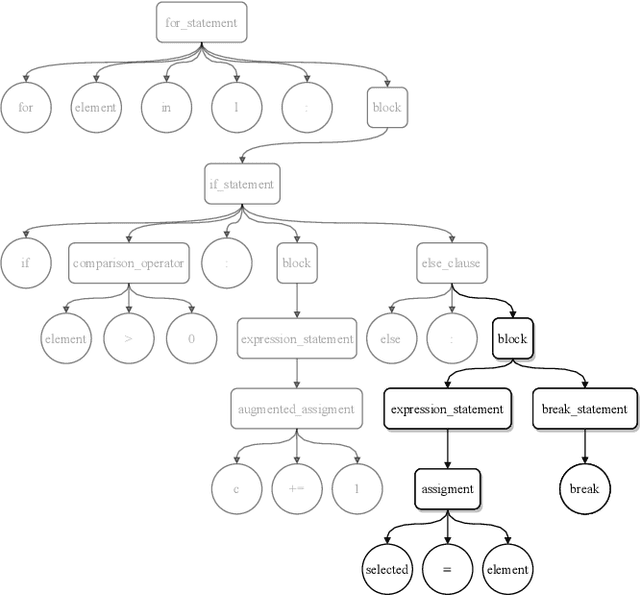
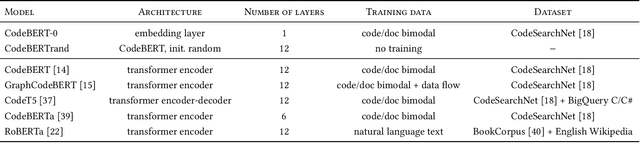
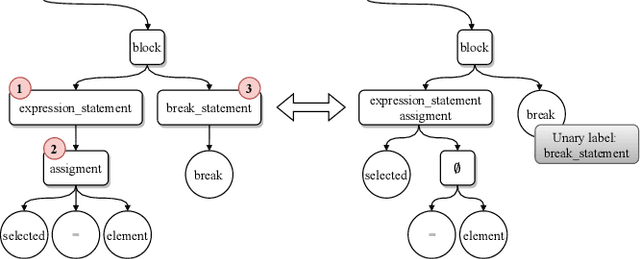
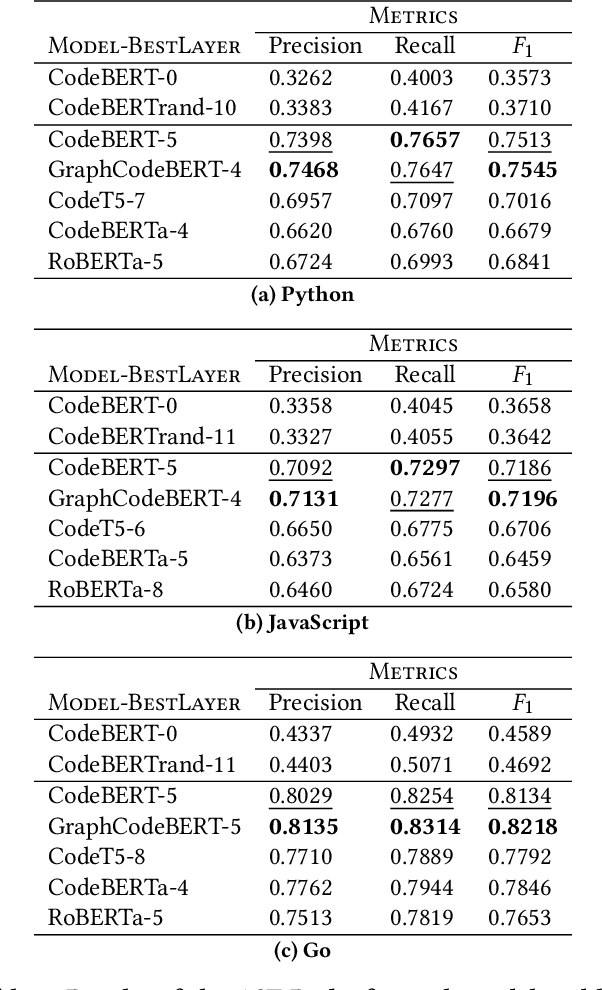
Abstract:The objective of pre-trained language models is to learn contextual representations of textual data. Pre-trained language models have become mainstream in natural language processing and code modeling. Using probes, a technique to study the linguistic properties of hidden vector spaces, previous works have shown that these pre-trained language models encode simple linguistic properties in their hidden representations. However, none of the previous work assessed whether these models encode the whole grammatical structure of a programming language. In this paper, we prove the existence of a \textit{syntactic subspace}, lying in the hidden representations of pre-trained language models, which contain the syntactic information of the programming language. We show that this subspace can be extracted from the models' representations and define a novel probing method, the AST-Probe, that enables recovering the whole abstract syntax tree (AST) of an input code snippet. In our experimentations, we show that this syntactic subspace exists in five state-of-the-art pre-trained language models. In addition, we highlight that the middle layers of the models are the ones that encode most of the AST information. Finally, we estimate the optimal size of this syntactic subspace and show that its dimension is substantially lower than those of the models' representation spaces. This suggests that pre-trained language models use a small part of their representation spaces to encode syntactic information of the programming languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge