Jongjin Kim
LampQ: Towards Accurate Layer-wise Mixed Precision Quantization for Vision Transformers
Nov 14, 2025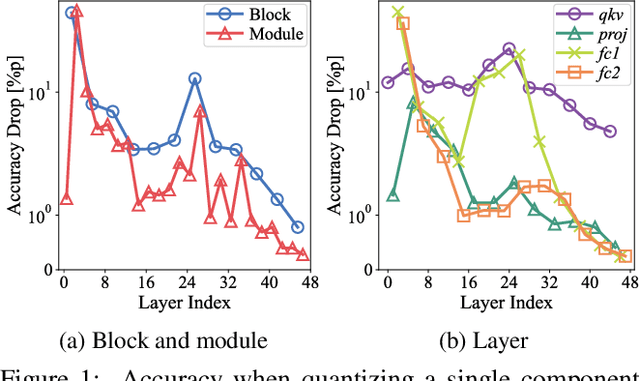
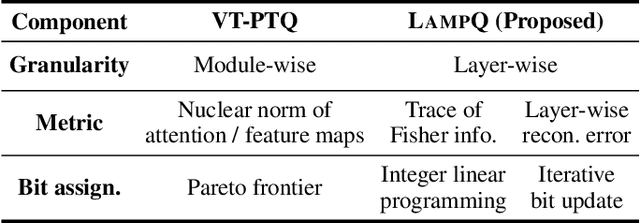
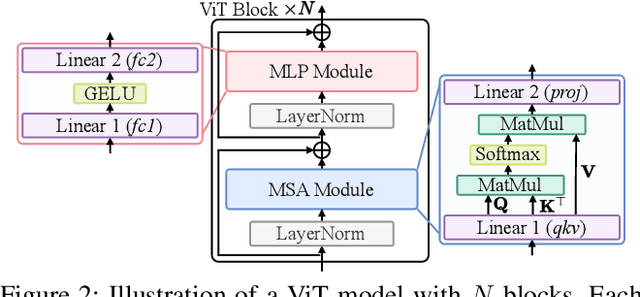
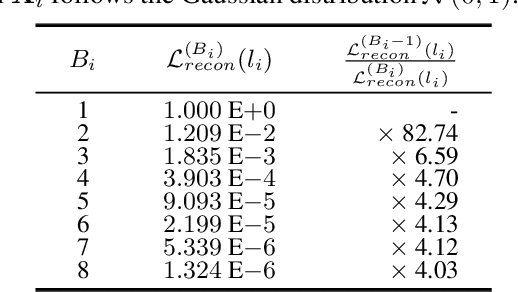
Abstract:How can we accurately quantize a pre-trained Vision Transformer model? Quantization algorithms compress Vision Transformers (ViTs) into low-bit formats, reducing memory and computation demands with minimal accuracy degradation. However, existing methods rely on uniform precision, ignoring the diverse sensitivity of ViT components to quantization. Metric-based Mixed Precision Quantization (MPQ) is a promising alternative, but previous MPQ methods for ViTs suffer from three major limitations: 1) coarse granularity, 2) mismatch in metric scale across component types, and 3) quantization-unaware bit allocation. In this paper, we propose LampQ (Layer-wise Mixed Precision Quantization for Vision Transformers), an accurate metric-based MPQ method for ViTs to overcome these limitations. LampQ performs layer-wise quantization to achieve both fine-grained control and efficient acceleration, incorporating a type-aware Fisher-based metric to measure sensitivity. Then, LampQ assigns bit-widths optimally through integer linear programming and further updates them iteratively. Extensive experiments show that LampQ provides the state-of-the-art performance in quantizing ViTs pre-trained on various tasks such as image classification, object detection, and zero-shot quantization.
Accurate Action Recommendation for Smart Home via Two-Level Encoders and Commonsense Knowledge
Aug 12, 2022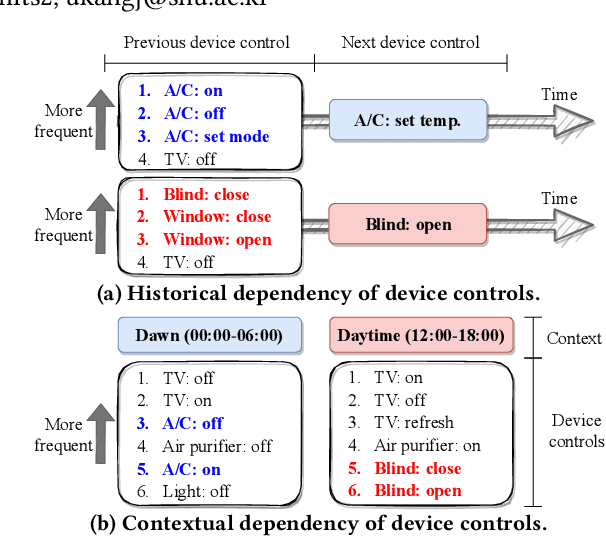
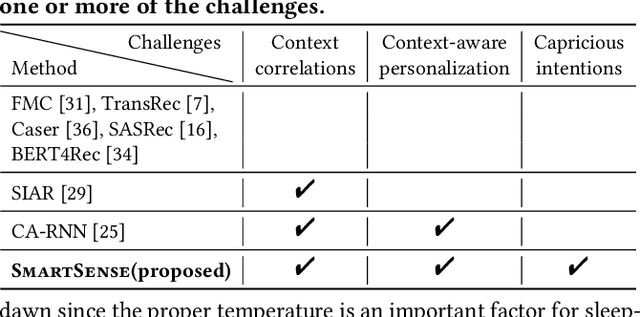
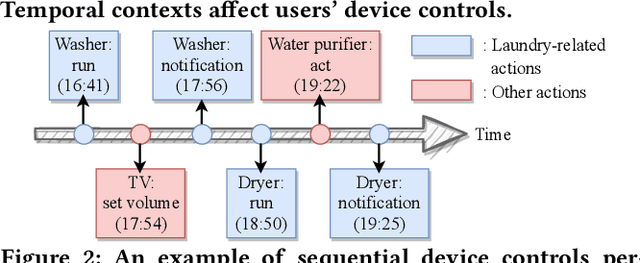
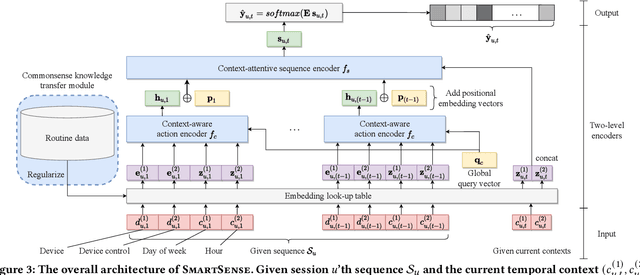
Abstract:How can we accurately recommend actions for users to control their devices at home? Action recommendation for smart home has attracted increasing attention due to its potential impact on the markets of virtual assistants and Internet of Things (IoT). However, designing an effective action recommender system for smart home is challenging because it requires handling context correlations, considering both queried contexts and previous histories of users, and dealing with capricious intentions in history. In this work, we propose SmartSense, an accurate action recommendation method for smart home. For individual action, SmartSense summarizes its device control and its temporal contexts in a self-attentive manner, to reflect the importance of the correlation between them. SmartSense then summarizes sequences of users considering queried contexts in a query-attentive manner to extract the query-related patterns from the sequential actions. SmartSense also transfers the commonsense knowledge from routine data to better handle intentions in action sequences. As a result, SmartSense addresses all three main challenges of action recommendation for smart home, and achieves the state-of-the-art performance giving up to 9.8% higher mAP@1 than the best competitor.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge